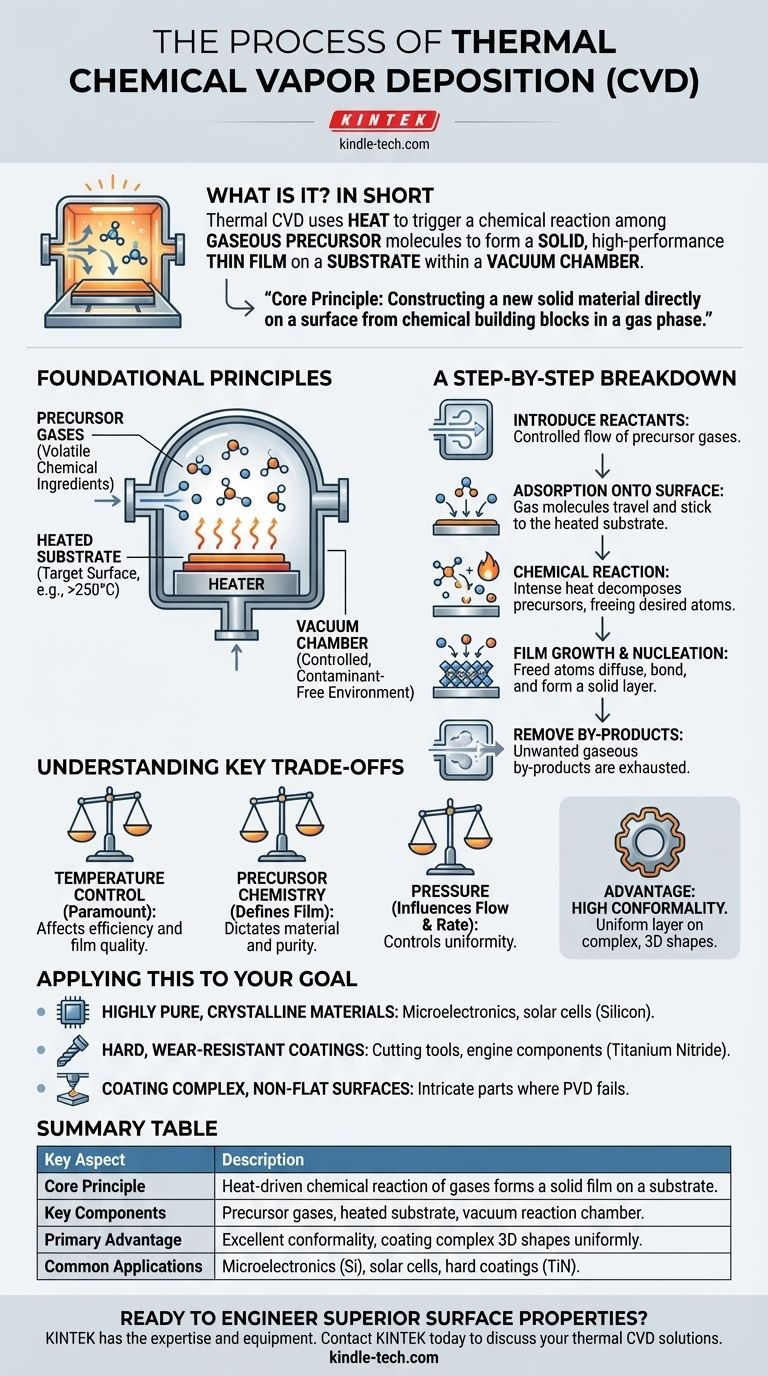
In short, thermal chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a process that uses heat to trigger a chemical reaction among gaseous precursor molecules, causing them to form a solid, high-performance thin film on a target surface, known as a substrate. This all occurs within a controlled environment, typically a vacuum chamber, where the heat provides the necessary energy for the precursors to decompose and bond to the substrate, building up the desired coating layer by layer.
The core principle of thermal CVD is not simply depositing a material, but rather constructing a new solid material directly on a surface from chemical building blocks in a gas phase. The process transforms volatile gases into a stable, solid film through a precise, heat-driven chemical reaction.
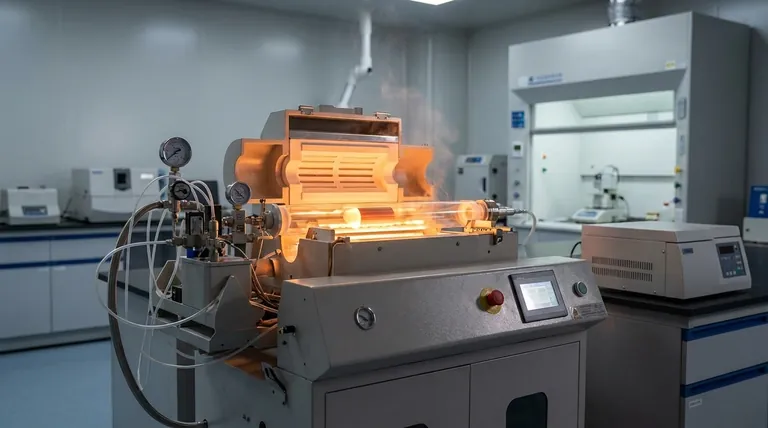

The Foundational Principles of CVD
To fully grasp the process, it's essential to understand the key components and the environment in which the reaction takes place. Each element plays a critical role in the final quality of the deposited film.
