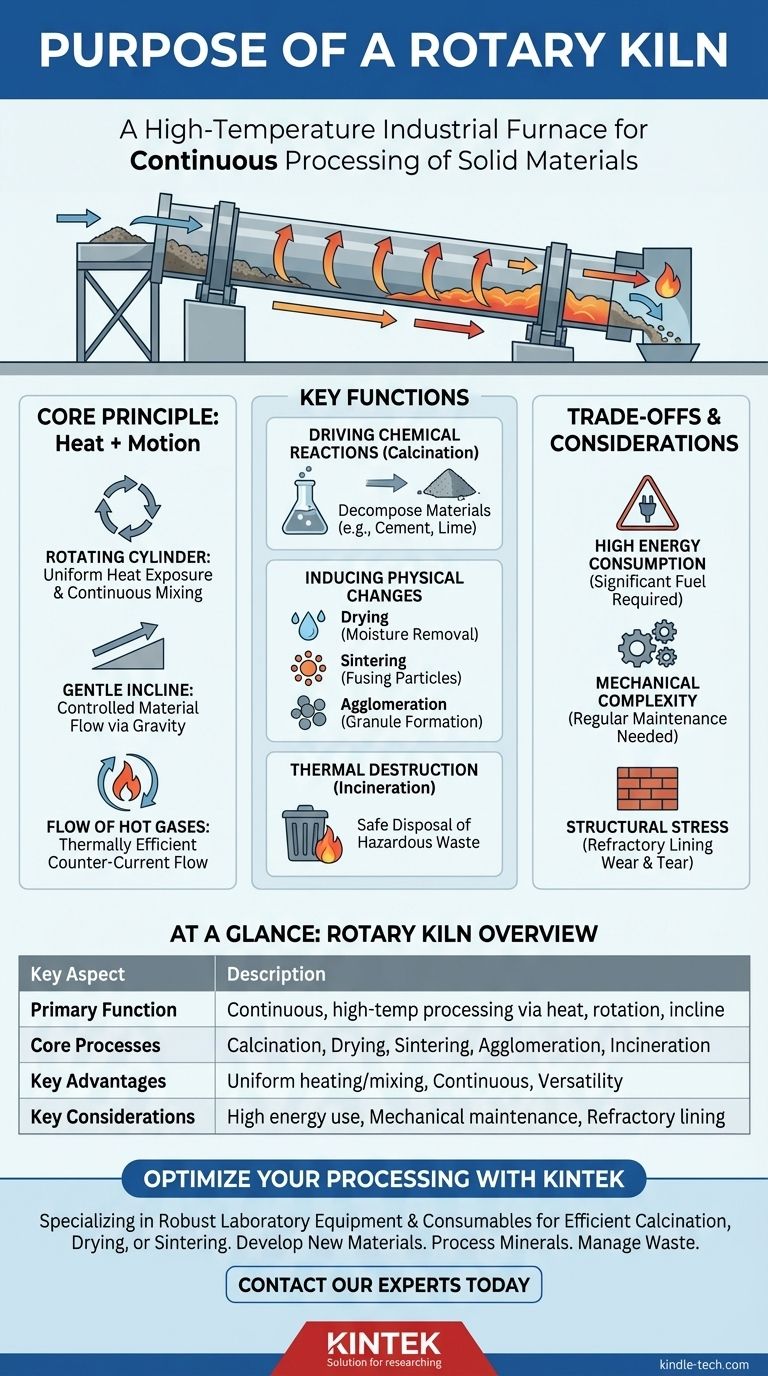
At its core, a rotary kiln is a high-temperature industrial furnace designed for the continuous processing of solid materials. It consists of a long, rotating cylindrical vessel inclined at a slight angle. This unique combination of high heat, constant rotation, and gentle slope allows it to uniformly heat, mix, and transport materials to induce specific chemical reactions or physical changes.
A rotary kiln is more than just a furnace; it is a highly controlled dynamic reactor. Its primary purpose is to transform solid materials by combining extreme heat with continuous mixing, a process that is impossible to achieve in a static oven or furnace.

The Core Principle: Combining Heat with Motion
The effectiveness of a rotary kiln comes from its ability to manipulate materials in a way that static heating cannot. This is achieved through three fundamental design elements working in concert.
