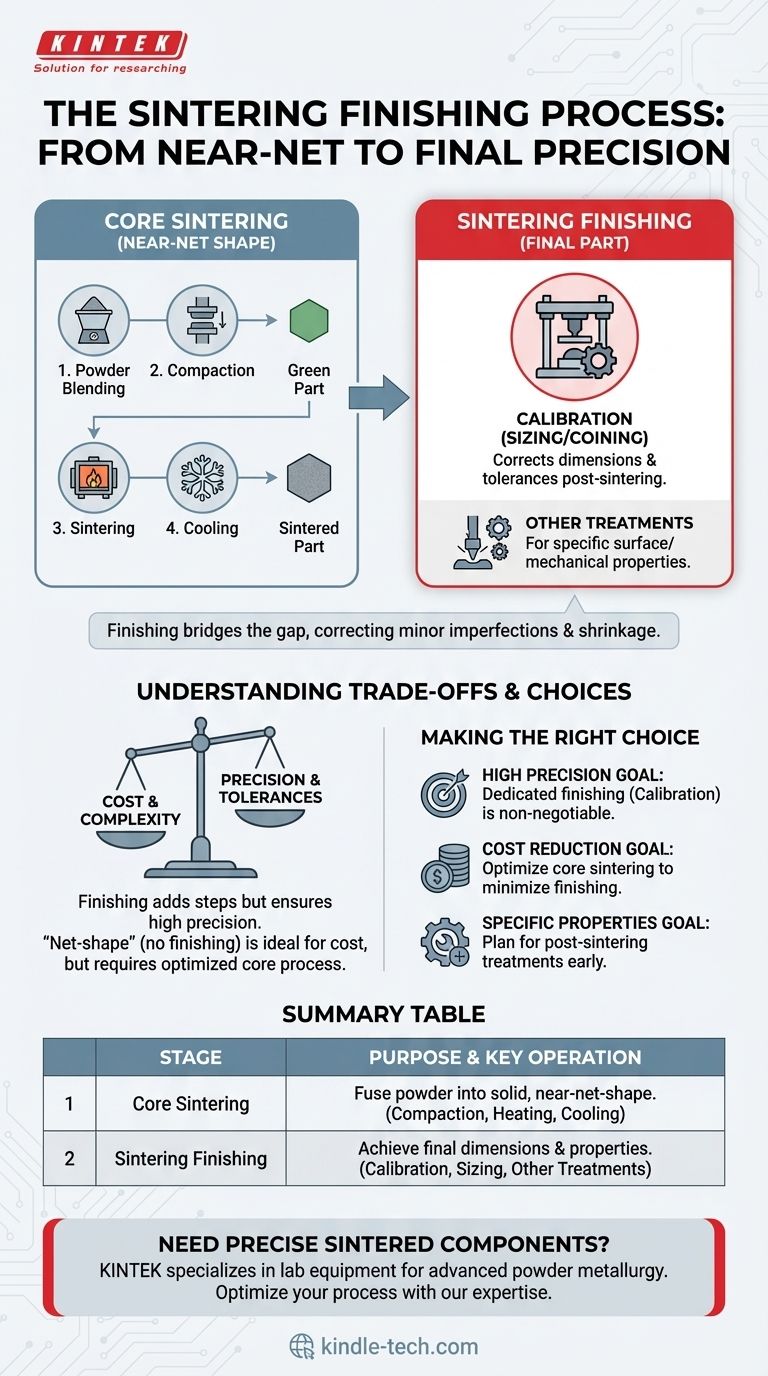
Sintering finishing is not part of the core sintering process itself, but rather a collection of secondary, post-sintering operations. After a metal powder component has been compacted and heated, it may undergo finishing treatments like calibration to correct its dimensions. This final stage ensures the part meets the precise specifications and tolerances required for its application.
Sintering creates a component that is close to its final dimensions, known as a "near-net shape." Sintering finishing is the critical, subsequent stage that bridges the gap from "near-net" to "final," correcting the minor imperfections and dimensional changes that occur during heating and cooling.

