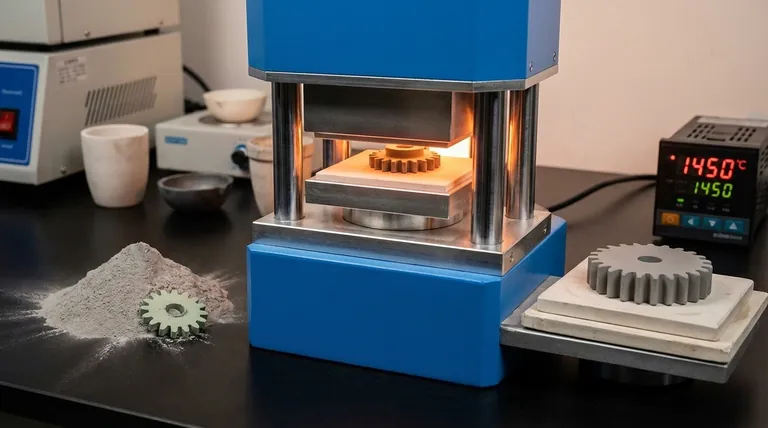
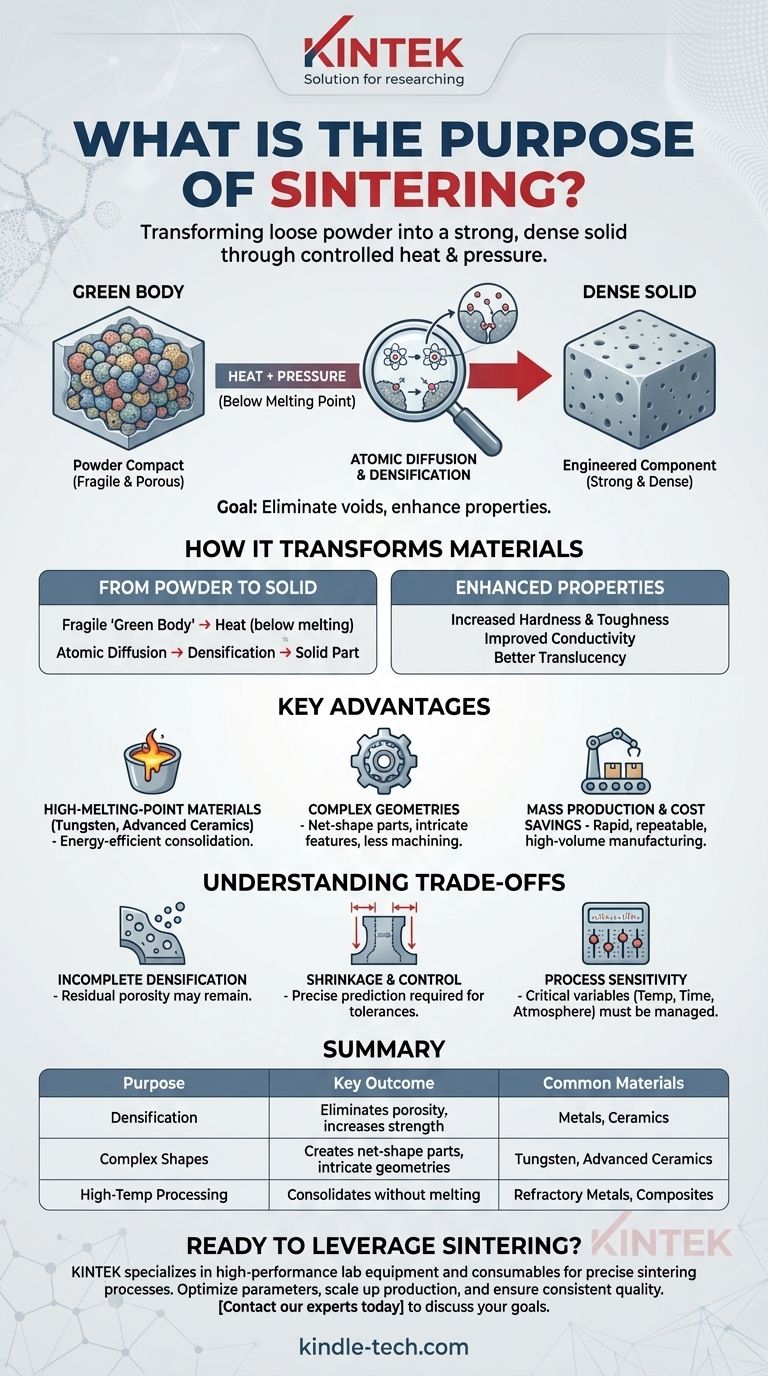
At its core, the purpose of sintering is to transform a collection of loose powder particles into a strong, dense, solid object. This is achieved by applying heat at a temperature below the material's melting point, often combined with pressure, to fuse the particles together and eliminate the empty spaces between them.
