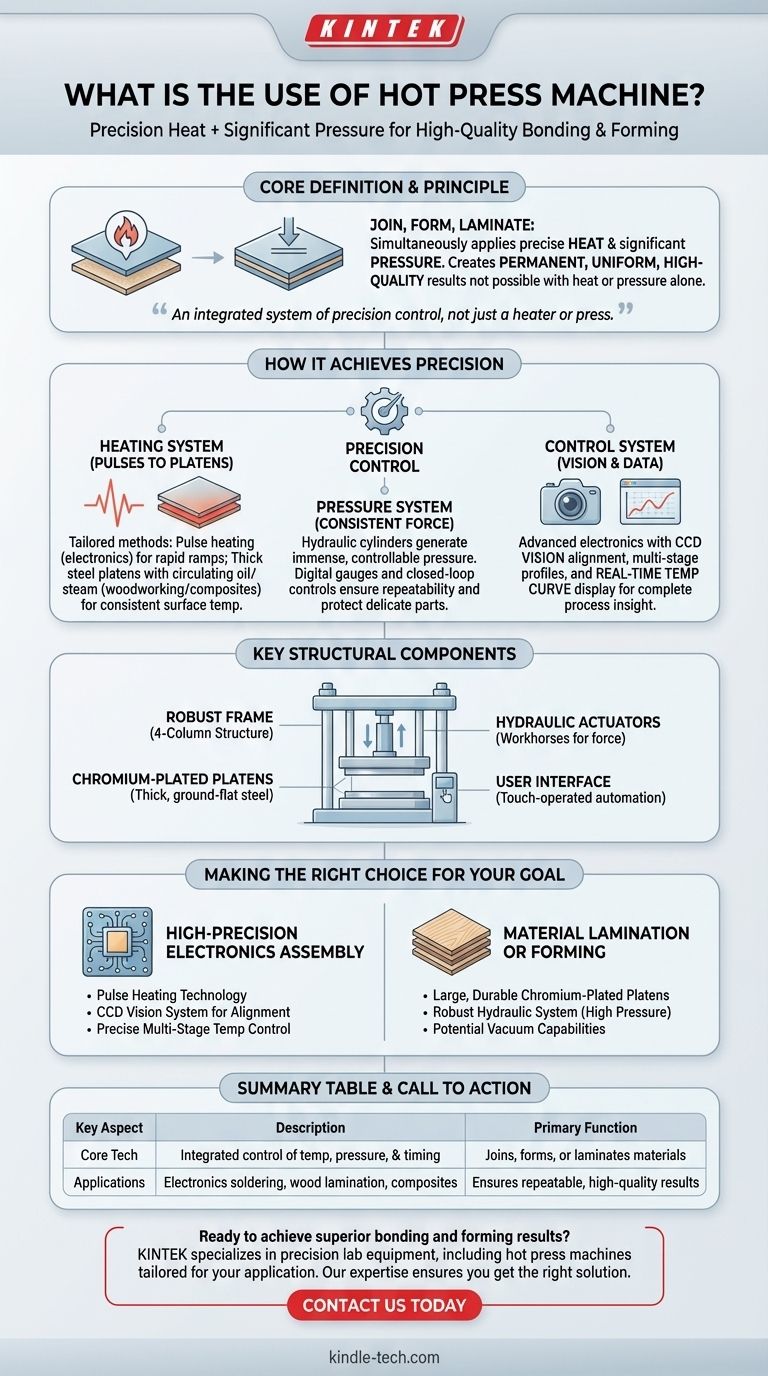
At its core, a hot press machine is a specialized piece of equipment designed to join, form, or laminate materials by simultaneously applying precise heat and significant pressure. It is used in applications ranging from the delicate soldering of electronic components onto circuit boards to the large-scale production of laminated wood panels. The machine ensures a high-quality, permanent, and uniform result that could not be achieved by applying heat or pressure alone.
A hot press is not merely a heater or a press; it is an integrated system of precision control. Its primary function is to create a highly repeatable and controlled environment where heat and force work together to create strong, reliable bonds or shapes in various materials.
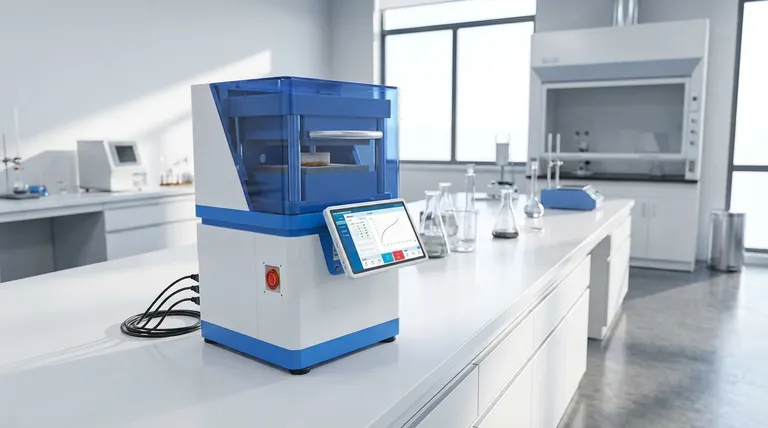

How a Hot Press Achieves Precision
The effectiveness of a hot press comes from its ability to meticulously control every variable in the process. This transforms what could be a crude application of force and heat into a refined manufacturing technique.
