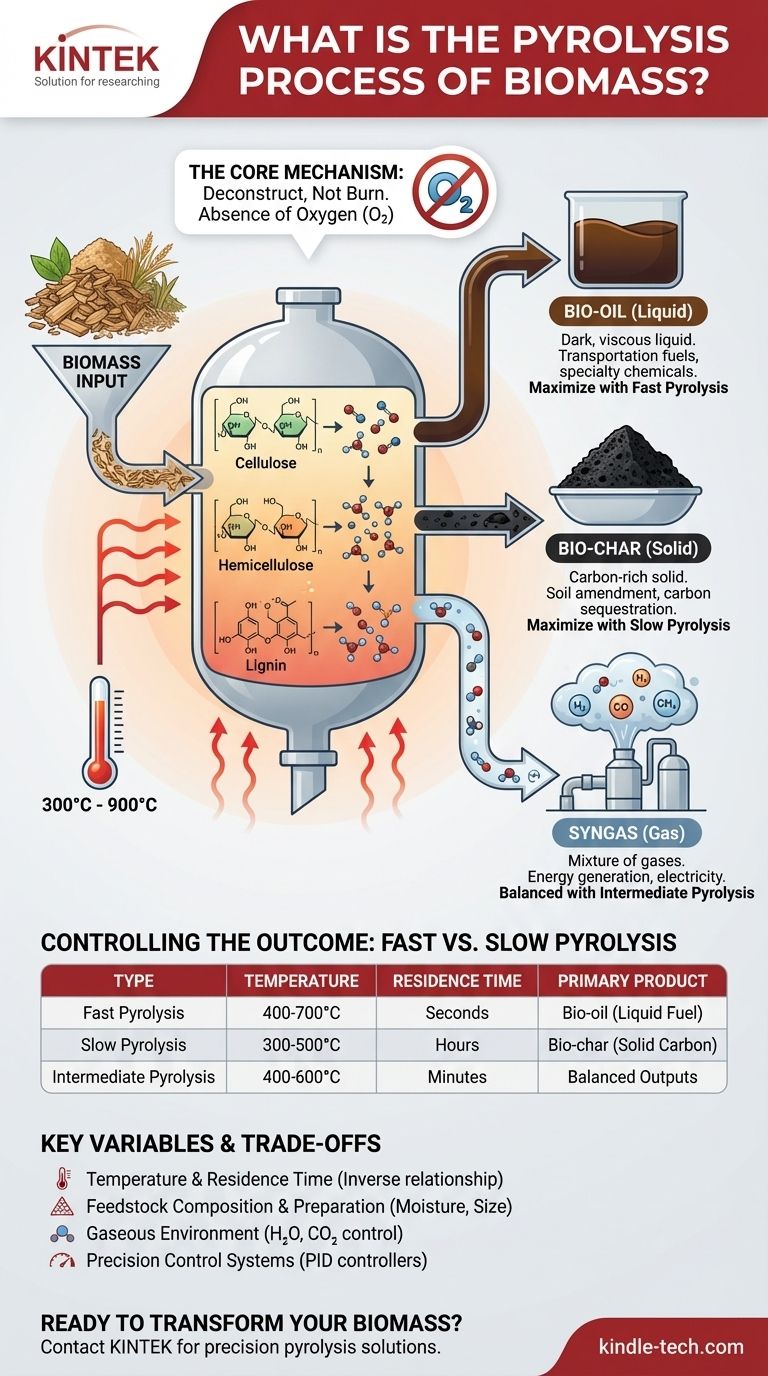
In essence, biomass pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that decomposes organic materials, like wood or agricultural waste, by heating them to high temperatures in an environment completely devoid of oxygen. This prevents the material from burning and instead breaks it down into a solid, a liquid, and a gas. The resulting products—bio-char, bio-oil, and syngas—are all valuable resources.
The central concept to grasp is that pyrolysis is not waste disposal; it is a highly controlled conversion technology. By precisely manipulating temperature and time, you can dictate whether the process yields primarily liquid fuel, a carbon-rich solid, or combustible gas, transforming low-value biomass into high-value products.

The Core Mechanism: How Pyrolysis Works
To understand pyrolysis, you must first understand that its goal is to deconstruct, not to burn. This is achieved by carefully controlling the chemical environment and heat application.
Heating in an Oxygen-Free Environment
The defining characteristic of pyrolysis is the absence of oxygen. When biomass is heated with oxygen, it undergoes combustion, releasing most of its energy as heat and producing ash.
By removing oxygen, we prevent combustion. The applied heat energy, therefore, has a different effect: it breaks the complex chemical bonds within the biomass itself.
