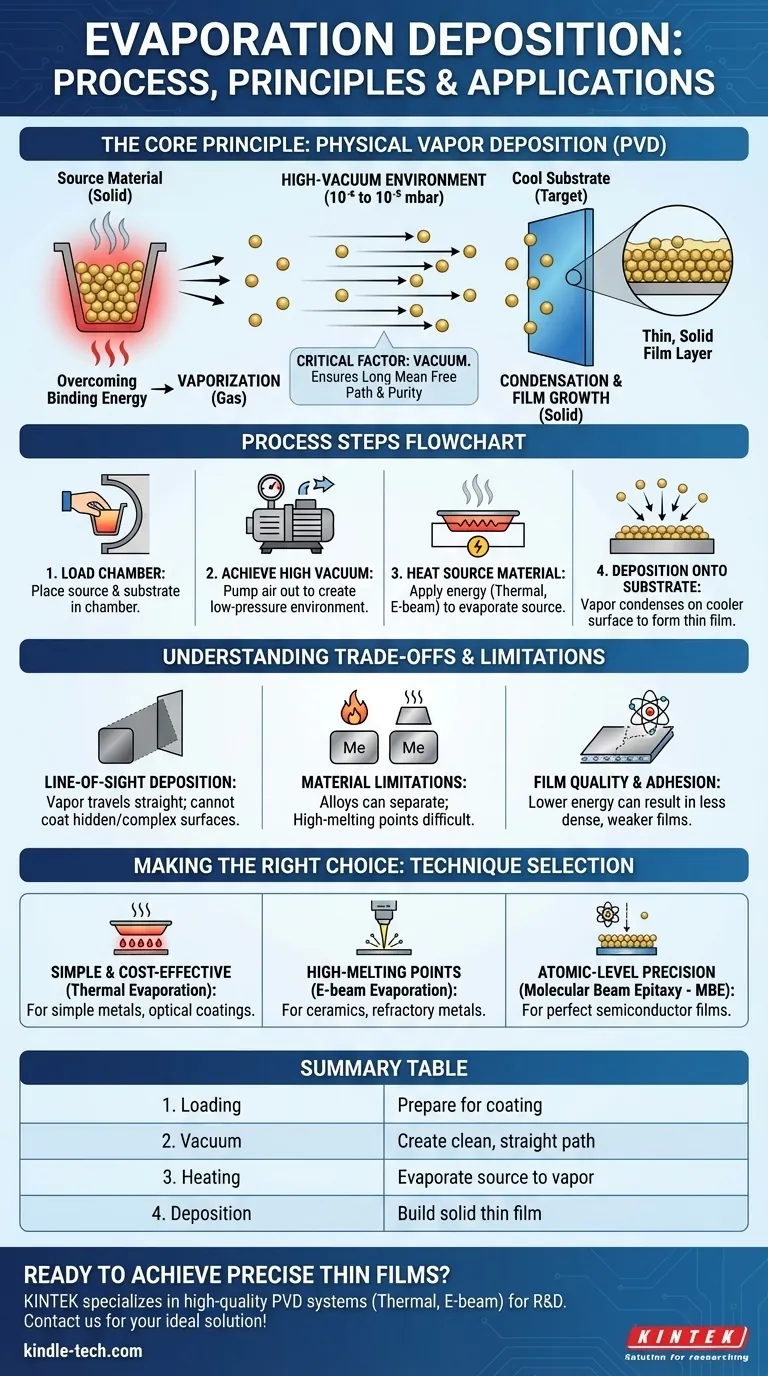
At its core, evaporation deposition is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) method for creating a thin film. The process involves heating a source material inside a high-vacuum chamber until it evaporates, turning into a gas. This vapor then travels through the vacuum and condenses onto a cooler target surface, known as a substrate, forming a solid, uniform coating.
The success of evaporation deposition hinges on one critical factor: the vacuum. A high-vacuum environment is not just for preventing contamination; it is essential for ensuring the vaporized atoms have a clear, straight path from the source to the substrate, which dictates the quality and purity of the final film.

The Fundamental Principle: From Solid to Vapor
Overcoming Binding Energy
Evaporation occurs when the atoms or molecules of a material gain enough thermal energy to break free from the forces holding them in a solid or liquid state. In deposition technology, this is achieved by actively heating the source material.
