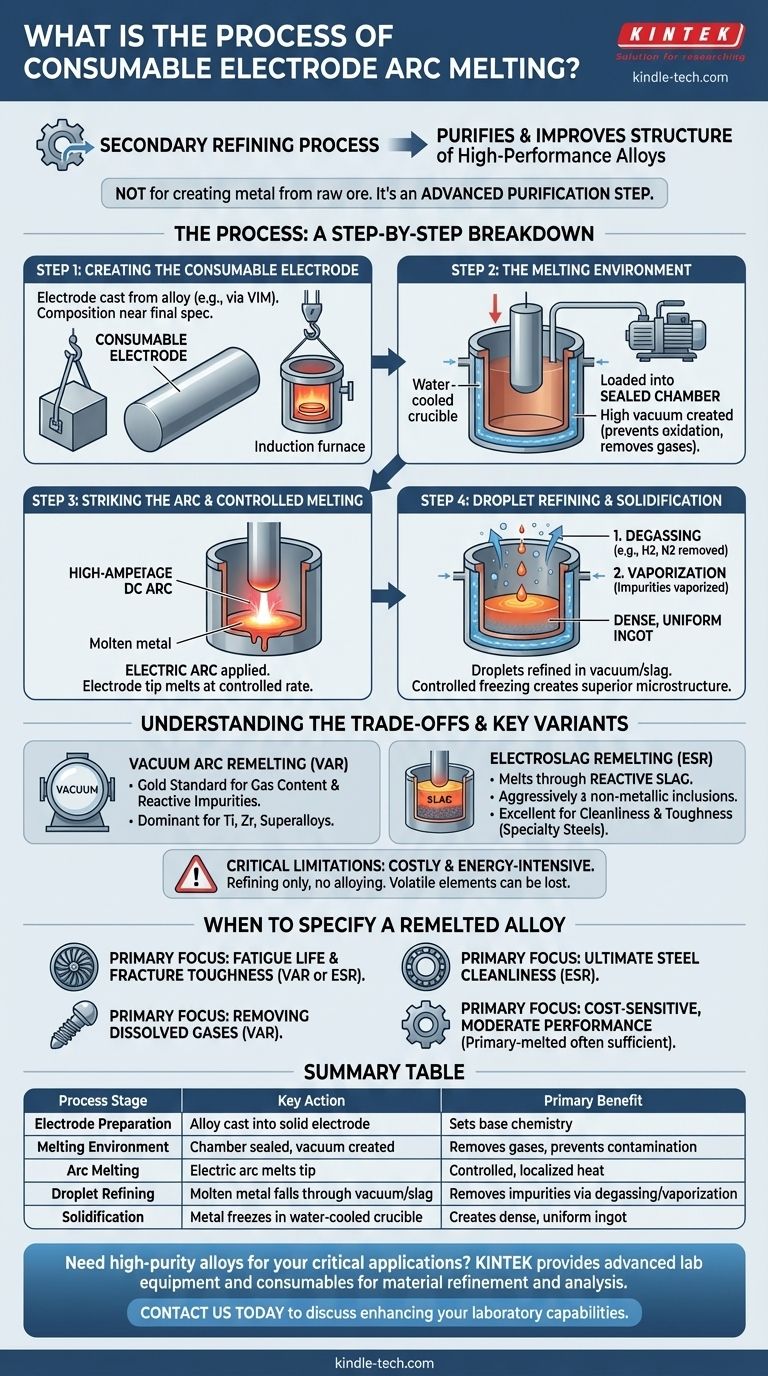
Consumable electrode arc melting is a secondary refining process used to purify and improve the structure of high-performance metal alloys. It works by using an electrode cast from the alloy itself, which is progressively melted by an electric arc inside a controlled environment, typically a vacuum, and re-solidified in a water-cooled copper crucible to form a new, highly purified ingot.
This process is not for creating metal from raw ore. It is an advanced purification step that takes an already-formed alloy and refines it to achieve the extreme levels of cleanliness and structural integrity required for critical applications in aerospace, medical implants, and power generation.

The Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
At its core, consumable electrode melting is a controlled remelting operation designed to remove impurities and perfect the alloy's internal structure. The most common variant is Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR), which we will use as the primary example.
Step 1: Creating the Consumable Electrode
The process begins not with scrap or ore, but with a large, solid cylinder of the alloy to be refined. This cylinder, called the consumable electrode, is typically produced through a primary melting process like Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM).
The composition of this electrode is already very close to the final desired specification. The goal of the remelting process is not to change the alloy's chemistry, but to purify it.
Step 2: The Melting Environment
The electrode is loaded vertically into a sealed, water-cooled copper crucible. The air is then pumped out of the chamber, creating a high vacuum.
