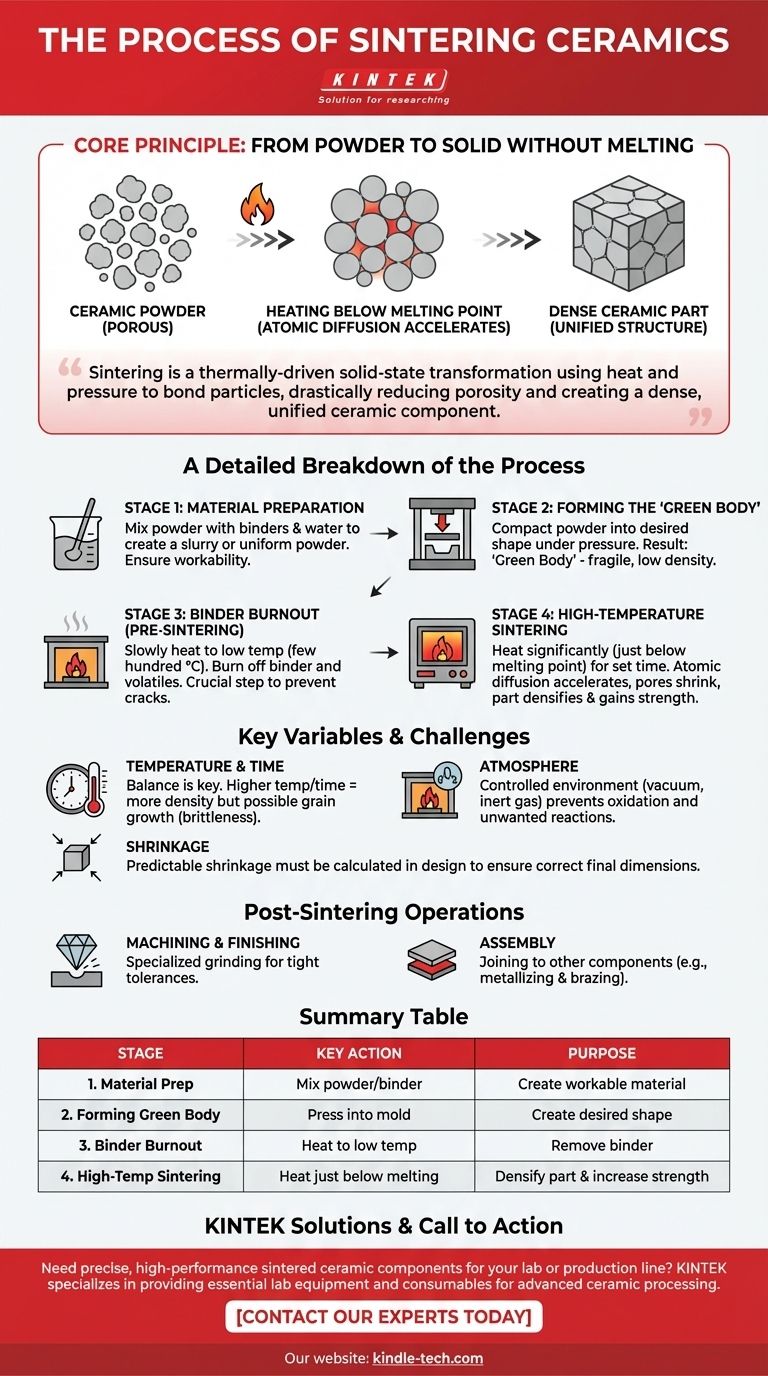
At its core, the process of sintering ceramics involves three primary stages: meticulously preparing a ceramic powder, pressing that powder into a desired shape called a "green body," and then heating it to a high temperature. This heating, conducted below the material's melting point, causes the individual powder particles to fuse together through atomic diffusion, transforming the fragile green body into a strong, dense, solid part.
Sintering is not a melting process. It is a thermally-driven solid-state transformation that uses heat and pressure to bond particles together, drastically reducing porosity and creating a dense, unified ceramic component.

The Core Principle: From Powder to Solid Without Melting
Before breaking down the steps, it's critical to understand the mechanism at work. The goal of sintering is to eliminate the empty spaces, or porosity, between the initial ceramic powder particles.
The Power of Atomic Diffusion
When heated to a high temperature (but below its melting point), the atoms within the ceramic particles become highly energized. This energy allows them to move and diffuse across the boundaries where particles touch.
This atomic migration effectively closes the gaps between particles, merging them into a single, interconnected structure. The result is a significant increase in density and strength, turning a loose powder compact into a robust ceramic object.
