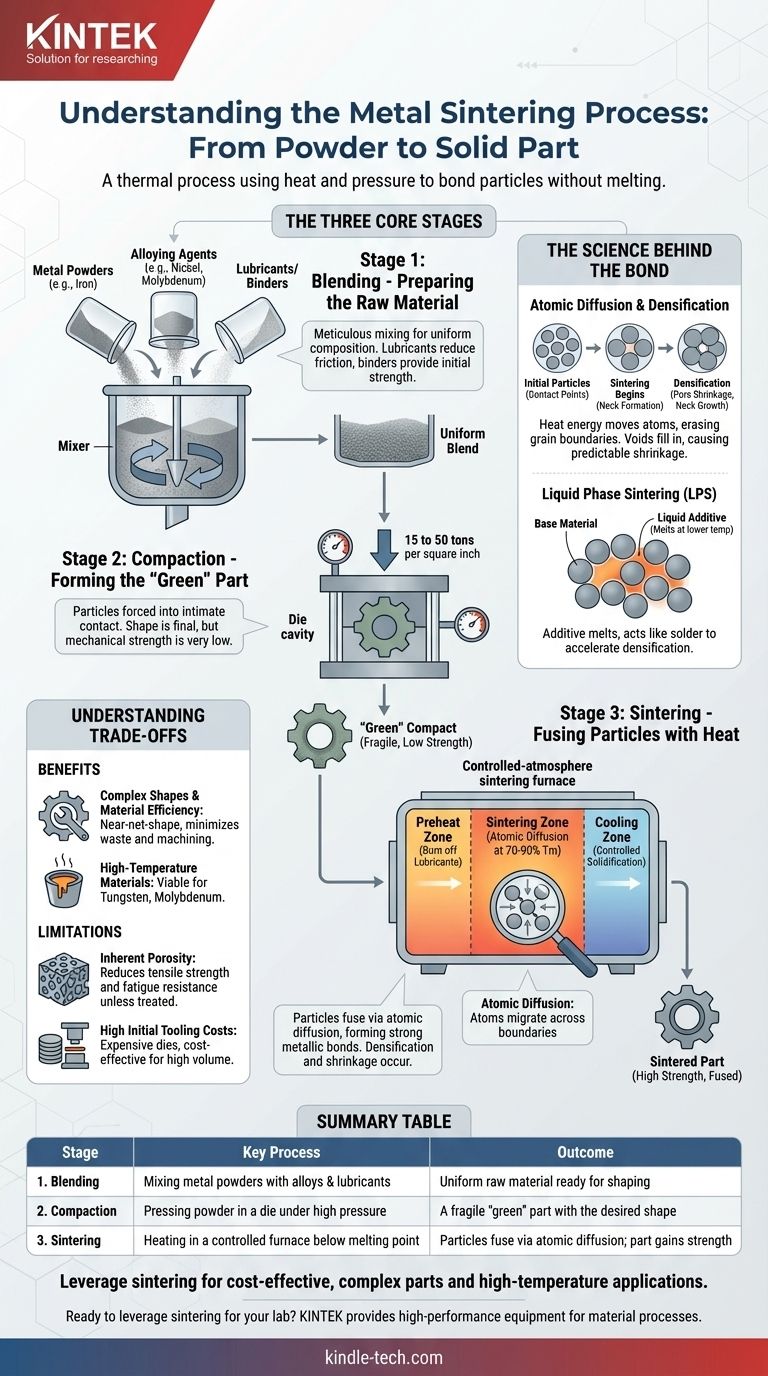
At its core, metal sintering is a manufacturing process that transforms metal powder into a solid, functional part without melting it. The process is defined by three primary stages: blending the powders, compacting them under high pressure into a desired shape, and then heating the shape in a controlled furnace to bond the individual particles together through atomic diffusion.
Sintering is not about melting metal; it is a thermal process that uses heat and pressure to make individual powder particles fuse into a single, solid mass. Its primary value lies in its ability to create complex, net-shape parts from materials that are otherwise difficult to machine or cast.

The Three Core Stages of Sintering
The sintering workflow is a precise, sequential method. Each stage builds upon the last to achieve the final part's desired geometry and mechanical properties.
Stage 1: Blending - Preparing the Raw Material
Before any shaping occurs, the base materials must be prepared. This involves meticulously mixing fine metal powders, such as iron or aluminum, with other elements.
These additions can include alloying agents (like nickel or molybdenum for strength) and lubricants or binders. The lubricants reduce friction during the next stage, while binders provide initial strength.
Stage 2: Compaction - Forming the "Green" Part
The blended powder is dispensed into a precision die cavity. A press then applies extreme pressure (typically ranging from 15 to 50 tons per square inch) to the powder.
This pressure forces the particles into intimate contact, creating a fragile, pre-sintered component known as a "green" compact. This part has the desired shape and dimensions but possesses very low mechanical strength, similar to a piece of chalk.