The Rotating Cylinder
The slow rotation of the kiln's cylindrical body, or shell, is the heart of the process. This rotation continuously lifts and tumbles the material bed, ensuring that every particle is uniformly exposed to the heat source. This constant stirring and mixing is critical for achieving a consistent final product.
The Gentle Incline
Every rotary kiln is mounted on a slight horizontal slope. As the cylinder rotates, gravity gently draws the material from the higher feed end down toward the lower discharge end. This creates a continuous, controlled flow of material through the reactor.
The Flow of Hot Gases
The necessary process energy is supplied by hot gases, typically generated by a powerful burner at the discharge end of the kiln. This gas can flow in the opposite direction of the material (counter-current) or in the same direction (co-current). Counter-current flow is more common and thermally efficient, as the hottest gases meet the most processed material, maximizing heat transfer.
Key Functions of a Rotary Kiln
Because of its unique design, a rotary kiln is not a single-purpose tool but a versatile piece of equipment that can serve several distinct functions, often in the same process.
Driving Chemical Reactions (Calcination)
The most common use for a rotary kiln is to drive endothermic chemical reactions that require high temperatures. This process, known as calcination, involves heating a material to decompose it. The production of cement clinker from limestone is the most prominent example of this.
Inducing Physical Changes
A rotary kiln can also be used to alter the physical state of a material. This includes:
- Drying: Removing moisture from bulk solids.
- Sintering: Fusing material particles together at high heat without melting them.
- Agglomeration: Causing fine particles to clump together into larger granules.
Thermal Destruction (Incineration)
The extremely high and stable temperatures inside a rotary kiln make it an effective incinerator. It is frequently used for the safe thermal destruction of various types of industrial and hazardous waste.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a rotary kiln is a complex piece of industrial equipment with specific operational considerations.
High Energy Consumption
Achieving and maintaining temperatures often in excess of 1400°C (2550°F) requires a significant amount of energy. The choice of burner, fuel source (gas, oil, pulverized coal), and gas flow design are critical for managing operational costs and efficiency.
Mechanical Complexity
Unlike a static furnace, a rotary kiln involves large moving parts. The drive system, support rollers (tyres), and seals that prevent air leakage or material spillage all require regular maintenance to ensure reliable operation.
Structural Stress
The combination of immense weight, high temperature, and continuous rotation places significant stress on the kiln's steel shell. This is managed by a thick refractory lining made of specialized bricks, which insulates the steel shell but can be susceptible to wear and deformation over its lifespan.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a rotary kiln depends entirely on your specific processing objective.
- If your primary focus is producing a new chemical compound (e.g., cement or lime): The rotary kiln is essential, as its uniform heating and mixing are required to drive the necessary calcination reactions throughout the entire material bed.
- If your primary focus is creating a consistent, physically altered product: The kiln's ability to dry, sinter, or agglomerate material while it is in motion ensures a homogenous output that is difficult to achieve otherwise.
- If your primary focus is destroying hazardous waste safely: The kiln's high, stable temperatures and long residence time provide the perfect environment for complete thermal destruction.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln is chosen when a process requires not just heat, but a dynamic and controlled environment to continuously transform materials on an industrial scale.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Continuous, high-temperature processing of solid materials via heat, rotation, and incline. |
| Core Processes | Calcination (e.g., cement production), Drying, Sintering, Agglomeration, Incineration. |
| Key Advantages | Uniform heating and mixing, continuous operation, versatility for various materials. |
| Key Considerations | High energy consumption, mechanical complexity, regular maintenance of refractory lining. |
Ready to optimize your material processing with a reliable rotary kiln?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust laboratory equipment and consumables tailored to your industrial needs. Whether you are developing new materials, processing minerals, or managing waste, our expertise ensures you get the right solution for efficient calcination, drying, or sintering.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our equipment can enhance your process efficiency and product consistency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
People Also Ask
- How does precision temperature control impact TiAl alloy sintering? Master Microstructure Development
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What is the drying zone in a rotary kiln? Boost Efficiency with Modern Drying Solutions
- How is the operational mode of bed motion selected for a rotary kiln? Optimize Heat Transfer and Material Homogeneity
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding



















