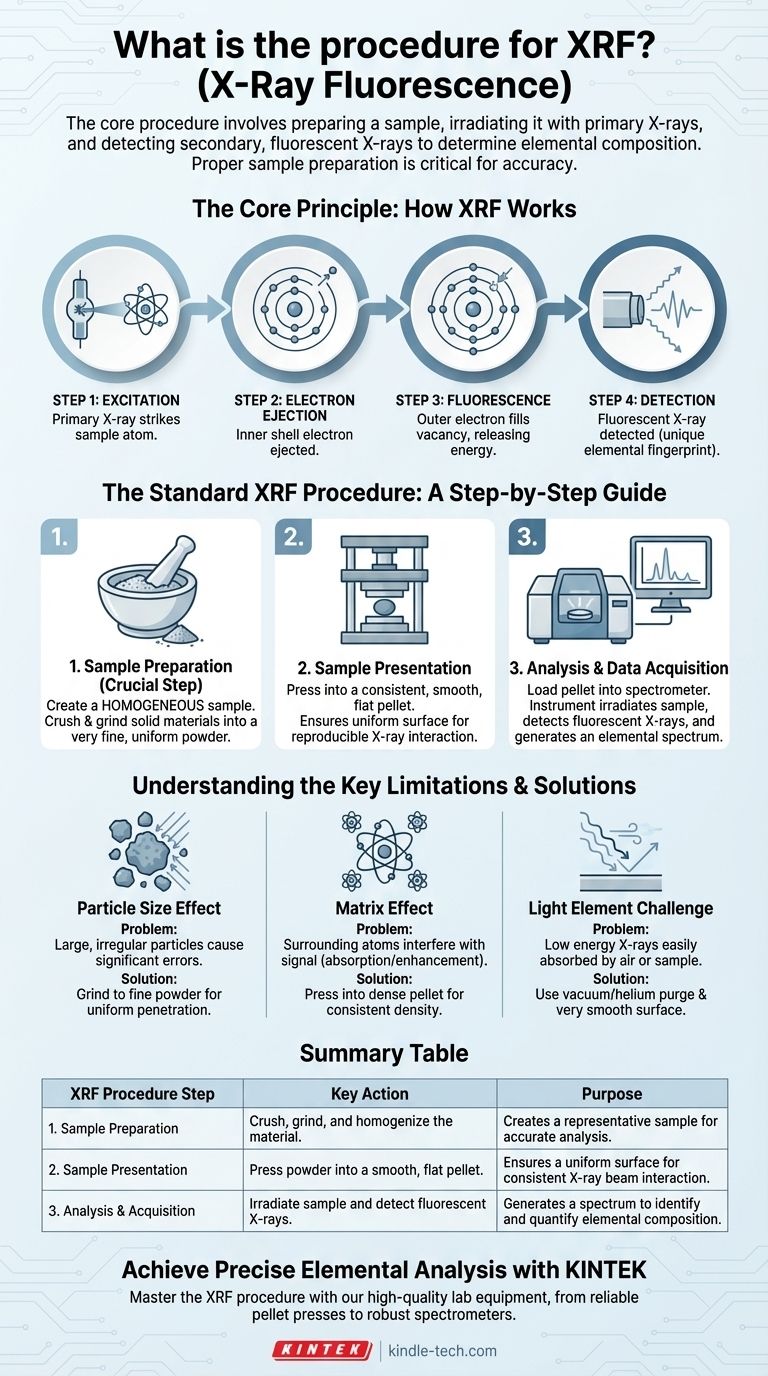
The core procedure for X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) involves preparing a sample, placing it in an XRF spectrometer, irradiating it with a primary X-ray source, and then detecting the secondary, "fluorescent" X-rays emitted by the sample. These secondary X-rays have energies characteristic of each element present, allowing the instrument's software to determine the sample's elemental composition. Proper sample preparation is the most critical step for obtaining accurate results.
The accuracy of any XRF analysis is not determined by the instrument alone, but by the quality and appropriateness of the sample preparation. A poorly prepared sample will always yield a poor result, regardless of the quality of the spectrometer.
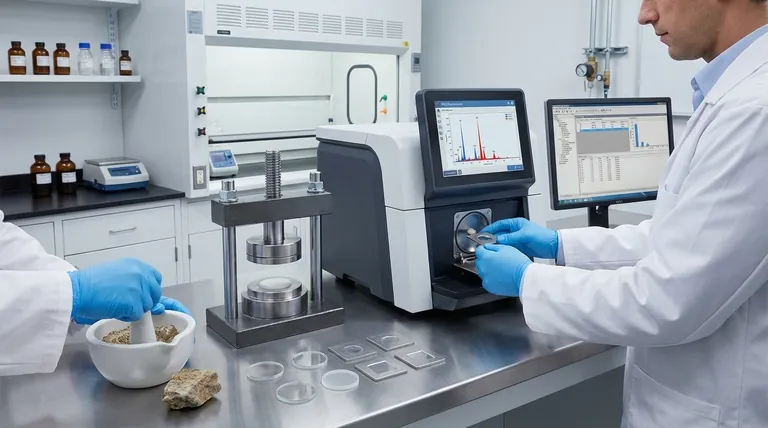

The Core Principle: How XRF Works
To understand the procedure, you must first understand the principle. XRF is a process of atomic "interrogation" where the instrument asks a question with one X-ray and listens for the answer in another.
