In potentiometry, a reference electrode is a half-cell with a known, stable, and constant electrode potential. This electrode acts as a fixed baseline, or "zero point," against which the potential of another electrode—the working or indicator electrode—can be measured accurately. It is designed to be completely insensitive to the composition of the sample solution being analyzed.
The core challenge in electrochemistry is that you can only measure a potential difference, not the absolute potential of a single electrode. The reference electrode solves this by providing one half of that measurement with a value that is precisely known and does not change, ensuring any measured variation is due solely to the chemical reaction at the working electrode.

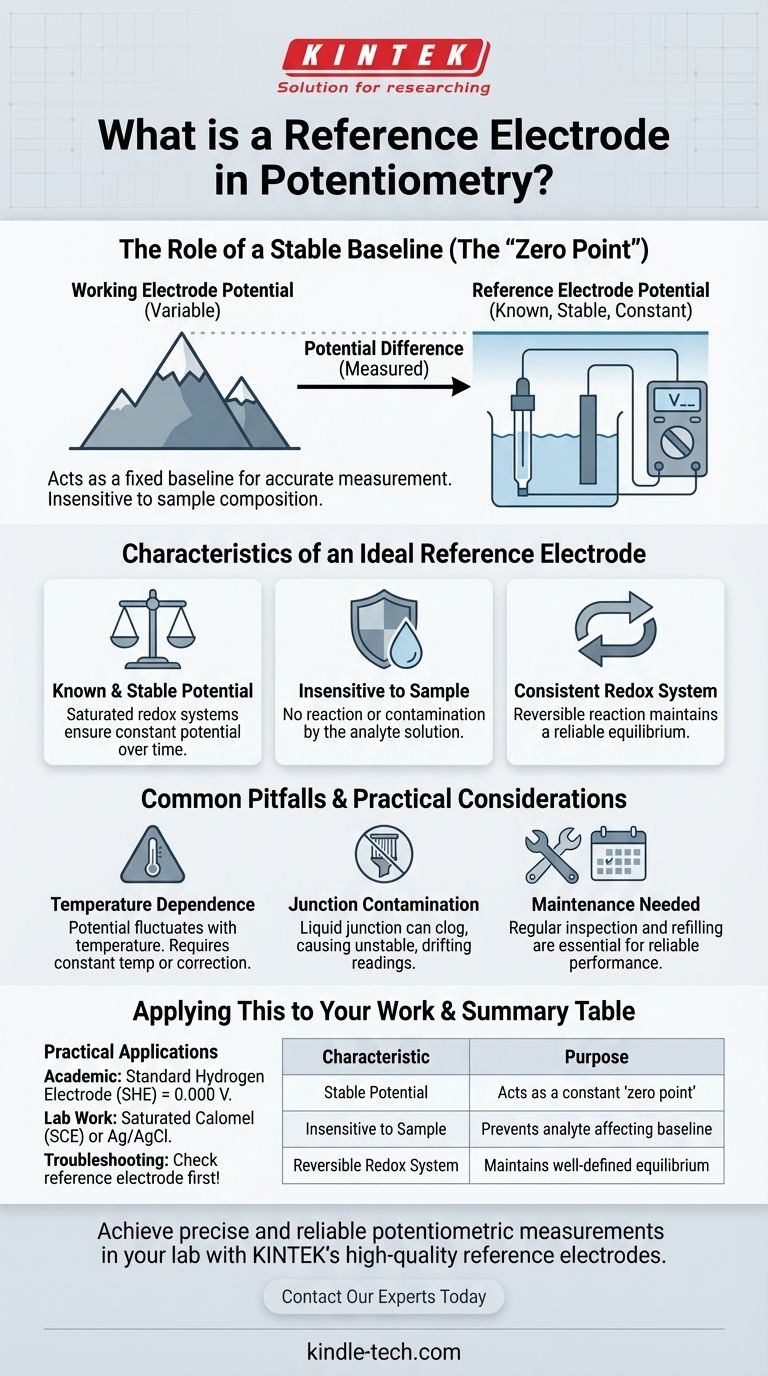
The Role of a Stable Baseline
Why Potential is a Relative Measurement
An electrode potential cannot be measured in isolation. It only has meaning when compared to another electrode.
Think of it like measuring the height of a mountain. You can't just state its height in empty space; you measure its height relative to a standard reference point, which is sea level.
Creating an Electrochemical "Sea Level"
A reference electrode functions as the "sea level" for electrochemical measurements.
By providing a potential that is constant and well-defined, it allows the potential of the other electrode (the "mountain peak") to be determined accurately. Any change in the overall cell voltage is attributed directly to the analyte's interaction with the working electrode, not to drift in your reference point.
Characteristics of an Ideal Reference Electrode
Known and Stable Potential
This is the most critical requirement. The stability is typically achieved by using a redox system where the components are kept at saturated or constant concentrations. This ensures the potential doesn't fluctuate during the experiment.
Insensitivity to the Sample
An ideal reference electrode's potential is not affected by the composition of the analyte solution. It must not react with or be contaminated by the sample it is immersed in.
A Consistent Redox System
The internal components of the electrode are carefully chosen to create a reversible redox reaction with a well-established potential. This reaction must be able to maintain its equilibrium reliably over time.
Common Pitfalls and Practical Considerations
Temperature Dependence
The potential of most reference electrodes is temperature-dependent. For highly accurate work, measurements must be performed at a constant, known temperature, or the results must be mathematically corrected.
Junction Contamination
Reference electrodes connect to the sample solution through a liquid junction or porous frit. This junction can become clogged or contaminated by the sample, which can cause the electrode's potential to become unstable and drift, leading to erroneous readings.
The Need for Maintenance
These electrodes do not last forever. The internal filling solution can become depleted or contaminated over time. Regular inspection and refilling are often necessary to ensure stable and reliable performance.
Applying This to Your Work
The concept of the reference electrode is fundamental to achieving accurate results in any potentiometric analysis.
- If your primary focus is academic understanding: Recognize the Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) as the universal thermodynamic standard, defined as having a potential of exactly 0.000 V.
- If your primary focus is practical lab work: Use robust and convenient secondary reference electrodes like the Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) or the Silver/Silver Chloride (Ag/AgCl) electrode.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting erratic results: Always check the condition of your reference electrode first; a clogged junction or depleted filling solution is the most common cause of measurement instability.
By providing an unwavering point of comparison, the reference electrode transforms a relative measurement into a precise and powerful analytical tool.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Stable Potential | Acts as a constant "zero point" for measurement. |
| Insensitive to Sample | Prevents analyte from affecting the baseline reading. |
| Reversible Redox System | Maintains a well-defined and consistent equilibrium. |
Achieve precise and reliable potentiometric measurements in your lab. A stable reference electrode is fundamental to data integrity. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including reliable reference electrodes, to support your analytical needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Copper Sulfate Reference Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
People Also Ask
- Which electrode is used as a reference? A Guide to Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- What are the characteristics of a saturated calomel electrode for neutral solutions? Understanding its stability and limitations.
- Why and how should the electrodes of an electrolytic cell be calibrated? Ensure Reliable Results
- Why is the calomel electrode used as a secondary reference electrode? A Practical Guide to Stable Measurements
- What is the reference electrode for mercury mercurous sulfate? A Guide to Chloride-Free Electrochemistry



















