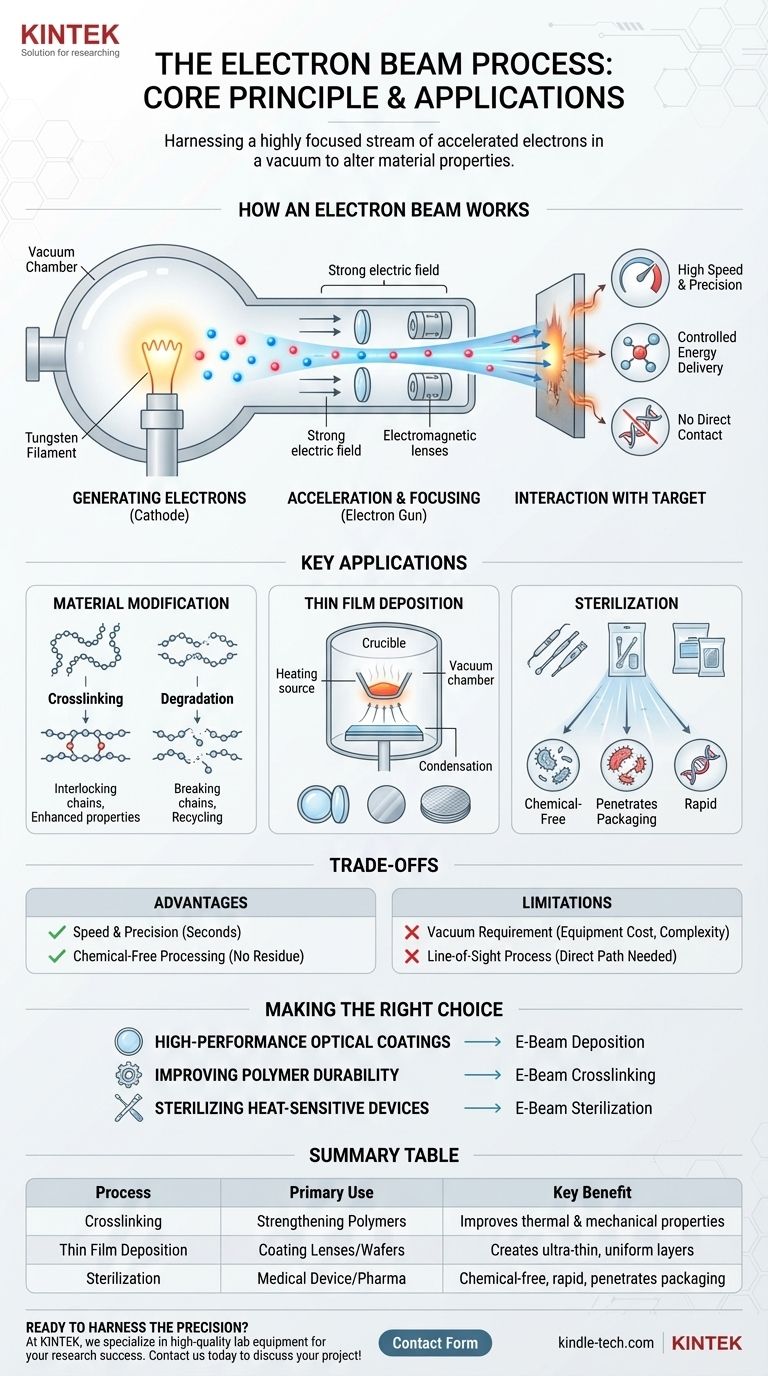
At its core, an electron beam process is a method that uses a highly focused stream of accelerated electrons inside a vacuum to alter a material's properties. This energy transfer can be used to heat, vaporize, chemically change, or sterilize a target object with incredible precision and speed. It is not a single technique but a versatile platform technology with applications ranging from manufacturing advanced optics to sterilizing medical devices.
The central concept is the controlled delivery of energy. By generating and directing a beam of high-energy electrons, engineers can induce specific physical or chemical changes in a material without direct contact or the use of chemical agents.

How an Electron Beam Works: The Core Principle
The fundamental technology behind any electron beam process is the electron gun, which operates in a high-vacuum environment.
