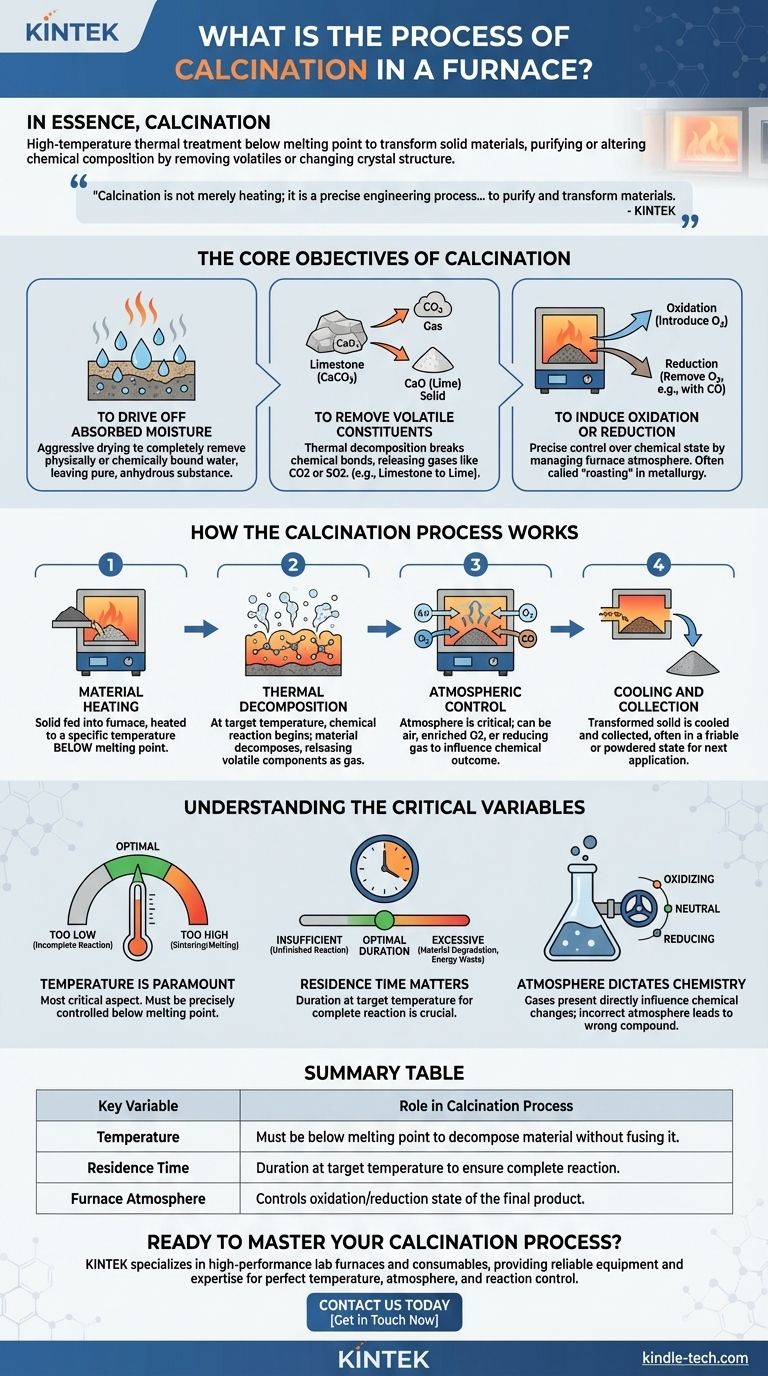
In essence, calcination is a high-temperature thermal treatment process used to transform solid materials. By heating a substance in a furnace to a point below its melting temperature, calcination induces a chemical reaction or a physical phase change, primarily to purify the material or alter its chemical composition. This is done to remove volatile components like water and carbon dioxide, or to trigger changes in the material's crystal structure.
Calcination is not merely heating; it is a precise engineering process designed to purify and transform materials. By controlling temperature and atmosphere, it removes unwanted components like CO2 and water, fundamentally altering a substance to prepare it for critical industrial applications.

The Core Objectives of Calcination
Calcination is performed to achieve specific, transformative goals. The process is defined by its outcome, which typically falls into one of three categories.
To Drive Off Absorbed Moisture
In its simplest form, calcination acts as an aggressive drying process. Heating the material to a high temperature ensures the complete removal of any physically or chemically bound water molecules, leaving a pure, anhydrous substance.