This vacuum is critical. It prevents the molten metal from reacting with oxygen and nitrogen from the air, and more importantly, it helps pull dissolved gases like hydrogen out of the alloy.
Step 3: Striking the Arc and Controlled Melting
A high-amperage, low-voltage DC current is applied, and an electric arc is struck between the bottom tip of the electrode and a small amount of "starter" material at the base of the crucible.
The intense heat of the arc, which can exceed the metal's melting point, begins to melt the tip of the electrode. The melt rate is very carefully controlled by adjusting the arc current.
Step 4: Droplet Refining and Solidification
As the electrode melts, a superheated film of liquid metal forms on its tip. This metal falls as droplets through the vacuum and into the molten pool (or "sump") below.
During this fall, two key refining actions occur:
- Degassing: Exposure to the vacuum pulls out dissolved gases (e.g., hydrogen, nitrogen).
- Vaporization: Impurities with low boiling points are vaporized and removed by the vacuum system.
The molten metal collects and solidifies in the water-cooled copper crucible. Because the crucible is aggressively cooled, solidification is highly directional—it occurs from the bottom up and from the sides inward. This controlled freezing process produces a dense, uniform ingot with a superior microstructure and pushes remaining impurities into the last liquid to freeze at the very top.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Variants
Consumable electrode melting is a powerful but costly process. Understanding its variations and limitations is key to specifying it correctly.
Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR)
VAR is the gold standard for alloys where gas content and reactive impurities are the primary concern. The vacuum environment is exceptionally effective at removing dissolved hydrogen and volatile metallic elements. It is the dominant process for titanium, zirconium, and many nickel-based superalloys.
Electroslag Remelting (ESR)
ESR is a similar process, but instead of a vacuum, the electrode melts into a molten, highly reactive slag bath. The metal droplets must pass through this slag before joining the molten pool.
The slag acts as a chemical cleaning flux, aggressively absorbing non-metallic inclusions like oxides and sulfides. This makes ESR highly effective for improving the cleanliness and toughness of specialty steels, tool steels, and some nickel alloys.
Critical Limitations
This is not a universal solution. It is an expensive, energy-intensive process that adds significant cost to the material. Furthermore, it is a refining process, not an alloying one. The bulk chemistry is fixed from the start, and some desirable but volatile alloying elements can be lost during the vacuum process.
When to Specify a Remelted Alloy
Choosing this process is a strategic decision to invest in material purity for a specific performance goal.
- If your primary focus is fatigue life and fracture toughness (e.g., jet engine disks, landing gear): Specify a VAR or ESR alloy to minimize the microscopic inclusions that can initiate cracks.
- If your primary focus is removing dissolved gases (e.g., titanium aerospace components, medical implants): VAR is the definitive choice for its unmatched degassing capability.
- If your primary focus is ultimate steel cleanliness (e.g., high-performance bearings, injection molds): ESR is superior for its ability to scrub sulfur and oxide inclusions from the melt.
- If your primary focus is a cost-sensitive application with moderate performance needs: A primary-melted alloy is often sufficient, as the added cost of remelting may not provide a proportional benefit.
Ultimately, specifying a remelted alloy is how you ensure maximum material integrity for applications where performance and reliability are paramount.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Action | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Electrode Preparation | Alloy is cast into a solid electrode | Sets the base chemistry for refinement |
| Melting Environment | Chamber is sealed and a vacuum is created | Removes dissolved gases and prevents contamination |
| Arc Melting | Electric arc melts the electrode tip | Provides controlled, localized heat for precise melting |
| Droplet Refining | Molten metal falls through vacuum/slag | Removes impurities via degassing and vaporization |
| Solidification | Metal freezes in water-cooled copper crucible | Creates a dense, uniform ingot with superior structure |
Need high-purity alloys for your critical applications? The consumable electrode arc melting process is essential for achieving the extreme material integrity required in aerospace, medical, and power generation components. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed to support these demanding industries. Let our experts help you select the right tools for your material refinement and analysis needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does heat affect tensile strength? Understand the Strength-Ductility Trade-Off
- Which furnace gives the highest temperature? Find the Right Tool for Your Lab or Industrial Needs
- How does a high-precision heat treatment furnace contribute to the normalizing and tempering of 15Cr12MoVWN steel?
- What are the two processes of annealing? A Guide to Full and Process Annealing
- What is the role of a vacuum drying oven in PEO-based membrane treatment? Achieve Peak Solid-State Battery Purity
- What is the pressure for vacuum carburizing? Unlock Superior Control and Cleanliness
- What is the application of vacuum mold casting? Achieve Rapid, High-Fidelity Prototyping and Bridge-to-Production
- Why Use Vacuum Furnaces for MAX Phase Cladding? Achieve High Purity & Superior Oxidation Resistance



