Step 1: Excitation
A high-energy primary X-ray is fired from a source (like an X-ray tube) and strikes the atoms within your sample.
Step 2: Electron Ejection
This primary X-ray has enough energy to knock an electron out of one of the atom's inner orbital shells (for example, the K or L shell).
Step 3: Fluorescence
This creates an unstable vacancy. To regain stability, an electron from a higher-energy outer shell immediately drops down to fill the empty spot.
Step 4: Detection
As the electron drops, it releases a specific amount of energy in the form of a secondary, or fluorescent, X-ray. The energy of this X-ray is the unique "fingerprint" of that specific element, which is then captured by the instrument's detector.
The Standard XRF Procedure: A Step-by-Step Guide
While instrument specifics vary, the fundamental workflow for high-quality analysis remains consistent and is centered on creating a representative sample.
Step 1: Sample Preparation
This is the most crucial stage. The goal is to create a homogeneous sample that accurately represents the bulk material you want to analyze.
For solid samples like rocks or minerals, this often involves crushing and grinding the material into a very fine, uniform powder.
Step 2: Sample Presentation
The prepared sample must be presented to the instrument in a consistent way. For powders, this typically means compressing them under high pressure into a smooth, flat pellet.
This reduces inconsistencies and creates a uniform surface for the X-ray beam, which is critical for reproducibility.
Step 3: Analysis and Data Acquisition
The sample (e.g., the prepared pellet) is loaded into the spectrometer. The operator selects the appropriate analytical program, and the instrument irradiates the sample.
The detector counts the fluorescent X-rays emitted at each characteristic energy level, generating a spectrum that shows peaks corresponding to the elements present.
Understanding the Key Limitations
The success of the procedure hinges on mitigating physical and chemical effects that can distort the results. Your preparation method is designed to overcome these challenges.
The Particle Size Effect
Large, irregular particles can cause significant errors. The primary X-ray beam may not penetrate them uniformly, and the fluorescent X-rays can be scattered or absorbed unpredictably.
Grinding samples to a fine powder, as noted in the references, is essential to minimize this effect and ensure the analysis is representative of the whole sample, not just a few large grains.
The Matrix Effect
The atoms surrounding the element of interest (the "matrix") can interfere with the signal. They can absorb the fluorescent X-rays you want to measure or enhance them through secondary fluorescence.
Compressing the powder into a dense, flat pellet helps create a uniform density and composition, making these matrix effects more consistent and correctable with software.
The "Light Element" Challenge
XRF is less sensitive to lighter elements (like sodium, magnesium, or aluminum). Their fluorescent X-rays have very low energy and are easily absorbed by air or even by the sample itself before reaching the detector.
This means that detecting light elements requires a vacuum or helium-purged sample chamber and a very smooth sample surface to minimize absorption.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Your analytical goal dictates the necessary level of procedural rigor.
- If your primary focus is high-accuracy quantitative analysis: Meticulous sample preparation, including fine grinding and pressing pellets, is absolutely essential.
- If your primary focus is rapid material identification or sorting: A handheld XRF may suffice with minimal preparation, but you must accept lower precision and accuracy.
- If your primary focus is analyzing liquids or loose powders: You must use specialized sample cups with a thin, X-ray-transparent film and calibrate the instrument specifically for that sample type.
Ultimately, mastering the XRF procedure is about understanding and controlling variables before the sample ever enters the instrument.
Summary Table:
| XRF Procedure Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Sample Preparation | Crush, grind, and homogenize the material. | Creates a representative sample for accurate analysis. |
| 2. Sample Presentation | Press powder into a smooth, flat pellet. | Ensures a uniform surface for consistent X-ray beam interaction. |
| 3. Analysis & Acquisition | Irradiate sample and detect fluorescent X-rays. | Generates a spectrum to identify and quantify elemental composition. |
Achieve Precise Elemental Analysis with KINTEK
Mastering the XRF procedure is the foundation of reliable results. Proper sample preparation and the right equipment are paramount. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your XRF needs, from reliable pellet presses for sample preparation to robust spectrometers.
Let our expertise enhance your laboratory's capabilities:
- Improve Accuracy: Ensure your sample preparation is flawless with our specialized equipment.
- Increase Efficiency: Streamline your workflow with reliable and easy-to-use instruments.
- Gain Support: Benefit from our deep understanding of analytical techniques and laboratory challenges.
Ready to optimize your XRF analysis? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable XRD Sample Holders for Diverse Research Applications
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Lab Internal Rubber Mixer Rubber Kneader Machine for Mixing and Kneading
People Also Ask
- Why is an airtight sample holder with a beryllium window required for XRD of sulfide solid electrolytes?
- What are the specific storage requirements for a sample holder? Protect Your Lab's Critical Assets
- How can corrosion of the sample holder be prevented when using corrosive chemicals? Protect Your Lab's Integrity
- Does higher heat capacity mean higher melting point? Unraveling the Critical Difference
- How should a sample holder be handled to ensure its longevity? Protect Your Lab Investment and Data Integrity















