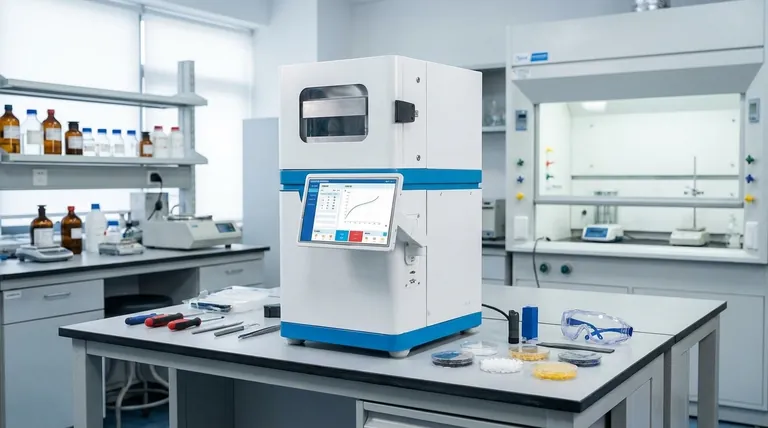
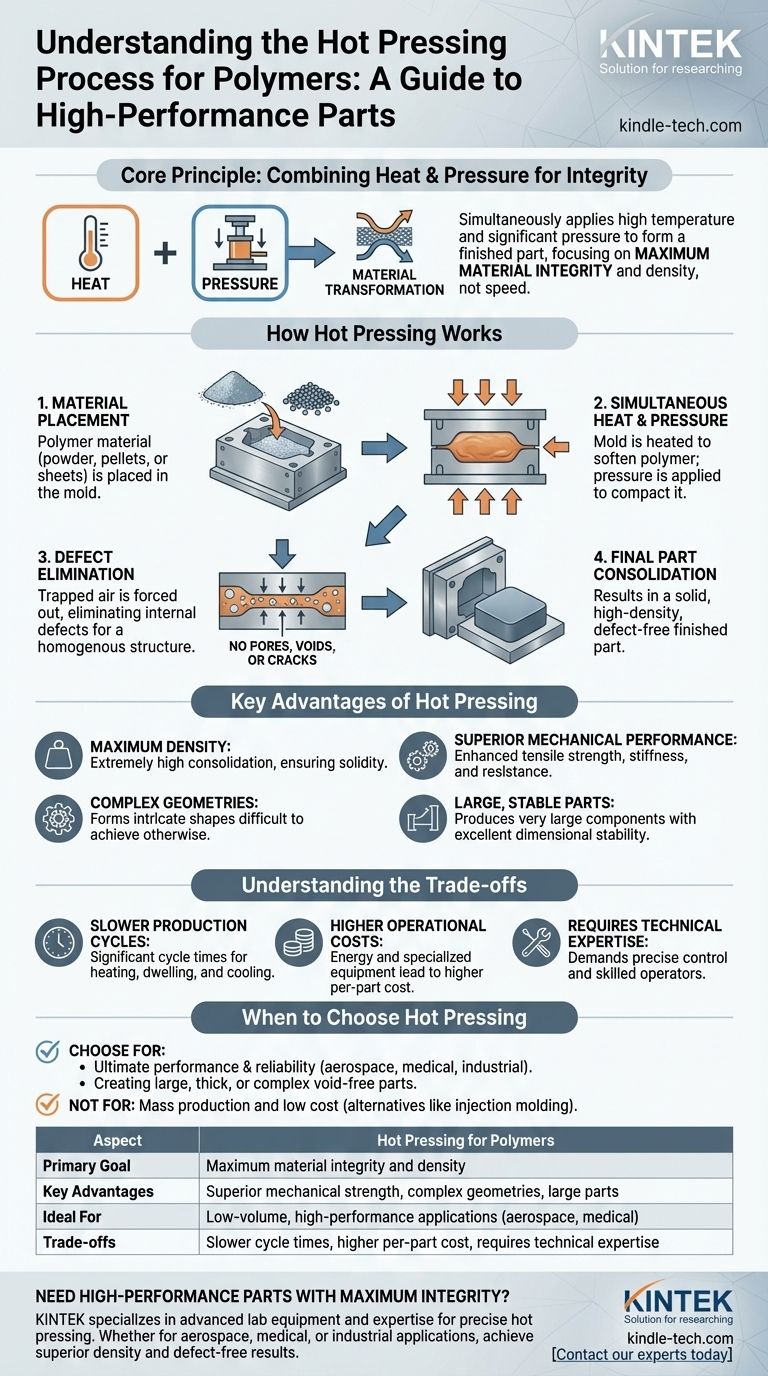
At its core, the hot pressing process for polymers is a manufacturing method that uses high temperature and significant pressure simultaneously to form a finished part. Unlike other methods that might inject molten material, hot pressing consolidates powders, pre-impregnated fibers, or layered sheets into a solid, high-density shape with exceptionally low internal defects.
