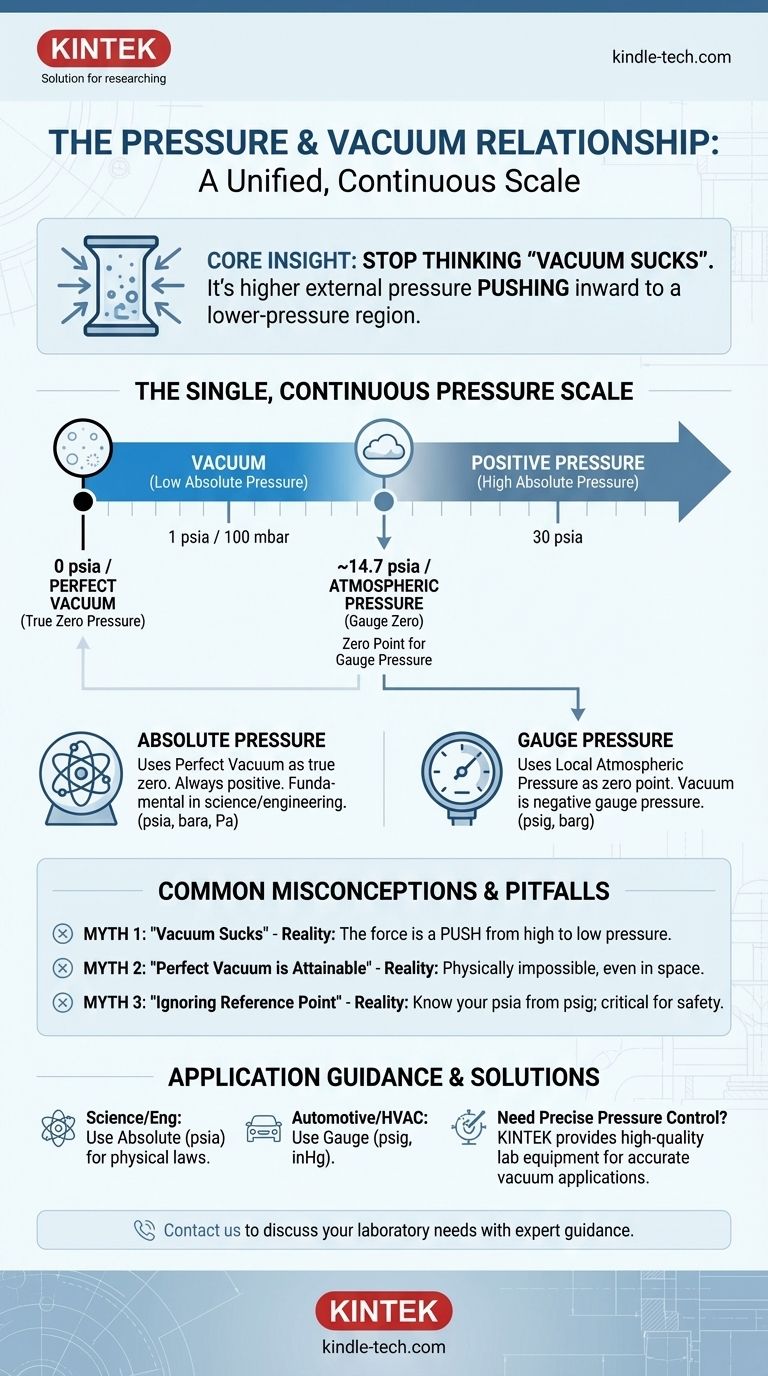
In short, pressure and vacuum are not separate forces; they are different points on the same continuous scale of pressure. Vacuum simply describes a state where the pressure in a system is lower than the pressure of the surrounding atmosphere. The relationship is defined by this reference point: positive pressure is above atmospheric pressure, while vacuum is below it.
The most critical insight is to stop thinking of vacuum as an active "sucking" force. Instead, understand it as a region of low pressure that allows the higher external atmospheric pressure to do the work of pushing inward.

The Key Reference Points: Absolute vs. Gauge
To truly understand vacuum, you first have to understand the two primary ways pressure is measured. The distinction between them is the "zero point" they use for reference.
What is Absolute Pressure?
Absolute pressure uses a perfect vacuum as its true zero point. A perfect vacuum is a theoretical space completely devoid of any matter and therefore has zero pressure.
All absolute pressure measurements are positive values, starting from 0. This scale is fundamental in science and engineering for calculations where the total energy or state of a gas is important, such as in chemistry or thermodynamics. Common units include Pascals (Pa), bar absolute (bara), or pounds per square inch absolute (psia).
What is Atmospheric Pressure?
Atmospheric pressure (or barometric pressure) is the force exerted by the weight of the air in the atmosphere. It isn't a constant; it changes with altitude and weather conditions.
At sea level, standard atmospheric pressure is approximately 1013 millibars (mbar), 14.7 psia, or 1 atmosphere (atm). This value serves as our everyday, natural reference point.
