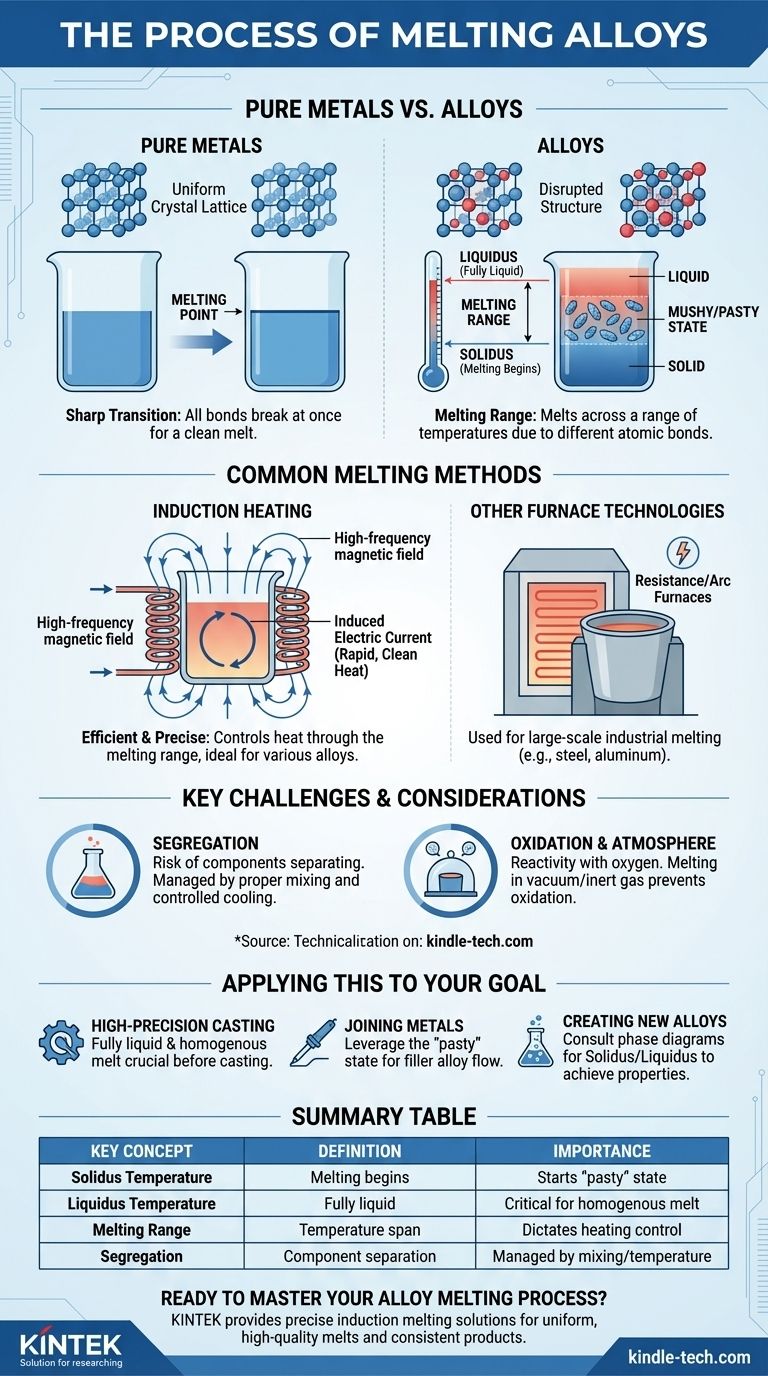
The fundamental difference is that most alloys do not melt at a single, specific temperature. Unlike pure metals, they transition from solid to liquid across a range of temperatures, passing through a semi-solid or "pasty" state in the process.
The key to understanding how alloys melt is to shift from the concept of a single "melting point" to a "melting range." This range is defined by two critical temperatures: the solidus, where melting begins, and the liquidus, where the alloy becomes fully liquid.

The Science of the Melting Range
The unique melting behavior of an alloy is a direct result of its atomic structure. It’s what distinguishes it from a pure element.
Pure Metals: A Sharp Transition
A pure metal, like iron or copper, has a uniform crystal lattice. All its atoms are the same size and are held together by bonds of equal strength.
When heated to its specific melting point, there is enough energy to break all these bonds at once, causing a rapid and clean transition from a solid to a liquid.