The central purpose of hot pressing is not speed or volume, but maximum material integrity. It is the process of choice when the final part's density, strength, and internal quality are more critical than production cost or cycle time.

The Core Principle: Combining Heat and Pressure
Hot pressing is a conceptually simple but powerful process. By applying heat and mechanical force at the same time, it fundamentally transforms the base material into a superior final product.
How It Works
The process involves placing the polymer material—often in powder, pellet, or sheet form—into a mold. The mold is then heated to a specific temperature that softens the polymer, making it pliable. Simultaneously, pressure is applied, compacting the material, forcing out trapped air, and ensuring it conforms perfectly to the mold's shape.
The Goal: Defect Elimination
The combination of heat and pressure is key to eliminating internal defects like pores, voids, and cracks. These imperfections, which can compromise a part's strength and lead to premature failure, are squeezed out during consolidation. The result is a dense, homogenous material structure with enhanced performance characteristics.
Key Advantages of Hot Pressing
Choosing this method provides several unique benefits, making it ideal for high-performance applications where material failure is not an option.
Achieving Maximum Density
The primary advantage is producing parts with extremely high density. By removing internal voids, the process ensures the final component is as solid and consolidated as possible. This directly contributes to its overall strength and durability.
Superior Mechanical Performance
A direct result of high density and the absence of defects is a significant improvement in mechanical properties. Hot-pressed polymer parts exhibit greater tensile strength, stiffness, and resistance to wear and environmental stress.
Forming Complex Geometries
Because the material is softened and then pressed, it can be forced into intricate and complex shapes that might be difficult to achieve with other manufacturing techniques.
Creating Large, Dimensionally Stable Parts
The process allows for relatively low pressing pressures compared to some cold-forming methods. This makes it feasible to produce very large components with excellent dimensional stability and minimal internal stress or deformation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, hot pressing is a specialized technique with clear limitations. Objectively weighing these against the benefits is critical for making an informed decision.
Slower Production Cycles
Hot pressing is not a high-speed process. The time required to heat the mold, apply pressure for a sufficient duration (the "dwell time"), and then cool the part down makes the cycle time significantly longer than methods like injection molding.
Higher Operational Costs
The energy required to maintain high temperatures and the specialized equipment lead to higher per-part costs. This makes the process less suitable for high-volume, low-cost consumer goods. It is best reserved for single-piece or low-volume production runs where performance justifies the expense.
Requires Technical Expertise
Achieving consistent, high-quality results demands precise control over temperature, pressure, and timing. This means the process requires skilled operators and high-level technical oversight, adding to the operational complexity.
When to Choose Hot Pressing
Your final decision should be guided by the non-negotiable requirements of your project.
- If your primary focus is ultimate performance and reliability: Choose hot pressing for critical components in aerospace, medical, or industrial applications where failure could have severe consequences.
- If your primary focus is creating large, thick, or complex parts without internal flaws: This process is uniquely suited for producing robust, void-free components that other methods struggle with.
- If your primary focus is mass production and low cost: You should look to alternative processes like injection molding or extrusion, which are optimized for speed and volume.
Ultimately, selecting the right manufacturing process is the first step in unlocking the full performance potential of your chosen material.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Hot Pressing for Polymers |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Maximum material integrity and density |
| Key Advantages | Superior mechanical strength, complex geometries, large parts |
| Ideal For | Low-volume, high-performance applications (e.g., aerospace, medical) |
| Trade-offs | Slower cycle times, higher per-part cost, requires technical expertise |
Need to produce high-performance polymer parts with maximum integrity?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and technical expertise required for precise hot pressing processes. Whether you are developing critical components for aerospace, medical devices, or industrial applications, our solutions help you achieve the superior density and defect-free results that hot pressing is known for.
Let's discuss your project requirements and how our specialized equipment can meet your needs. Contact our experts today to get started.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Touchscreen Automatic Vacuum Heat Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory hot press required after the spray-coating of polymer-ceramic composite electrolytes? Essential density.
- How does the pressure control system of vacuum hot press equipment contribute to preventing material defects? Learn More
- Why is precise temperature control in a vacuum hot pressing furnace essential for Ti2AlNb/TA15 laminates?
- How does the high-temperature and high-pressure environment provided by vacuum hot press equipment improve the interfacial bonding between Mo fibers and the TiAl matrix?
- What advantages does a vacuum hot press offer for ZIF-62 glass? Achieve Large, Bubble-Free, High-Density Results



