What is Gauge Pressure?
Gauge pressure uses the local atmospheric pressure as its zero point. This is the most common pressure measurement used in daily life, such as when checking tire pressure.
If your tire gauge reads 32 psi, it means the pressure inside the tire is 32 psi higher than the atmospheric pressure outside. Critically, gauge pressure can also be negative, which is precisely what we call a vacuum.
Defining Vacuum in This Context
With these reference points established, the relationship between pressure and vacuum becomes clear.
Vacuum is Negative Gauge Pressure
When we say a system is "under vacuum," we are describing a negative gauge pressure. This means the absolute pressure inside the system is less than the absolute pressure of the surrounding atmosphere.
For example, if the atmospheric pressure is 14.7 psia and a vacuum chamber has an internal pressure of 4.7 psia, its gauge pressure would be -10 psig.
The Single, Continuous Pressure Scale
It's helpful to visualize all these terms on a single line:
- 0 psia (Perfect Vacuum): The absolute zero of pressure.
- Low Absolute Pressures: This is the range we call "vacuum" (e.g., 1 psia, 100 mbar).
- ~14.7 psia (Standard Atmospheric Pressure): This is the zero point for gauge pressure.
- High Absolute Pressures: This is the range we call positive gauge pressure (e.g., 30 psia).
Vacuum isn't a separate phenomenon; it's simply the lower end of the universal pressure spectrum.
Common Misconceptions and Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding the true nature of pressure and vacuum helps clarify common but incorrect assumptions that can lead to errors in both thought and application.
Misconception 1: "Vacuum Sucks"
A vacuum does not create an inward-pulling force. The phenomenon we perceive as "suction" is actually the higher-pressure fluid (like the air outside) being pushed into the lower-pressure region by the surrounding atmospheric pressure.
The force is always a push from high pressure to low pressure.
Misconception 2: "Perfect Vacuum is Attainable"
Achieving a perfect, absolute zero vacuum is considered physically impossible. Even in the depths of outer space, there are still a few particles per cubic meter. In a lab, material surfaces will always release atoms (a process called outgassing), preventing a perfect void.
Misconception 3: Ignoring the Reference Point
Confusing absolute pressure (psia) and gauge pressure (psig) is a frequent source of error. For any critical application, you must know which reference is being used. A vessel designed to hold 100 psig might fail if subjected to 100 psia at sea level, which is actually 114.7 psig.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your interpretation of pressure and vacuum should depend on your specific context.
- If your primary focus is scientific research or engineering: Always be explicit about using absolute pressure (psia, bara, Torr) for calculations involving physical laws, as this removes the variable of local atmospheric conditions.
- If your primary focus is in automotive or HVAC: You are almost certainly dealing with gauge pressure. "Vacuum" will refer to pressure below atmospheric and is often measured in inches of mercury (inHg).
- If your primary focus is general physics: Anchor your understanding on absolute pressure as the fundamental concept, with a perfect vacuum as the true zero, and treat atmospheric pressure as a convenient but variable local benchmark.
By seeing pressure and vacuum as parts of a unified whole, you can analyze and control physical systems with greater accuracy and clarity.
Summary Table:
| Concept | Definition | Key Reference Point | Example Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Absolute Pressure | Pressure measured from a perfect vacuum (true zero). | Perfect Vacuum (0 pressure) | psia, bara, Pa |
| Atmospheric Pressure | Pressure exerted by the atmosphere at a given location. | Variable (approx. 14.7 psia at sea level) | psia, mbar, atm |
| Gauge Pressure | Pressure measured relative to local atmospheric pressure. | Atmospheric Pressure (zero point) | psig, barg |
| Vacuum | A state where absolute pressure is lower than atmospheric pressure. | Negative Gauge Pressure | inHg, mbar (vacuum) |
Need precise pressure control for your lab processes? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables designed for accurate pressure and vacuum applications. Whether you're conducting research, performing material testing, or managing environmental simulations, our solutions ensure reliability and clarity in your measurements. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs with tailored equipment and expert guidance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Touchscreen Automatic Vacuum Heat Press
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Wall Mounted Water Distillation Unit
People Also Ask
- How does heat treatment affect the mechanical properties of metals? Optimize Hardness, Toughness, and Ductility
- What is the function of a high-temperature vacuum annealing furnace? Optimize Your Zr2Al3C4 Coating Formation
- What is partial pressure in vacuum heat treatment? Prevent Alloy Depletion & Ensure Metallurgical Control
- Can I vacuum the inside of my furnace? A Guide to Safe DIY Cleaning vs. Professional Service
- How is a high-temperature heating furnace used to evaluate the thermal shock resistance of refractory materials?
- What is the time and temperature of heat treatment? A Guide to Tailoring Material Properties
- What is the sintering cycle? A Guide to Transforming Powders into Dense, Strong Parts
- What are the most commonly used metals in a vacuum furnace's hot zone? Discover the Key to High-Purity Processing

