As the temperature rises, the atoms on the material's surface vibrate with increasing energy. Eventually, they gain enough kinetic energy to escape into the gaseous phase, creating a stream of vapor.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
The entire process takes place in a high-vacuum chamber, typically at pressures of 10⁻⁶ to 10⁻⁵ mbar. This environment is crucial for two reasons.
First, it removes air and other unwanted gases that could react with the hot vapor, contaminating the film. Second, it dramatically increases the mean free path—the average distance a particle can travel before colliding with another. In a high vacuum, vaporized atoms travel in a straight line directly to the substrate without being scattered by background gas.
Condensation and Film Growth
When the hot vapor stream reaches the comparatively cool substrate, the atoms rapidly lose their energy and condense back into a solid state. They attach to the substrate's surface, gradually building up layer by layer to form a thin, solid film.
A Closer Look at the Process Steps
Step 1: Loading the Chamber
The process begins by placing the source material and the substrate into the chamber. The source material is typically held in a resistive container, such as a crucible, boat, or basket, often made of a high-temperature material like tungsten.
Step 2: Achieving High Vacuum
The chamber is sealed, and a series of vacuum pumps removes the air to create the necessary low-pressure environment. This step is vital for ensuring the purity and integrity of the deposition process.
Step 3: Heating the Source Material
Once the target vacuum level is reached, the source material is heated. In the most common method, thermal evaporation, a high electrical current is passed through the boat or crucible holding the material. The resistance of the boat causes it to heat up rapidly, transferring that heat to the source material and causing it to evaporate.
Step 4: Deposition onto the Substrate
The stream of vapor particles travels upward, or in a "line-of-sight" path, from the source. It coats the substrate, which is strategically placed in the path of the vapor. The thickness of the deposited film is controlled by monitoring the deposition rate and time.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Line-of-Sight Deposition
A significant characteristic of evaporation is that it is a line-of-sight process. The vapor travels in straight lines, meaning it can only coat surfaces that are directly visible from the source. This makes it challenging to achieve uniform coatings on complex, three-dimensional objects with hidden surfaces or undercuts.
Material Limitations
Thermal evaporation works best for materials with relatively low melting points, such as aluminum, gold, and chromium. Materials with very high melting points, like ceramics or refractory metals, are difficult to evaporate using simple resistive heating.
Furthermore, depositing alloys can be problematic. If the constituent elements have different evaporation temperatures, one material may vaporize faster than the other, resulting in a film composition that does not match the source alloy.
Film Quality and Adhesion
Compared to higher-energy processes like sputtering, the atoms in thermal evaporation arrive at the substrate with relatively low kinetic energy. This can sometimes result in films that are less dense and have weaker adhesion to the substrate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The choice of evaporation technique is determined by the material to be deposited, the required film quality, and the specific application.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and cost-effectiveness: Standard thermal evaporation is often the best choice for depositing simple metals for applications like optical coatings or electrical contacts.
- If your primary focus is depositing high-melting-point materials or ceramics: Electron-beam (e-beam) evaporation, which uses a focused beam of electrons to heat the source, is necessary to reach the required temperatures.
- If your primary focus is creating perfect, single-crystal films for semiconductors: Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE), a highly precise and slow form of evaporation, offers the atomic-level control needed for these demanding applications.
Understanding these core principles allows you to select the precise deposition technique to achieve your desired thin-film properties.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Loading | Place source material & substrate in chamber | Prepare for coating process |
| 2. Vacuum | Pump air out to achieve high vacuum (10⁻⁶ mbar) | Create a clean, straight path for vapor |
| 3. Heating | Apply heat to source material (e.g., thermal, e-beam) | Evaporate source material into a vapor |
| 4. Deposition | Vapor condenses on cooler substrate | Build a solid, uniform thin film layer |
Ready to achieve precise thin films in your lab? The right evaporation deposition system is key to your success. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including thermal and e-beam evaporation systems, designed to meet the rigorous demands of research and development. Our experts can help you select the ideal PVD solution for your specific materials and application goals. Contact our team today to discuss how we can enhance your thin film capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods



