To Understand Finishing, First Understand the Core Process
Before a part can be finished, it must first be created through the primary sintering stages. This process turns loose powder into a solid object.
Step 1: Powder Blending and Preparation
First, the primary metal powder is precisely mixed with other elements. These can include alloying agents to enhance properties or bonding agents (like wax or polymers) that help the powder hold its shape during initial compaction.
Step 2: Compaction into a "Green" Part
The powder blend is placed into a die or mold and subjected to high pressure. This compaction process forms the powder into the desired shape, now referred to as a "green part." This part is fragile but solid enough to be handled.
Step 3: Sintering (Heating and Fusing)
The green part is placed in a controlled-atmosphere furnace. It is heated to a temperature just below the primary metal's melting point. During this phase, the bonding agent burns away, and the metal particles begin to fuse at their contact points, dramatically increasing the part's density and strength.
Step 4: Cooling and Solidification
The component is cooled in a controlled manner, allowing it to solidify into a single, unified mass. At this point, the primary sintering process is complete. However, the part has likely shrunk slightly and may not yet meet exact dimensional requirements.
The Purpose of Sintering Finishing
This is where finishing becomes essential. It addresses the changes that happen during the heating and cooling cycle to produce a part ready for use.
Why Finishing is Necessary
The fusion of particles and reduction of porosity during sintering inevitably causes the part to shrink. While this shrinkage is anticipated in the initial design, slight variations are common. Finishing corrects these small deviations from the target specifications.
Calibration: The Primary Finishing Operation
The most common finishing process is calibration, also known as sizing or coining. The sintered part is placed back into a precision die, which is often the same press used for initial compaction. A final press operation adjusts the part, refining its dimensions to meet very tight tolerances.
Other Post-Sintering Treatments
Beyond calibration, parts may undergo other treatments to achieve their final, desired properties. These processes are determined by the specific quality standards and functional requirements of the component.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Adding a finishing stage is a strategic decision with clear benefits and costs.
Cost vs. Precision
Each finishing step adds time, complexity, and cost to the overall production cycle. For components that do not require extremely high precision, an optimized sintering process that minimizes the need for finishing is more economical.
The "Net-Shape" Ideal
The ultimate goal in powder metallurgy is to achieve "net-shape" manufacturing, where the part comes out of the furnace with perfect dimensions and requires no secondary operations. The need for extensive finishing can indicate that the initial compaction and heating stages are not fully optimized.
Material Constraints
Finishing operations like calibration exert force on the sintered part. The material composition must be designed to have sufficient ductility to withstand this final pressing without cracking or failing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to incorporate a robust finishing stage depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is high-precision components: A dedicated finishing stage, especially calibration, is a non-negotiable part of your manufacturing plan to meet tight tolerances.
- If your primary focus is cost reduction on high-volume parts: Your effort should be on optimizing the powder blend and sintering cycle to produce consistent, predictable shrinkage, thereby minimizing the need for costly secondary operations.
- If your primary focus is specific mechanical or surface properties: You must plan for post-sintering treatments from the very beginning, as the core sintering process alone may not be sufficient.
By viewing sintering and finishing as two distinct but connected stages, you can design a more deliberate and effective manufacturing process.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Stage | Purpose | Key Operation |
|---|---|---|
| Core Sintering | Fuse powder into a solid, near-net-shape part | Compaction, Heating, Cooling |
| Sintering Finishing | Achieve final dimensions and properties | Calibration, Sizing, Other Treatments |
Need precise, high-quality sintered components? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced powder metallurgy. Our expertise ensures your sintering and finishing processes are optimized for superior results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does precise temperature control affect FeCoCrNiMnTiC high-entropy alloys? Master Microstructural Evolution
- Why is a high vacuum required for sintering Ti-43Al-4Nb-1Mo-0.1B? Ensure Purity & Fracture Toughness
- How does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace facilitate the post-treatment of Zirconia coatings?
- What is sintering reaction? Transform Powders into Dense Solids Without Melting
- Why is a high vacuum environment necessary in sintering equipment for TiAl alloys? Ensure High-Purity Metal Bonding



















