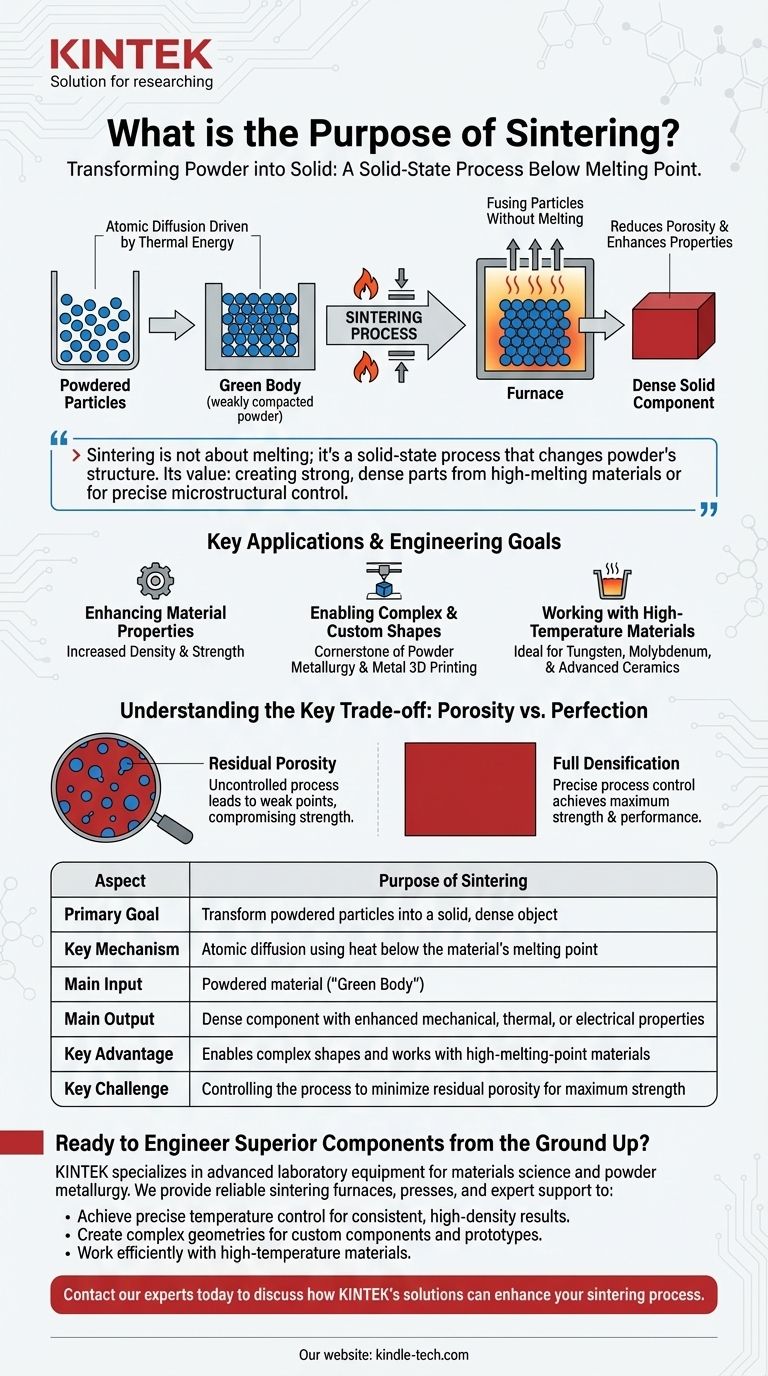
The fundamental purpose of sintering is to transform a collection of powdered particles into a solid, dense object using heat and pressure, all without reaching the material's melting point. This process fuses the particles together, reducing porosity and enhancing the final component's mechanical, electrical, or thermal properties.
Sintering is not about melting a material into a liquid; it's a solid-state process that fundamentally changes a powder's structure. Its true value lies in creating strong, dense parts from materials that are difficult to melt or when precise control over the final product's microstructure is critical.

The Core Mechanism: From Powder to Solid
Sintering is a transformative process that builds a functional component from the ground up, starting with a simple powder. It relies on atomic diffusion driven by thermal energy.
Fusing Particles Without Melting
The defining characteristic of sintering is that it operates at temperatures below the material's melting point. This is a significant advantage, especially for materials like tungsten, molybdenum, or advanced ceramics, which have extremely high melting temperatures.