Alloys: The Solidus and Liquidus
Alloys are mixtures of two or more metals. The different-sized atoms of the constituent elements disrupt the neat, uniform crystal structure.
This disruption creates areas with weaker bonds. As the alloy is heated, these weaker areas begin to melt first at a temperature known as the solidus.
The "Mushy" or "Pasty" State
Between the solidus and the liquidus temperatures, the alloy exists as a mixture of solid crystals and molten liquid. This semi-solid state is often described as "pasty" or "mushy."
Only when the temperature reaches the liquidus is there enough energy to break all the remaining crystalline bonds, rendering the entire alloy fully molten.
Common Methods for Melting Alloys
Controlling the temperature precisely through the melting range is critical for achieving a uniform, high-quality final product. Modern techniques are designed for this level of control.
Induction Heating
Induction heating is a highly efficient and widely used method for melting alloys, from precious metals like gold and silver to industrial alloys like brass and bronze.
This process uses a powerful, high-frequency alternating magnetic field to induce an electric current directly within the metal. This internal current generates rapid, clean, and highly controllable heat.
The precision of induction heating is ideal for managing an alloy's journey through its solidus-liquidus range without overheating or burning away valuable elements.
Other Furnace Technologies
While induction is prevalent, other methods like resistance furnaces (using heating elements) or arc furnaces (using a high-power electric arc) are also used, particularly for large-scale industrial melting of steel and aluminum alloys.
Key Challenges and Considerations
The gradual melting process of alloys presents unique challenges that must be managed to ensure the quality of the final material.
The Risk of Segregation
Because different components of the alloy may melt or freeze at different rates, there is a risk of them separating. This is known as segregation.
If not managed by proper mixing and controlled cooling, segregation can lead to an inconsistent final casting with weak spots or poor performance.
Controlling the Atmosphere
Many metals, such as aluminum, are highly reactive with oxygen, especially when molten.
Melting is therefore often done in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon) to prevent oxidation, which can introduce impurities and compromise the alloy's integrity.
Applying This to Your Goal
Understanding an alloy's melting range is not just academic; it directly impacts how you should approach your work.
- If your primary focus is high-precision casting (e.g., jewelry or aerospace): You must use a precisely controlled heating method like induction to ensure the alloy becomes fully liquid and homogenous before casting.
- If your primary focus is joining metals (e.g., soldering or brazing): You are intentionally leveraging the "pasty" state of the filler alloy to allow it to flow into the joint before it fully solidifies.
- If your primary focus is creating new alloys: You must carefully consult phase diagrams to predict the solidus and liquidus temperatures to achieve the desired material properties.
Mastering an alloy requires understanding its unique journey from solid to liquid.
Summary Table:
| Key Concept | Definition | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Solidus Temperature | The temperature at which melting begins. | Marks the start of the semi-solid "pasty" state. |
| Liquidus Temperature | The temperature at which the alloy is fully liquid. | Critical for achieving a homogenous melt for casting. |
| Melting Range | The temperature span between the solidus and liquidus. | Dictates the heating process and control required. |
| Segregation | The risk of alloy components separating during melting/cooling. | Managed by proper mixing and controlled temperature. |
Ready to master your alloy melting process?
Whether you are involved in high-precision casting, metal joining, or alloy development, precise temperature control is non-negotiable. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including precisely controlled induction melting furnaces, designed to help you navigate the solidus-liquidus range efficiently.
We provide solutions that help you:
- Achieve uniform, high-quality melts.
- Minimize oxidation and segregation.
- Improve the consistency and integrity of your final product.
Let's discuss your specific laboratory needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect melting solution for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between RF and DC power? Choosing the Right Power for Your Application
- What is the meaning of vacuum pyrolysis? Maximize Liquid Fuel Yield from Waste
- Why DC sputtering is not used for insulators? Overcome the Charge-Up Effect with RF Sputtering
- What is a laboratory evaporator? Choosing the Right System for Your Lab
- How long does it take for a house to cool down after heat treatment? A Guide to Safe & Speedy Recovery
- What does sintering decrease? Mastering Porosity, Surface Area, and Material Properties
- What role does an alumina-supported substrate play in CCD? Unlock the 'Gate' Effect for MFI Zeolite Membranes
- What is the physical sputtering method? A Guide to High-Performance Thin Film Deposition



