A Detailed Breakdown of the Ceramic Sintering Process
While the principle is simple, the industrial application involves several carefully controlled stages to ensure a final product with the desired properties.
Stage 1: Material Preparation
The process begins long before any heat is applied. The starting ceramic powder is mixed with other substances to form a uniform, workable material.
This often involves creating a slurry by mixing the powder with water, a binder to hold the particles together in their pressed shape, and other agents like deflocculants to ensure even mixing. This slurry is then typically spray-dried to create a uniform, flowable powder ready for pressing.
Stage 2: Forming the "Green Body"
The prepared powder is compacted into the desired shape. This is most commonly done by pressing the powder into a mold or die under high pressure.
The resulting part is known as a "green body." At this stage, it is coherent and holds its shape due to the binder and the mechanical interlocking of particles, but it is extremely fragile and has low density.
Stage 3: Binder Burnout (Pre-Sintering)
The green body is heated to a relatively low temperature, typically a few hundred degrees Celsius. The sole purpose of this step is to slowly burn off the binder and any other volatile components added during mixing.
Performing this step carefully is crucial. If heated too quickly, the rapid outgassing of the binder can create cracks and defects that will ruin the final part.
Stage 4: High-Temperature Sintering
This is the main event. The temperature is raised significantly, to just below the ceramic's melting point, and held for a specific duration.
During this phase, atomic diffusion accelerates, particle boundaries merge, and the part densifies. The pores between particles shrink and are largely eliminated, causing the entire component to shrink in size while gaining immense strength and hardness.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Variables
Achieving a successful outcome requires precise control over several factors. Mismanaging these variables can lead to failed parts or inconsistent properties.
The Role of Temperature and Time
Higher sintering temperatures and longer hold times generally lead to greater densification. However, excessive heat or time can cause undesirable grain growth, which can sometimes make the ceramic more brittle. The key is finding the optimal balance for the specific material and application.
The Importance of Atmosphere
The furnace atmosphere (e.g., air, vacuum, or an inert gas) plays a critical role. For many advanced ceramics, sintering in a controlled atmosphere is necessary to prevent oxidation or unwanted chemical reactions that could compromise the material's integrity.
The Challenge of Shrinkage
As the part densifies, it shrinks predictably. This shrinkage, which can be significant, must be accurately calculated and accounted for during the initial design of the mold and the green body. Failure to do so results in parts with incorrect final dimensions.
Post-Sintering Operations
After cooling, the process isn't always over. The now extremely hard ceramic part may undergo final finishing steps.
Machining and Finishing
Because of their hardness, sintered ceramics often require specialized machining using diamond-tipped tools or ultrasonic grinding to achieve final, tight tolerances.
Assembly
For certain applications, ceramic parts may need to be joined to other components. This can involve metallizing the ceramic surface to allow it to be brazed to a metal part, creating a strong, hermetic seal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific parameters of the sintering process are tuned to achieve a desired end result.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and strength: Your process will prioritize fine starting powders, high sintering temperatures, and sufficient time to minimize all porosity.
- If your primary focus is precise dimensional control: You will need to invest in highly consistent powder preparation, uniform pressing, and meticulous calculation of shrinkage rates.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production: You will optimize heating and cooling cycles to minimize energy consumption and furnace time without compromising the part's essential properties.
Mastering the sintering process is about precisely controlling heat and pressure to transform a simple powder into a high-performance ceramic component.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Material Preparation | Mix powder with binder/water to create a slurry | Ensure uniform, workable material |
| 2. Forming the Green Body | Press powder into a mold under high pressure | Create the desired shape (fragile state) |
| 3. Binder Burnout | Heat to low temperature to remove binder | Eliminate volatile components without cracking |
| 4. High-Temp Sintering | Heat just below melting point for a set time | Densify part via atomic diffusion, increasing strength |
Need precise, high-performance sintered ceramic components for your lab or production line? The sintering process is complex, but the results are critical for applications requiring extreme hardness, thermal stability, and chemical resistance. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables essential for advanced ceramic processing. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your sintering projects and help you achieve superior material properties.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the application of a muffle furnace? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is a muffle furnace used for in microbiology? Essential for Depyrogenation and Ashing
- What is the difference between a box furnace and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Lab Furnace for Your Application
- Dry Ashing vs Wet Ashing: Which Method is Best for Your Sample Analysis?
- What are the safety rules for all heating process in the laboratory? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