The Role of Precursor Gases
Precursors are the chemical ingredients for the final coating. They are volatile compounds, meaning they exist as a gas at the reaction temperature and pressure.
These gases are carefully selected to contain the specific atoms required for the desired film. For example, to create a silicon nitride film, precursors containing silicon and nitrogen would be used.
The Substrate and Reaction Chamber
The substrate is the object or workpiece that is being coated. It is placed inside a sealed reaction chamber.
This chamber is typically under a vacuum. Creating a vacuum removes air and other potential contaminants that could interfere with the chemical reaction or become trapped in the film, compromising its purity and performance.
The Power of Thermal Energy
Heat is the engine of the thermal CVD process. The substrate is heated to a precise reaction temperature, often ranging from 250°C to well over 1000°C depending on the specific chemistry.
This thermal energy provides the activation energy needed to break the chemical bonds within the precursor gas molecules, allowing the desired chemical reaction to occur on the substrate's surface.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Deposition Process
The creation of a thin film via thermal CVD is a highly controlled sequence of events that occurs at the molecular level.
Step 1: Introduction of Reactants
A continuous, controlled flow of one or more precursor gases is introduced into the reaction chamber.
Step 2: Adsorption onto the Surface
The precursor gas molecules travel through the chamber and come into contact with the heated substrate, where they physically adsorb (stick) to the surface.
Step 3: The Chemical Reaction
The intense heat of the substrate provides the energy for the adsorbed precursor molecules to decompose or react with each other. This chemical reaction frees the desired atoms that will form the film.
Step 4: Film Growth and Nucleation
The newly freed atoms diffuse across the surface and bond with the substrate and with each other. This process, known as nucleation, forms a stable, solid layer that gradually builds up in thickness.
Step 5: Removal of By-products
The chemical reaction almost always produces unwanted gaseous by-products. These volatile by-products are removed from the chamber by the gas flow system, preventing them from contaminating the growing film.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
While powerful, thermal CVD is a process of precision. Success depends on carefully balancing several critical variables.
Temperature Control is Paramount
The substrate temperature is the most critical variable. If it's too low, the reaction won't occur efficiently, leading to slow growth or poor film quality. If it's too high, unwanted reactions can occur in the gas phase before the precursors even reach the surface.
Precursor Chemistry Defines the Film
The choice of precursor gases fundamentally dictates the material being deposited. The purity of these gases is also essential, as any impurities can be incorporated into the final film, altering its properties.
Pressure Influences Everything
The pressure inside the chamber affects how the gases flow and how quickly they reach the substrate. It is a key variable used to control the deposition rate and the uniformity of the coating.
High Conformality is a Key Advantage
Because the coating is formed from a gas that surrounds the substrate, CVD is exceptionally good at creating a uniform layer over complex, three-dimensional shapes. This "conformality" is a significant advantage over line-of-sight deposition methods like PVD.
Applying This to Your Goal
Understanding the CVD process allows you to see why it's chosen for some of the most demanding applications in technology and manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is creating highly pure, crystalline materials: Thermal CVD is the industry standard for manufacturing the ultra-pure silicon films that form the basis of microchips and solar cells.
- If your primary focus is applying hard, wear-resistant coatings: The process is ideal for coating cutting tools, engine components, and bearings with materials like titanium nitride for exceptional durability.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, non-flat surfaces: CVD's gas-based nature ensures a uniform (conformal) layer that physical deposition methods struggle to achieve, making it perfect for intricate parts.
Ultimately, thermal CVD provides a powerful method for engineering materials with superior properties directly onto the surface of a component.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Heat-driven chemical reaction of gases forms a solid film on a substrate. |
| Key Components | Precursor gases, heated substrate, vacuum reaction chamber. |
| Primary Advantage | Excellent conformality, coating complex 3D shapes uniformly. |
| Common Applications | Microelectronics (silicon films), solar cells, hard coatings (titanium nitride). |
Ready to Engineer Superior Surface Properties?
Thermal CVD is a precise science, and the right equipment is critical for success. Whether your goal is creating ultra-pure materials for electronics, applying durable wear-resistant coatings, or uniformly coating complex components, KINTEK has the expertise and laboratory equipment to support your R&D and production.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our thermal CVD solutions and consumables can help you build high-performance thin films that meet your exact specifications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- What function does CVD equipment serve in rhodium-modified coatings? Achieve Deep Diffusion and Microstructural Precision
- What are the advantages of industrial CVD for solid boriding? Superior Process Control and Material Integrity
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit



















