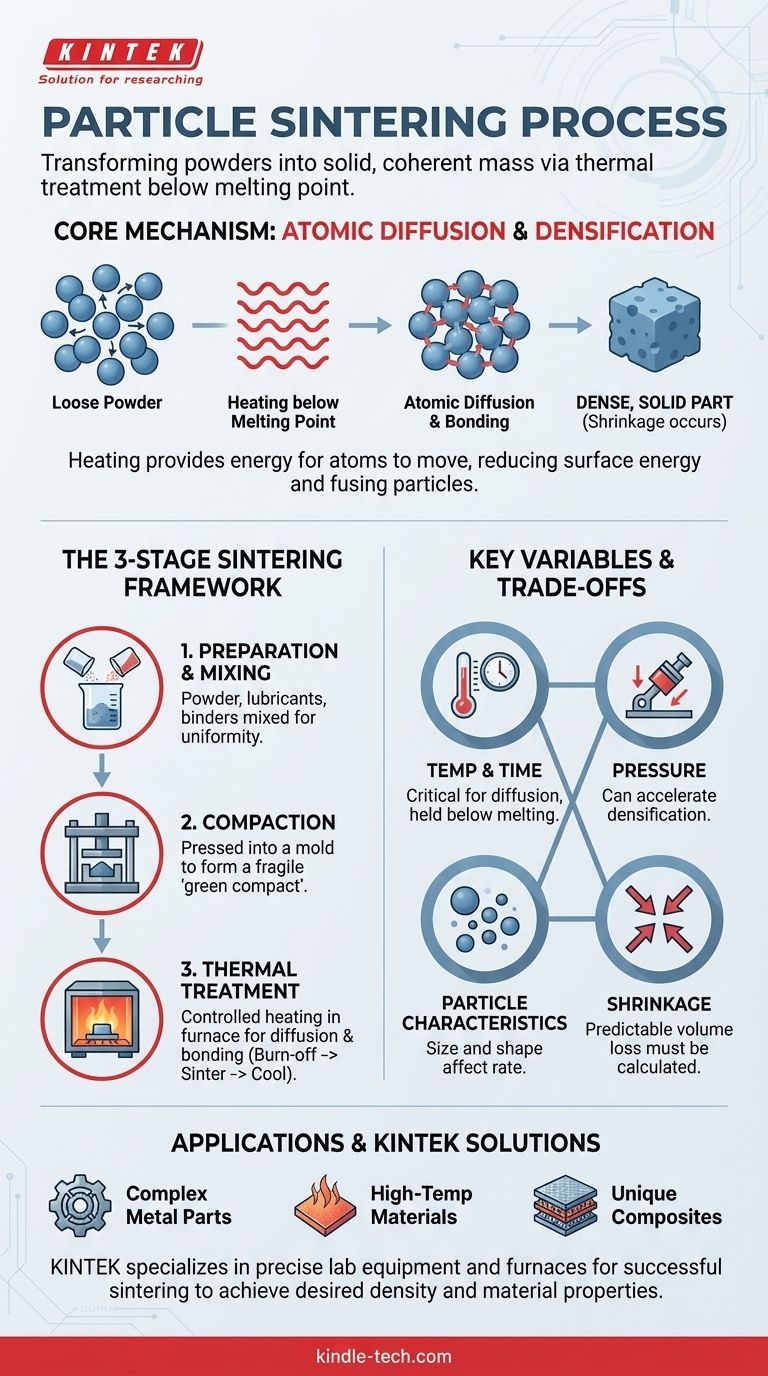
At its core, the process of particle sintering is a thermal treatment that transforms a collection of individual particles into a solid, coherent mass. It achieves this by heating the material to a temperature below its melting point, which provides enough energy for atoms to diffuse across particle boundaries, fusing them together and reducing the empty space, or porosity, between them.
Sintering is fundamentally a manufacturing method for creating dense, solid objects from powders. It relies on atomic diffusion, driven by heat and sometimes pressure, to bond particles together into a strong, unified part without ever melting the base material.

The Core Mechanism: How Sintering Actually Works
To truly understand the process, you must first grasp the underlying physics. Sintering is not simply a matter of "gluing" particles together; it is a fundamental transformation at the atomic level.
The Driving Force: Atomic Diffusion
A mass of powder has an incredibly high total surface area. From a physics perspective, this represents a high state of surface energy. Sintering works by lowering this energy.