To Remove Volatile Constituents
This is the most common objective. Many raw materials, like limestone (calcium carbonate), contain volatile components that are released as gas when heated. The heat breaks the chemical bonds, driving off substances like carbon dioxide (CO2) or sulfur dioxide (SO2).
This process of thermal decomposition is central to many industrial applications.
To Induce Oxidation or Reduction
Calcination allows for precise control over a material's chemical state. By managing the atmosphere within the furnace, you can either introduce oxygen to oxidize a substance or use a reducing atmosphere (like carbon monoxide) to remove oxygen from it. This is often referred to as "roasting" in metallurgy.
How the Calcination Process Works
The process is more than just applying heat; it involves a sequence of controlled steps inside a specialized furnace, such as a rotary kiln or tube furnace.
Step 1: Material Heating
The raw solid material is fed into the furnace and heated to a specific, predetermined temperature. This temperature is always below the material's melting point to ensure it remains in a solid state throughout the process.
Step 2: Thermal Decomposition
As the material reaches the target temperature, the intended chemical reaction begins. The heat provides the energy needed to break chemical bonds, causing the material to decompose and release its volatile components as gas.
A classic example is the decomposition of limestone (CaCO3) into lime (calcium oxide, CaO) and carbon dioxide gas (CO2).
Step 3: Atmospheric Control
The atmosphere inside the furnace is a critical variable. For simple decomposition, air may be sufficient. For more advanced processes like roasting metal ores, the atmosphere may be enriched with oxygen (for oxidation) or a reducing gas to achieve a specific chemical outcome.
Step 4: Cooling and Collection
Once the reaction is complete, the transformed solid material is cooled and collected. The final product, such as lime, is often in a more friable or easily powdered condition, ready for its next application.
Understanding the Critical Variables
Success in calcination depends on the precise control of several factors. Mismanaging these can lead to an incomplete reaction or a ruined final product.
Temperature is Paramount
Controlling the temperature is the most critical aspect. If the temperature is too low, the thermal decomposition will be incomplete. If it is too high, the material may begin to sinter (fuse together) or even melt, destroying the desired properties of the final product.
Residence Time Matters
The duration the material spends at the target temperature, known as residence time, is crucial. Insufficient time results in an unfinished reaction, while excessive time can degrade the material and waste significant energy.
Atmosphere Dictates Chemistry
The gases present within the furnace directly influence the chemical changes. An incorrect atmosphere—for instance, an oxidizing environment when a reducing one is needed—will result in the wrong final chemical compound.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this process effectively, you must align your operational parameters with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is material purification: Concentrate on precise temperature control to drive off specific volatiles like H2O or CO2 without thermally damaging the desired final product.
- If your primary focus is chemical synthesis: Your main concern is managing the furnace atmosphere to achieve the correct state of oxidation or reduction for your target compound.
- If your primary focus is industrial production (e.g., cement): Optimize the balance between temperature and residence time to ensure complete decomposition at the highest possible throughput, maximizing efficiency.
Mastering calcination is mastering the controlled transformation of raw materials into the foundational products that build our world.
Summary Table:
| Key Variable | Role in Calcination Process |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Must be below melting point to decompose material without fusing it. |
| Residence Time | Duration at target temperature to ensure complete reaction. |
| Furnace Atmosphere | Controls oxidation/reduction state of the final product. |
Ready to Master Your Calcination Process?
Calcination is a precise thermal treatment critical for purifying materials and driving chemical changes. Whether your goal is to remove volatiles like CO2 or synthesize a specific compound, the right furnace and expert support are essential for success.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and consumables, providing the reliable equipment and technical expertise your laboratory needs to achieve perfect temperature control, atmosphere management, and reaction outcomes.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application, and let our experts help you select the ideal furnace for your calcination needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Is heat treatment a strengthening mechanism? Unlock Tailored Material Strength
- What is the movement of heat in a vacuum? Mastering Thermal Radiation for Precise Control
- What is the necessity of heat treatment after carburizing? Unlock Superior Hardness and Toughness
- What is the main disadvantage of quenching a part rapidly in water? High Risk of Cracking and Distortion
- How does the heat reflection efficiency of a molybdenum heat shield compare to a steel heat shield? | 7-to-1 Performance
- Why is a vacuum drying oven required for PEO-based SPE? Ensure Anhydrous Stability in Solid-State Battery Prep
- Why is a high-temperature annealing furnace used for Zircaloy-2 before irradiation? Essential Sample Preparation Guide
- What physical conditions must a high-temperature gasification furnace provide? Optimize Lignin to Syngas Conversion



