Stage 3: Sintering - Fusing Particles with Heat
The "green" compact is placed into a sintering furnace with a controlled atmosphere to prevent oxidation. The part is heated to a temperature significantly below the melting point of the primary metal—usually around 70-90% of its melting temperature.
This heating process is often conducted in a tunnel kiln with distinct zones:
- Preheat Zone: The part is heated slowly to burn off the lubricants and binders from the blending stage.
- Sintering Zone: At peak temperature, atomic diffusion occurs. Atoms migrate across the boundaries of the particles, causing them to fuse together and form strong metallic bonds.
- Cooling Zone: The newly solidified part is cooled at a controlled rate. This rate can be adjusted to achieve specific microstructures and final properties, such as hardness.
The Science Behind the Bond
Understanding what happens at a microscopic level is key to appreciating the power and limitations of sintering. The process is a careful manipulation of material science principles.
Atomic Diffusion: The Engine of Sintering
Sintering works because heat provides the energy for atoms to move. At high temperatures, atoms at the surface of each powder particle become mobile and migrate across the contact points between adjacent particles.
This atomic movement effectively erases the boundaries between the individual grains, creating a single, continuous crystalline structure. It is this fusion at an atomic level that gives the sintered part its strength.
Densification and Shrinkage
As particles fuse, the voids or pores between them are gradually filled in. This process, known as densification, causes the entire component to shrink.
This shrinkage is a predictable and essential part of sintering. Engineers must design the initial compaction tooling to be slightly larger than the final desired part to compensate for this planned reduction in size.
Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS): An Enhancement
To accelerate densification and achieve higher final densities, a technique called Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS) is often used.
This involves adding a small amount of an alloying powder with a lower melting point than the base material. During heating, this additive melts and flows into the pores between the solid particles, acting like a solder to pull them together more quickly and effectively.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Sintering
Like any manufacturing process, sintering offers a unique set of advantages and disadvantages. Choosing it requires understanding these trade-offs.
Benefit: Complex Shapes and Material Efficiency
Sintering is a near-net-shape process. It produces parts that are very close to their final dimensions, drastically reducing or eliminating the need for secondary machining. This minimizes material waste, making it highly efficient compared to subtractive methods.
Benefit: Processing High-Temperature Materials
The process is uniquely suited for materials with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten and molybdenum. Melting and casting these materials is often impractical or impossible, making sintering one of the few viable manufacturing methods.
Limitation: Inherent Porosity
Unless secondary operations are performed, sintered parts almost always retain some level of porosity. While this can be beneficial for applications like self-lubricating bearings, it typically reduces the part's overall tensile strength and fatigue resistance compared to a fully dense wrought or forged equivalent.
Limitation: High Initial Tooling Costs
The hardened steel dies required for the compaction stage are expensive to produce. This high upfront investment means sintering is most cost-effective for medium-to-high-volume production runs where the tooling cost can be amortized over thousands of parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision to use sintering should be based on your project's specific priorities regarding cost, material, and performance.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of complex parts: Sintering is an excellent choice for production volumes high enough to justify the initial tooling investment.
- If your primary focus is high-performance or high-temperature applications: Sintering is one of the only methods capable of forming parts from refractory metals and certain advanced ceramics.
- If your primary focus is maximum mechanical strength: Be aware of porosity's impact. If your application cannot tolerate any voids, you may need to consider secondary densification steps or choose an alternative process like forging.
Ultimately, understanding sintering empowers you to leverage its unique ability to transform simple powder into complex, functional components with precision and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Blending | Mixing metal powders with alloys & lubricants | Uniform raw material ready for shaping |
| 2. Compaction | Pressing powder in a die under high pressure | A fragile "green" part with the desired shape |
| 3. Sintering | Heating in a controlled furnace below melting point | Particles fuse via atomic diffusion; part gains strength |
Ready to leverage sintering for your lab's manufacturing or R&D projects?
KINTEK specializes in providing the high-performance lab equipment and consumables essential for advanced material processes like sintering. Whether you need robust furnaces for precise thermal treatment or expert consultation on material science applications, we are here to support your laboratory's innovation.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve superior results in powder metallurgy and beyond.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is a resistance heating furnace? Achieve Precise, Clean High-Temperature Processing
- What is a furnace used for sintering? Creating High-Performance Solid Components from Powder
- Why do we use vacuum in evaporation? Unlock Precision and Purity in Your Lab Processes
- What is vacuum brazing and how does it work? Achieve High-Strength, Flux-Free Metal Joints
- What is the function of a high-vacuum heat treatment furnace in IDHT? Master Silicide Diffusion Bonding
- How do high-temperature furnaces affect bio-oil yield? Optimize Pyrolysis with Precision Control
- What materials are used in vacuum braze? A Guide to Metals, Alloys, and Filler Selection
- What is the critical role of a vacuum oven in PEO/LiTFSI membrane preparation? Optimize Solid-State Battery Performance



