When heated, the atoms in the particles gain enough energy to move, or diffuse, from one particle to another at their points of contact. This atomic migration fills the gaps and pores between particles, effectively creating a solid bridge.
The Goal: Densification and Bonding
As atoms migrate and bridges form, the individual particles pull closer together. This causes the overall component to shrink and become more dense.
The end result is a single, solid piece with a low-porosity microstructure. The final material is significantly stronger and more durable than the initial powder compact.
The Three Primary Stages of Sintering
While the specifics can vary by material and application, the industrial sintering process follows a consistent, three-stage framework.
Stage 1: Powder Preparation and Mixing
The process begins with the base material in powder form. This powder is often mixed with other elements to create an alloy or composite.
Lubricants or binding agents are also frequently added. These additives help the powder flow smoothly into the mold and hold the compacted shape together before the final heating.
Stage 2: Compaction
Next, the prepared powder is compacted into the desired shape. This is typically done by pressing the powder into a die or mold under high pressure.
This step creates what is known as a "green compact." The part has its final shape but is still fragile, with the particles held together only by mechanical friction and the binding agent. The key purpose of compaction is to create intimate particle-to-particle contact.
Stage 3: Thermal Treatment (Heating)
The green compact is then placed into a sintering furnace with a precisely controlled atmosphere to prevent oxidation. This heating stage is not a single step but a carefully controlled cycle.
First, a lower-temperature phase burns off any lubricants or binders. Then, the temperature is raised to the sintering point, where it is held for a specific duration. This is where atomic diffusion occurs, and the particles bond together. Finally, the part is cooled in a controlled manner to solidify into its final, unified state.
Understanding the Key Variables and Trade-offs
The success of the sintering process depends on the careful control of several interconnected parameters. Misunderstanding these can lead to failed parts.
Temperature and Time
The sintering temperature is the most critical variable. It must be high enough to allow for atomic diffusion but remain below the material's melting point. The amount of time the part is held at this temperature determines the extent of densification.
Applied Pressure
While not always required, applying external pressure during the heating phase can significantly accelerate the densification process. This is common in advanced sintering techniques.
Particle Characteristics
The initial size and shape of the powder particles have a major impact. Smaller, more uniform particles generally have higher surface energy and will sinter more quickly and to a higher final density.
Material Shrinkage
Because the process removes the empty space between particles, the final part will always be smaller than the initial green compact. This shrinkage is predictable and must be precisely calculated and accounted for in the initial mold design.
Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS)
In some processes, an additive with a lower melting point is included in the powder mix. During heating, this additive melts and becomes a liquid that flows into the pores between the solid particles, accelerating densification through capillary action. This is known as Liquid Phase Sintering.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Sintering is not a universal solution, but it is an indispensable process for specific manufacturing goals.
- If your primary focus is producing complex, high-volume metal parts: Sintering, as part of powder metallurgy, is an exceptionally efficient method for creating near-net-shape components with minimal machining.
- If your primary focus is working with high-temperature materials: Sintering is often the only viable method for processing ceramics or refractory metals with melting points too high for conventional casting.
- If your primary focus is creating unique material compositions: The process allows for the creation of custom alloys, metal-matrix composites, and cermets that cannot be produced by melting and mixing.
By controlling the fusion of particles at an atomic level, sintering provides a powerful tool for engineering materials with specific, highly controlled properties.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Mixing powders & binders | Ensure uniform composition and flowability |
| 2. Compaction | Pressing powder into a mold | Create a 'green' part with initial shape |
| 3. Thermal Treatment | Heating below melting point | Fuse particles via atomic diffusion for strength |
Ready to leverage sintering for your lab's material or part production?
KINTEK specializes in the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for successful sintering processes. Whether you are developing new materials, creating custom components, or need reliable furnaces for thermal treatment, our expertise ensures you achieve the desired density and material properties.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's sintering and powder metallurgy needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum furnace for reaction sintering? Precision for Large Boron Carbide Parts
- What is the purpose of a sintering furnace? Create High-Performance Components Without Melting
- What is the operating temperature of a furnace? From Home Heating to Industrial Processing
- How does vacuum brazing work? Achieve Superior, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- What are the specific functions of introducing reducing atmospheres or inert gas environments in vacuum brazing?
- What is meant by physical Vapour deposition? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Coating
- What is the temperature range of the brazing process? Achieve Perfect Joints with Precise Heat Control
- What is the temperature of the arc melting furnace? Achieve 3000°C for Refractory Metals



