Instead of liquefying the material, the applied heat gives atoms at the contact points between particles enough energy to move and bond, effectively fusing the powder into a single, solid piece.
The Role of Heat and Pressure
Heat is the primary driver, providing the energy for atomic diffusion. This process naturally reduces the space, or pores, between the individual particles.
In some advanced methods like Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), high pressure is applied simultaneously with heat. This pressure mechanically aids in collapsing the pores, dramatically increasing the final density and strength of the material.
From "Green Body" to Dense Component
The initial, weakly-compacted powder form is often called a "green body" or a powder compact. It has minimal mechanical strength.
The sintering process transforms this fragile green body into a dense, strong, and functional article with specific, engineered characteristics.
Key Applications and Engineering Goals
Engineers choose sintering when other manufacturing methods are impractical or cannot deliver the required material properties. Its applications are a direct result of its unique mechanism.
Enhancing Material Properties
The primary goal of sintering is often to improve a material's intrinsic properties. By removing the pores between particles, sintering significantly increases density.
This densification leads to enhanced mechanical strength, better thermal and electrical conductivity, and in some ceramics, even translucency.
Enabling Complex and Custom Shapes
Sintering is the cornerstone of powder metallurgy and many forms of metal 3D printing.
Because it starts with a powder, it allows for the creation of intricate geometries and custom forms that would be difficult or prohibitively expensive to produce through traditional casting or machining.
Understanding the Key Trade-off: Porosity vs. Perfection
While powerful, sintering is a precision process where control is paramount. The primary trade-off revolves around achieving full densification.
The Challenge of Residual Porosity
If the sintering process (temperature, time, and pressure) is not perfectly controlled, some microscopic pores may remain within the material.
This residual porosity can become a weak point, potentially compromising the component's ultimate strength and performance under stress.
The Need for Process Control
Unlike melting, which creates a homogenous liquid, sintering relies on atomic processes occurring throughout a solid mass.
Achieving a uniformly dense final product requires precise control over the powder's quality, the compaction of the green body, and the thermal cycle. Any inconsistency can lead to an imperfect final part.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing sintering is an engineering decision based on material, complexity, and desired final properties.
- If your primary focus is working with high-temperature materials: Sintering is the ideal choice as it bypasses the extreme energy costs and technical challenges of melting.
- If your primary focus is creating complex or custom geometries: Sintering, especially when combined with 3D printing, offers unparalleled design freedom.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific material properties: Sintering provides granular control over density and microstructure to engineer components for specific performance needs.
Ultimately, sintering empowers engineers to build superior components from the particle level up.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Purpose of Sintering |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Transform powdered particles into a solid, dense object |
| Key Mechanism | Atomic diffusion using heat below the material's melting point |
| Main Input | Powdered material ("Green Body") |
| Main Output | Dense component with enhanced mechanical, thermal, or electrical properties |
| Key Advantage | Enables complex shapes and works with high-melting-point materials |
| Key Challenge | Controlling the process to minimize residual porosity for maximum strength |
Ready to Engineer Superior Components from the Ground Up?
Sintering is a precise process that requires the right equipment and expertise to achieve optimal density and performance. KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for materials science and powder metallurgy.
We provide the reliable sintering furnaces, presses, and expert support you need to:
- Achieve precise temperature control for consistent, high-density results.
- Create complex geometries for custom components and prototypes.
- Work efficiently with high-temperature materials like ceramics and refractory metals.
Let's build your next breakthrough together. Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your sintering process and help you create stronger, more reliable parts.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the range of sintering? Master the Temperature Window for Optimal Material Performance
- How does a vacuum reduction furnace facilitate the separation of magnesium from boron? Master Thermal Purity
- Which of the following is a disadvantage of the brazing process? High Heat Can Weaken Base Metals
- What are the disadvantages of annealing? The Critical Trade-offs in Material Strength and Cost
- What type of brazing works at lower temperature? Silver Alloys for Heat-Sensitive Materials
- Can stainless steel be annealed? Discover the Key to Restoring Corrosion Resistance
- What is the temperature of debinding? A Guide to Mastering the Thermal Profile for MIM/CIM
- Can a furnace pressure switch cause short cycling? Diagnose the Real Cause of Intermittent Shutdowns



