Generating the Electrons
The process begins with a cathode, typically a tungsten filament. When heated to a very high temperature, this filament releases a cloud of electrons through a process called thermionic emission.
Acceleration and Focusing
These free electrons are then accelerated to extremely high speeds by a strong electric field, created by applying a high voltage. Electromagnetic lenses then focus these fast-moving electrons into a narrow, precise beam, much like a glass lens focuses light.
Interaction with the Target
When this high-energy beam strikes a target material, it rapidly transfers its kinetic energy. This energy transfer is what drives the desired modification, whether it's melting a substance, breaking chemical bonds, or destroying microbial DNA.
Key Applications of Electron Beam Technology
The versatility of the electron beam allows it to be adapted for several distinct industrial processes.
Material Modification: Crosslinking and Degradation
For polymer-based products, the electron beam can initiate crosslinking. The beam's energy creates free radicals, causing polymer chains to form new bonds with each other. This enhances the material's mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability.
Conversely, at very high doses, the beam can be used for material degradation. It systematically breaks down long polymer chains, which is a useful technique in the recycling of certain materials.
Thin Film Deposition
In electron beam deposition, the beam is aimed at a source material (like a ceramic or metal) held in a crucible inside a vacuum chamber. The intense, localized heating causes the material to vaporize.
This vapor then travels and condenses as an extremely thin, uniform film on a cooler substrate, such as a lens or a silicon wafer. This process is essential for creating high-performance optical coatings and electronic components.
Sterilization
For medical and pharmaceutical goods, the electron beam provides a highly effective method of terminal sterilization. The high-energy electrons penetrate sealed packaging and irreversibly damage the DNA of bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms, rendering the product sterile without high heat or residual chemicals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, electron beam technology has specific requirements and limitations that determine its suitability for a given task.
Advantage: Speed and Precision
Electron beam processes are incredibly fast, delivering a full sterilization or curing dose in a matter of seconds. The beam can be controlled with magnetic fields, allowing for precise and repeatable energy application.
Advantage: Chemical-Free Processing
Because the modification is driven purely by energy, no chemical agents are required. This is a critical advantage in medical sterilization and food processing, as it eliminates concerns about residual toxins.
Limitation: Vacuum Requirement
Nearly all electron beam processes must occur in a high vacuum. This is necessary to prevent the electrons from colliding with and scattering off air molecules. The need for a vacuum chamber increases equipment cost, complexity, and can limit the size of the product being treated.
Limitation: Line-of-Sight Process
The electron beam travels in a straight line. This means it can only treat surfaces that it can directly "see." For products with complex, shadowed geometries, ensuring complete coverage can be a challenge and may require rotating the part during exposure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" application of an electron beam depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is creating high-performance optical coatings: E-beam deposition offers unparalleled precision for controlling film thickness and density.
- If your primary focus is improving the durability of polymers: E-beam crosslinking is the ideal industrial process for enhancing thermal and mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive medical devices: E-beam sterilization provides a rapid, effective, and chemical-free method that works even after products are in their final packaging.
Ultimately, mastering an electron beam process is about harnessing a fundamental force of nature to build, change, or purify materials at an atomic level.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Use | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Crosslinking | Strengthening Polymers | Improves thermal & mechanical properties |
| Thin Film Deposition | Coating Lenses/Wafers | Creates ultra-thin, uniform layers |
| Sterilization | Medical Device/Pharma | Chemical-free, rapid, penetrates packaging |
Ready to harness the precision of electron beam technology for your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including electron beam systems, to help you achieve superior results in material modification, thin film deposition, and sterilization. Our expertise ensures you get the right solution for your specific application, enhancing your research and production capabilities.
Contact us today to discuss your project needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What is the most common machine used to sterilize medical supplies? The Definitive Guide to Autoclaves
- Do you need to autoclave glassware? A Guide to Sterilization vs. Cleaning
- How do you sterilize glassware by autoclave? Master the 3-Step Process for Reliable Sterility
- What are the sizes of autoclaves? A Guide to Choosing the Right Capacity for Your Lab
- How does the lab autoclave work? Achieve Complete Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam



















