In manufacturing, you don't "mold a mold"; rather, you use a mold to shape a material. The process you're likely asking about is blow molding, a common method for creating hollow plastic objects. It involves melting plastic into a tube-like shape called a preform, clamping it inside a custom mold, and then inflating it with compressed air until it takes the mold's shape.
The core concept of blow molding is simple yet powerful: it uses air pressure to shape a hot, soft plastic tube against the inside of a cavity, much like blowing up a balloon inside a bottle. This makes it an exceptionally efficient method for manufacturing hollow items like bottles and containers.
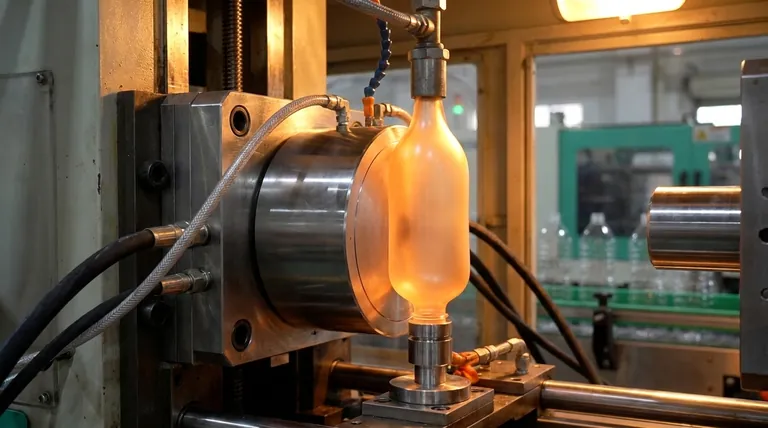
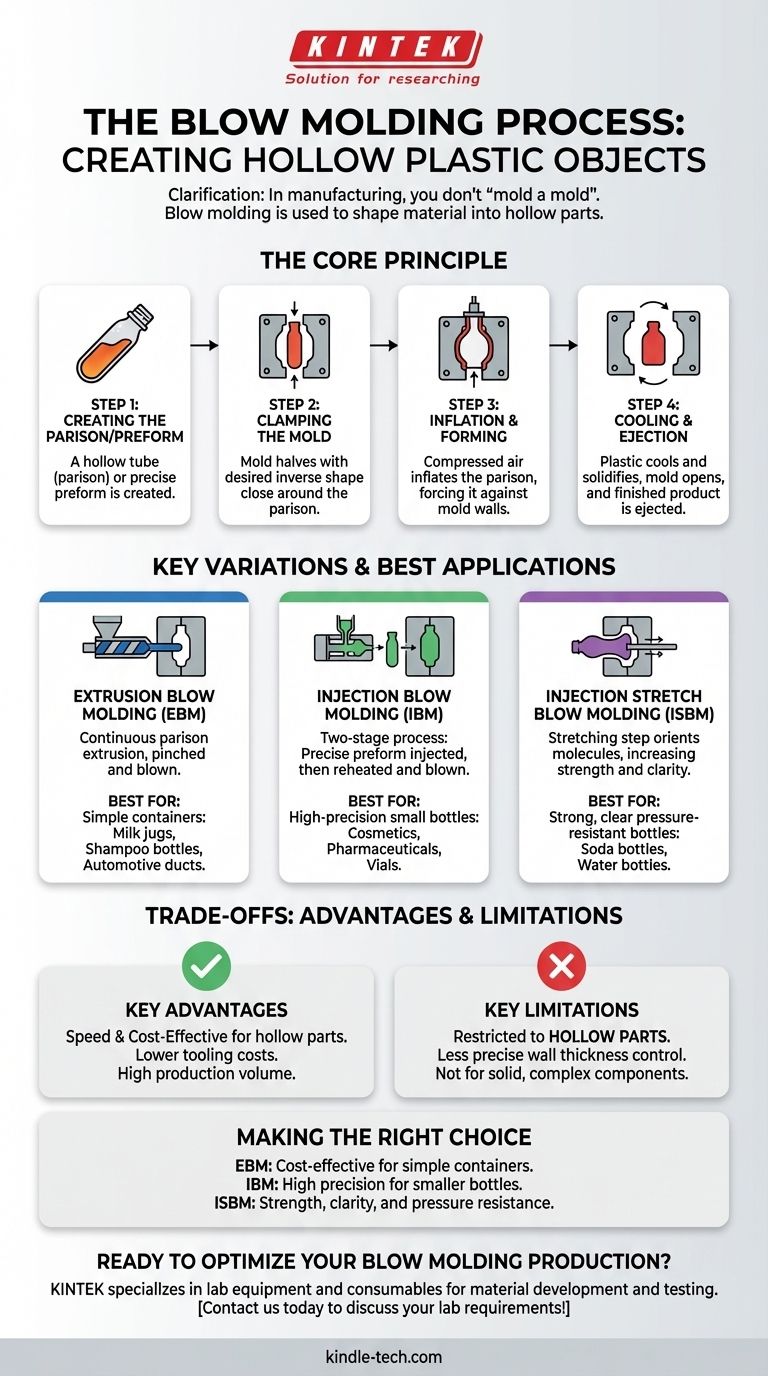
The Core Principle of Blow Molding
Blow molding is a multi-step process, but the fundamental physics remain consistent across its variations. The goal is always to transform a simple tube of plastic into a finished, hollow product.
