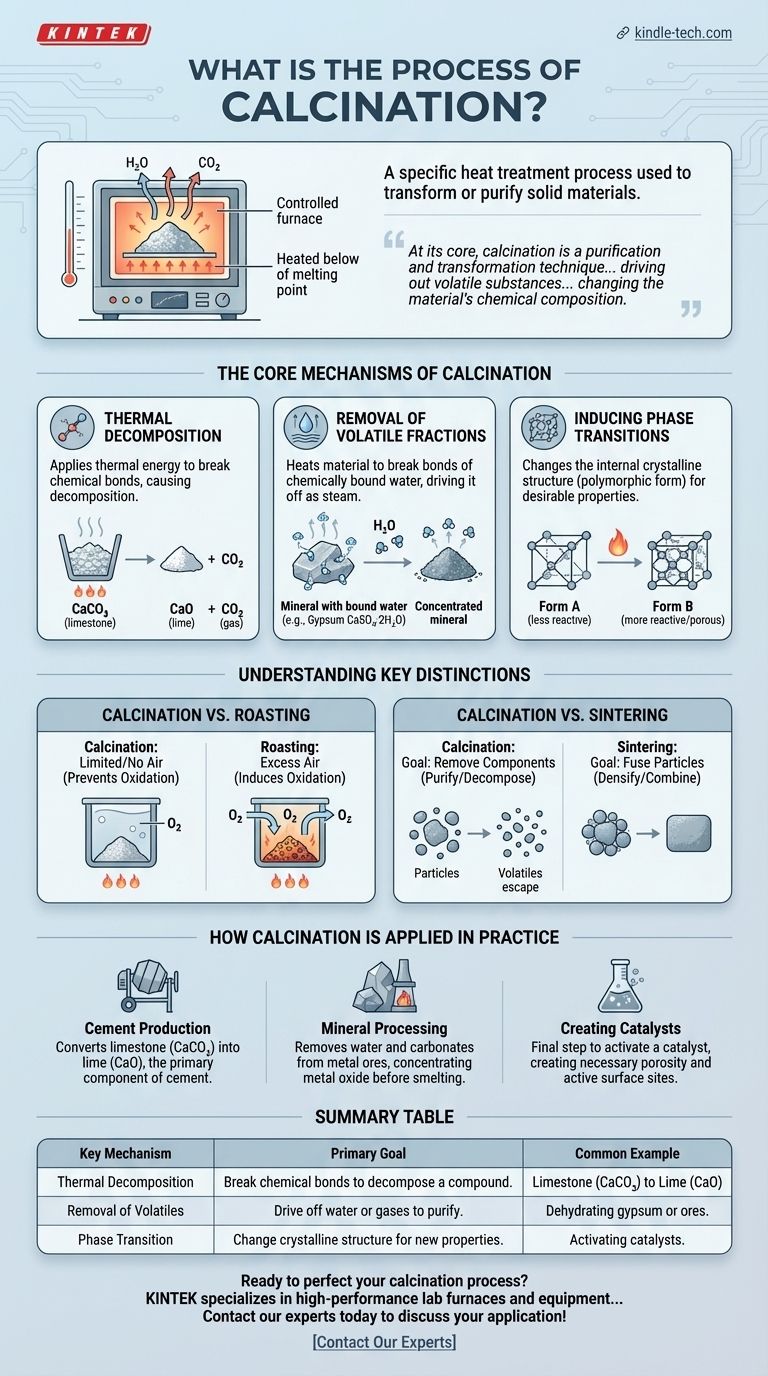
In materials science and metallurgy, calcination is a specific heat treatment process used to transform or purify solid materials. It involves heating a substance to a high temperature, but below its melting or fusing point, within a controlled atmosphere that has a limited supply of air or is absent of it entirely. This precise application of heat is designed to cause thermal decomposition or drive off volatile components like water and carbon dioxide.
At its core, calcination is a purification and transformation technique. By carefully applying heat below a material's melting point, it drives out volatile substances, fundamentally changing the material's chemical composition and preparing it for subsequent processing.

The Core Mechanisms of Calcination
Calcination achieves its results through several distinct physical and chemical changes induced by heat. The specific goal dictates which of these mechanisms is most important for a given application.
Thermal Decomposition
This is the most common objective of calcination. The process applies enough thermal energy to break chemical bonds within a compound, causing it to decompose.
A classic example is the production of lime (calcium oxide) from limestone (calcium carbonate). When heated, the calcium carbonate decomposes, releasing carbon dioxide gas and leaving behind the desired calcium oxide.
Removal of Volatile Fractions
Many raw materials, particularly minerals and ores, contain water that is chemically bound within their crystal structure (hydrates).
Calcination heats the material sufficiently to break these bonds and drive off the water as steam. This removes impurities and increases the concentration of the desired substance in the ore.
Inducing Phase Transitions
Heat can also be used to change the internal crystalline structure of a material, a process known as phase transition.
This is often done to convert a material from one polymorphic form to another that may have more desirable properties, such as higher reactivity or a better structure for use as a catalyst.
Understanding Key Distinctions
The term "calcination" is often confused with other thermal processes. Understanding the differences is critical to grasping its specific purpose.
Calcination vs. Roasting
The key difference is the atmosphere. Calcination occurs in the absence or limited supply of air to prevent oxidation.
Roasting, in contrast, is performed with an excess of air specifically to induce oxidation. It is often used on sulfide ores to convert them into metal oxides.
Calcination vs. Sintering
These processes have opposite goals. The purpose of calcination is to remove components from a material, effectively purifying or decomposing it.
Sintering, however, uses heat to fuse small particles together into a single, solid piece, a process known as densification. It aims to combine, not remove.
How Calcination is Applied in Practice
The choice to use calcination is driven by the desired end product. Its application is foundational in several major industries.
- If your primary focus is cement production: Calcination is the essential step to convert limestone (CaCO₃) into lime (CaO), the primary component of cement.
- If your primary focus is mineral processing: Calcination is used to remove water and carbonates from metal ores, concentrating the metal oxide before smelting.
- If your primary focus is creating catalysts: Calcination is often the final step to activate a catalyst, creating the necessary porosity and active surface sites.
Ultimately, mastering calcination is about precise thermal control to transform a raw material into a refined, purpose-driven product.
Summary Table:
| Key Mechanism | Primary Goal | Common Example |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Decomposition | Break chemical bonds to decompose a compound. | Limestone (CaCO₃) to Lime (CaO) |
| Removal of Volatiles | Drive off water or gases (e.g., CO₂) to purify. | Dehydrating gypsum or ores. |
| Phase Transition | Change a material's crystalline structure for new properties. | Activating catalysts. |
Ready to perfect your calcination process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and equipment for precise thermal treatment. Whether you're in cement production, mineral processing, or catalyst development, our solutions ensure the exact temperature control and atmosphere you need for superior results. Contact our experts today to discuss your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the suitable material of construction of a muffle furnace? A Guide to High-Temperature Performance
- What is the importance of muffle furnace in laboratory? Achieve Precise, Contaminant-Free Heating
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and an oven? Choose the Right High-Temperature Tool
- What are the applications of muffle furnaces? Essential Tools for High-Temperature Processes
- What is the main function of a muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing



