The Principle: Fusing Heat and Force
A hot press operates on a simple thermodynamic principle: applying heat increases the internal energy of materials, making them malleable or causing adhesives and solders to flow. By simultaneously applying controlled pressure via hydraulic or pneumatic systems, the machine ensures an intimate, uniform contact between surfaces, eliminating gaps and creating a solid, permanent bond upon cooling.
The Heating System: From Pulses to Platens
Heating methods are tailored to the application. For high-precision electronics, pulse heating technology is often used, allowing for rapid temperature ramps and precise control. For larger applications like woodworking or composites, the machine uses thick steel platens (plates) with internal channels where heated oil or steam circulates, providing consistent and even temperature across a large surface.
The Pressure System: Applying Consistent Force
The force is typically generated by one or more hydraulic cylinders. These systems can produce immense and highly controllable pressure. Advanced machines feature digital pressure gauges and closed-loop controls, allowing operators to program a specific pressure profile for the entire cycle, ensuring repeatability and protecting delicate parts from damage.
The Control System: Vision and Data
Modern hot presses are governed by advanced electronic systems. Many feature a CCD vision system for perfect alignment of components before pressing. The control interface allows for multi-stage temperature and pressure profiles, and a real-time temperature curve display gives the operator complete insight and control over the process.
Key Structural Components
Understanding the machine's physical makeup reveals how it maintains its precision and durability under constant stress.
Frame and Platens
Most industrial hot presses are built on a robust four-column and three-plate structure. This design ensures high rigidity and parallelism, which is critical for applying even pressure. The platens themselves are thick, ground-flat steel plates, often chromium-plated to prevent adhesives from sticking and to resist corrosion.
Actuators and Power
Hydraulic cylinders are the workhorses of the machine, providing the necessary pressing force. These are powered by a hydraulic pump unit. In some cases, compressed air is also used for auxiliary functions or in machines that require lower force levels.
User Interface and Automation
Operations are managed through a touch-operated interface. This allows users to select from pre-stored programs, create new recipes for different jobs, and protect sensitive settings with passwords. This level of automation ensures consistency from one cycle to the next.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a hot press is a specialized tool with specific operational considerations.
Application-Specific Design
A hot press designed for bonding flexible circuits is vastly different from one used for making plywood. The technology does not follow a one-size-fits-all model. Machines are often customized for a specific production requirement, which impacts cost and flexibility.
Requirement for Precision
The high precision of the machine demands equally high precision in the preparation of materials. Features like CCD alignment are only effective if the components are clean and correctly fixtured. The process is less forgiving of error than simpler bonding methods.
System Complexity
The integration of hydraulic, electronic, and thermal systems makes a hot press a complex piece of equipment. It requires skilled operators to program correctly and a dedicated maintenance schedule to ensure the hydraulic and control systems function reliably over time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The critical features of a hot press depend entirely on the intended application.
- If your primary focus is high-precision electronics assembly: Prioritize machines with pulse heating technology, a CCD vision system for alignment, and precise multi-stage temperature control.
- If your primary focus is material lamination or forming: Look for features like large, durable chromium-plated platens, a robust hydraulic system for high pressure, and potential vacuum capabilities to ensure ideal adhesion.
Ultimately, a hot press provides an unparalleled level of control to achieve superior material bonding and forming results.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Joins, forms, or laminates materials using simultaneous heat and pressure. |
| Core Technology | Integrated control of temperature, pressure, and timing for repeatable results. |
| Common Applications | Electronics soldering, wood panel lamination, composite material production. |
| Key Components | Heating platens, hydraulic/pneumatic pressure system, digital control interface. |
Ready to achieve superior bonding and forming results in your lab or production line?
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment, including hot press machines tailored for applications from electronics assembly to material lamination. Our expertise ensures you get the right solution for high-quality, repeatable outcomes.
Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can enhance your process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory plate hot press play in the vulcanization and molding of fluorosilicone rubber (F-LSR)?
- How is pressure generated and applied in a hot press? Master High-Intensity Hydraulic & Pneumatic Systems
- Why is a laboratory precision hot press necessary for processing high-performance composite solid-state electrolyte membranes?
- Why is a laboratory hot press required for Oxygen Depolarized Cathodes? Ensure Precision Molding and Conductivity.
- What role does a hot press play in treating the CAL-GPE interface? Optimize Performance for Flexible Lithium Batteries



