Sintering is not about melting a material, but about energizing its particles just enough to bond them into a solid mass. This fundamental principle makes it an indispensable process for creating high-performance components from materials that are difficult to melt or require highly complex shapes.

How Sintering Fundamentally Transforms Materials
Sintering is a thermal treatment that dramatically alters a material's internal structure, turning a fragile powder compact into a robust, engineered component.
From a "Green Body" to a Dense Solid
The process begins with a powder compact, often called a "green body." This is a loosely-bound shape, typically formed by pressing the powder into a mold.
This green body is fragile and porous. The goal of sintering is densification—the removal of the pores, or voids, between the powder particles.
The Role of Heat and Atomic Diffusion
During sintering, the material is heated to a temperature high enough to promote atomic diffusion but still below its melting point.
This thermal energy causes atoms on the surfaces of adjacent particles to move and form new, stronger bonds. The particles effectively merge, closing the gaps between them and shrinking the overall part.
The Result: Enhanced Material Properties
By eliminating porosity and creating a solid microstructure, sintering significantly improves a material's characteristics.
This includes enhancing mechanical properties like hardness and toughness, as well as functional properties like thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, or even optical translucency in certain ceramics.
Key Advantages of the Sintering Process
Engineers and manufacturers choose sintering when other methods are impractical, inefficient, or cannot achieve the desired outcome.
Working with High-Melting-Point Materials
Sintering is essential for processing materials with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten, molybdenum, and many advanced ceramics.
Melting these materials would require immense energy and specialized equipment. Sintering provides an energy-efficient path to creating solid parts from them.
Creating Complex Geometries with Precision
The process allows for the creation of intricate, "net-shape" or near-net-shape parts that would be difficult or wasteful to produce with traditional subtractive methods like machining.
Because the initial shape is formed from powder, complex internal features and unique geometries can be incorporated from the start, minimizing post-processing.
Enabling Mass Production and Cost Savings
For complex components, the tooling required for pressing powder is often less expensive than the setups for other manufacturing processes.
Sintering enables the rapid and repeatable mass production of high-precision parts, making it a cornerstone of industries like automotive manufacturing and consumer electronics.
Modern Applications in 3D Printing
Sintering is also a key technology in metal additive manufacturing (3D printing). In processes like selective laser sintering (SLS), a laser fuses metal powder layer by layer to build a custom part, offering unparalleled design freedom.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sintering is a highly technical process with critical variables that must be controlled for success.
Incomplete Densification and Porosity
Achieving 100% density is often difficult. Some residual porosity can remain in the final part, which may act as a stress concentration point and affect the ultimate mechanical strength compared to a fully molten and cast equivalent.
Shrinkage and Dimensional Control
As the pores are eliminated, the component shrinks. This shrinkage must be precisely predicted and controlled to ensure the final part meets its required dimensional tolerances.
Process Sensitivity
The final properties of a sintered part are highly dependent on process parameters. Factors like initial particle size, heating rate, peak temperature, time at temperature, and furnace atmosphere must all be meticulously managed to achieve consistent results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting sintering depends entirely on your material, geometry, and performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing with high-temperature materials: Sintering is the most practical and energy-efficient method for consolidating materials like advanced ceramics or refractory metals.
- If your primary focus is producing complex, net-shape parts in high volumes: Sintering offers significant cost and design freedom advantages over machining for components with intricate geometries.
- If your primary focus is combining material properties: Sintering is an effective way to create composites that merge distinct characteristics, such as the hardness of a ceramic with the toughness of a metal.
Ultimately, sintering empowers the creation of advanced materials and components that would otherwise be impossible or prohibitively expensive to make.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Purpose | Key Outcome | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Densification | Eliminates porosity, increases strength | Metals, Ceramics |
| Complex Shapes | Creates net-shape parts with intricate geometries | Tungsten, Advanced Ceramics |
| High-Temp Processing | Consolidates materials without melting | Refractory Metals, Composites |
Ready to leverage sintering for your advanced material needs?
KINTEK specializes in providing the high-performance lab equipment and consumables essential for precise sintering processes. Whether you are developing new materials, optimizing sintering parameters, or scaling up production, our solutions ensure the consistent, high-quality results you demand.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's sintering and materials synthesis goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- How much psi can a hydraulic press make? From 2,000 PSI to over 50,000 PSI Explained
- Why do you need to follow the safety procedure in using hydraulic tools? Prevent Catastrophic Failure and Injury
- What is the function of a laboratory high-temperature hydraulic press? Optimize MEA Fabrication for HCl Electrolysis
- What does a hydraulic heat press do? Achieve Industrial-Scale, Consistent Pressure for High-Volume Production
- What is a hot hydraulic press? Harness Heat and Pressure for Advanced Manufacturing



