Step 1: Creating the Parison or Preform
The process begins with a parison, which is a hollow tube of molten plastic. In some methods, this is created as a more precisely shaped preform that already includes finished features, like the threads on a bottle cap.
Step 2: Clamping the Mold
Next, the two halves of a metal mold close around the parison. The mold contains a cavity that is the exact inverse shape of the desired final product.
Step 3: Inflation and Forming
With the parison sealed inside the mold, compressed air is injected into it. This internal air pressure forces the soft, pliable plastic outward, pushing it against the cool walls of the mold cavity until it conforms to every detail.
Step 4: Cooling and Ejection
The plastic makes contact with the cooled mold and rapidly solidifies, locking in its new shape. Once the part is rigid enough, the mold opens, and the finished product is ejected.
Key Variations of the Blow Molding Process
While the core principle is the same, there are three primary methods of blow molding, each suited for different applications and production requirements.
Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM)
This is the simplest and most common method. A parison is continuously extruded downwards from a die, much like squeezing toothpaste from a tube. The mold closes around a section of this tube, pinches it off, and then inflates it. EBM is ideal for containers like milk jugs, shampoo bottles, and automotive ducts.
Injection Blow Molding (IBM)
IBM is a two-stage process that offers higher precision. First, a preform is created using injection molding, which allows for extremely accurate and detailed features like bottle necks and threads. This preform is then transferred to a second "blow mold" station where it is heated and inflated. This method is favored for smaller, high-volume items like pharmaceutical and cosmetic bottles.
Injection Stretch Blow Molding (ISBM)
ISBM builds upon the IBM process by adding a crucial step: stretching. After the preform is reheated, it is stretched lengthwise with a core rod and simultaneously inflated with air. This stretching orients the polymer molecules, significantly increasing the part's strength, clarity, and gas barrier properties. This is the standard process for making carbonated beverage bottles from PET plastic.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Blow molding is a highly effective technique, but it's essential to understand its specific strengths and weaknesses compared to other manufacturing processes.
Key Advantages
The primary benefits of blow molding are its speed and cost-effectiveness for hollow parts. Tooling costs are generally lower than for solid-part processes like injection molding, and cycle times can be very fast, enabling massive production volumes.
Key Limitations
The most obvious limitation is that blow molding is restricted to producing hollow parts. It also offers less precise control over wall thickness compared to a process like rotational molding. It is not a suitable choice for creating solid, complex geometric components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct blow molding method depends entirely on the requirements of your final product.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of simple containers: Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM) is the most direct and economical choice for items like jugs and tanks.
- If your primary focus is high precision and finish for smaller bottles: Injection Blow Molding (IBM) provides superior control over neck and thread details, essential for cosmetics or pharmaceuticals.
- If your primary focus is strength, clarity, and pressure resistance: Injection Stretch Blow Molding (ISBM) is the required method for creating durable and clear containers like soda bottles.
Ultimately, blow molding is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling the efficient production of countless everyday hollow plastic goods.
Summary Table:
| Blow Molding Method | Best For | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM) | Simple containers (milk jugs, shampoo bottles) | Cost-effective, continuous parison extrusion |
| Injection Blow Molding (IBM) | High-precision small bottles (cosmetics, pharmaceuticals) | Accurate neck and thread details from a preform |
| Injection Stretch Blow Molding (ISBM) | Strong, clear pressure-resistant bottles (soda bottles) | Stretching step increases strength and clarity |
Ready to manufacture your hollow plastic parts with precision and efficiency? KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables essential for developing and testing materials for blow molding processes. Whether you're optimizing preform design or ensuring material quality, our solutions support your production goals. Contact us today to discuss how we can equip your lab for success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high-strength graphite molds in the hot press sintering of Ti6Al4V-based composites?
- What role do high-strength graphite molds play during vacuum hot pressing? Enhance Precision in CuAlMn Composites
- What role does a high-purity graphite mold play during hot pressing? Optimize Boron Carbide Sintering at 1850°C
- What roles do graphite molds play during vacuum hot pressing of Al-Sc alloys? Ensure Precision & Purity
- Why is hot press molding preferred over traditional solution casting? Expert Comparison for Polymer Electrolytes



