Deconstructing Biomass Components
Biomass is primarily composed of large organic polymers like cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin.
At temperatures ranging from 300°C to 900°C, these strong polymer chains become unstable and fracture into smaller, simpler molecules. The specific temperature and heating duration determine which types of molecules are formed.
The Three Primary Outputs
The decomposition process results in three distinct product streams, each with its own applications.
-
Bio-char (Solid): A black, carbon-rich solid similar to charcoal. It is the non-volatile material left after the lighter components have vaporized. It is an excellent soil amendment and can be used for carbon sequestration or to produce activated carbon.
-
Bio-oil (Liquid): A dark, viscous liquid that results from cooling and condensing the vaporized organic molecules. Also known as pyrolysis oil, it can be upgraded into transportation fuels or used as a source for specialty chemicals.
-
Syngas (Gas): A mixture of non-condensable gases, primarily hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane. This "synthesis gas" has a moderate heating value and can be combusted on-site to generate the heat needed to power the pyrolysis process or to produce electricity.
Controlling the Outcome: Fast vs. Slow Pyrolysis
The most critical insight is that the relative yields of bio-char, bio-oil, and syngas are not random. They are a direct result of the process conditions, primarily temperature and residence time—the duration the biomass spends in the reactor.
Fast Pyrolysis: Maximizing Bio-oil
This method uses very high temperatures and extremely short residence times, often just a few seconds. The goal is to rapidly vaporize the biomass and quickly cool the vapors to condense them into liquid bio-oil before they can break down further. This process typically yields the most liquid product.
Slow Pyrolysis: Maximizing Bio-char
Conversely, slow pyrolysis uses lower temperatures and much longer residence times, often several hours. This gradual heating process favors the formation of a stable, carbonized solid. This is the historical method for making charcoal and is ideal for maximizing bio-char production.
Intermediate Pyrolysis: A Balanced Approach
As the name suggests, this process operates with moderate temperatures and residence times (minutes rather than seconds or hours). It produces more balanced quantities of bio-char, bio-oil, and syngas, offering flexibility depending on immediate needs.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Variables
Achieving an efficient pyrolysis operation requires balancing several interconnected factors. Misunderstanding these can lead to inefficient conversion and poor product quality.
The Temperature vs. Residence Time Relationship
Temperature and residence time are inversely related. To achieve complete decomposition, higher temperatures require significantly shorter residence times. This relationship is the fundamental principle used to design reactors for either fast or slow pyrolysis.
Feedstock Composition and Preparation
The type and condition of the biomass feedstock are critical. Factors like moisture content, particle size, and the specific chemical makeup of the biomass (e.g., woody vs. grassy) directly impact the efficiency of the process and the composition of the final products. Dried and finely ground biomass generally reacts more quickly and completely.
The Role of the Gaseous Environment
While pyrolysis is defined by the absence of oxygen, advanced control can be exerted by introducing other gases. Varying the initial concentrations of water vapor (H2O) or carbon dioxide (CO2) in the reactor can influence the reaction pathways and alter the final product distribution.
Precision Control Systems
Modern pyrolysis plants rely on sophisticated process controls. PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) temperature controllers and sensitive sensors are used to precisely manage heating rates and maintain the set temperature, ensuring consistent and predictable results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" pyrolysis method is entirely dependent on your desired end product. Your primary objective should dictate your choice of technology and operating parameters.
- If your primary focus is liquid biofuel production: You must use fast pyrolysis to rapidly vaporize the biomass and maximize bio-oil yield.
- If your primary focus is soil improvement or carbon sequestration: You must use slow pyrolysis to maximize the production of stable, solid bio-char.
- If your primary focus is flexible, on-site energy generation: An intermediate process or a system optimized for syngas production offers the most practical path.
Ultimately, pyrolysis provides a powerful and versatile toolkit for converting biomass from a potential waste stream into a portfolio of valuable resources.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Type | Temperature Range | Residence Time | Primary Product |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fast Pyrolysis | 400-700°C | Seconds | Bio-oil (Liquid Fuel) |
| Slow Pyrolysis | 300-500°C | Hours | Bio-char (Solid Carbon) |
| Intermediate Pyrolysis | 400-600°C | Minutes | Balanced Outputs |
Ready to transform your biomass into valuable resources? KINTEK specializes in precision laboratory equipment for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're optimizing bio-oil yields, producing bio-char for soil enhancement, or generating syngas for energy, our reactors and control systems deliver the accuracy and reliability you need. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can advance your biomass conversion projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success

















