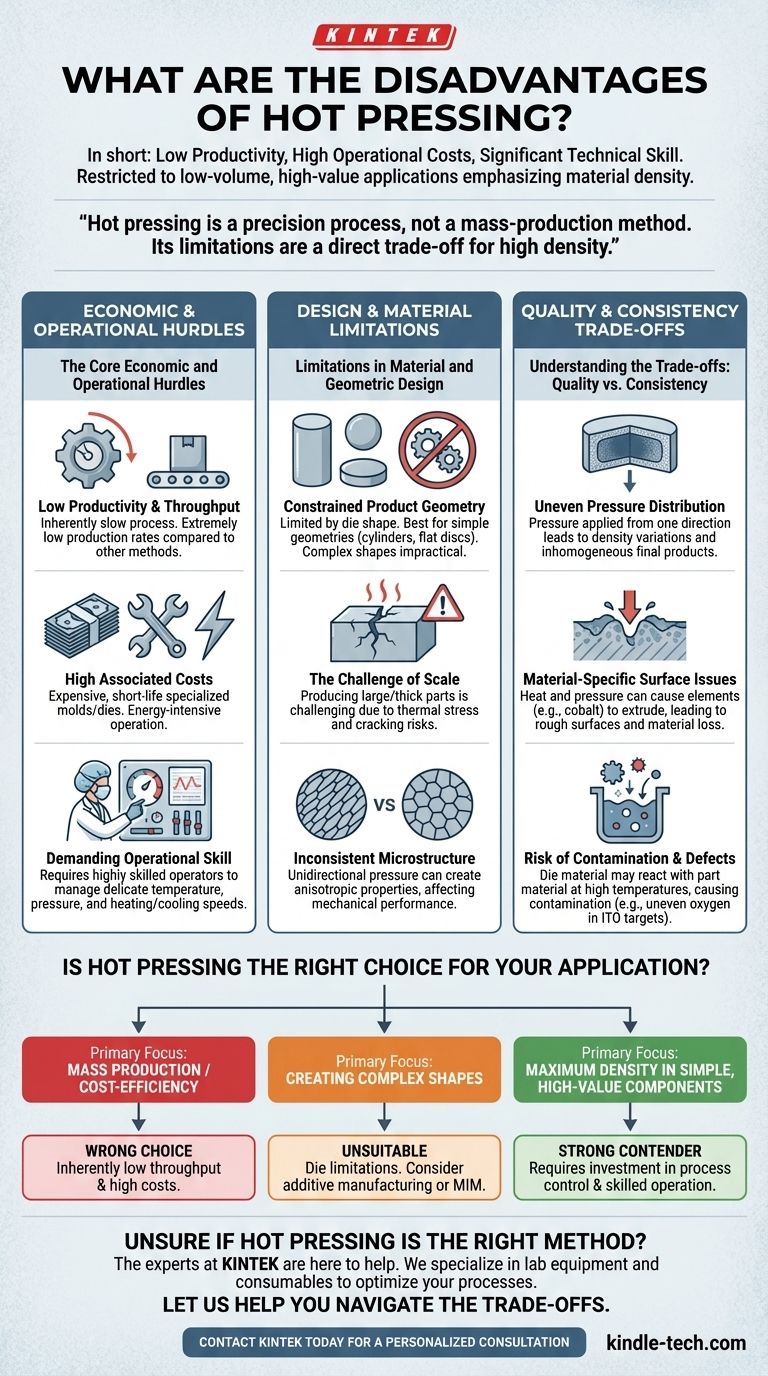
In short, the primary disadvantages of hot pressing are its low productivity, high operational costs, and the significant technical skill required to achieve consistent results. These factors generally restrict its use to low-volume, high-value applications where material density is the absolute priority.
Hot pressing is fundamentally a precision process, not a mass-production method. Its limitations are a direct trade-off for its ability to produce highly dense materials, meaning the process is defined by high costs, low throughput, and demanding operational complexity.
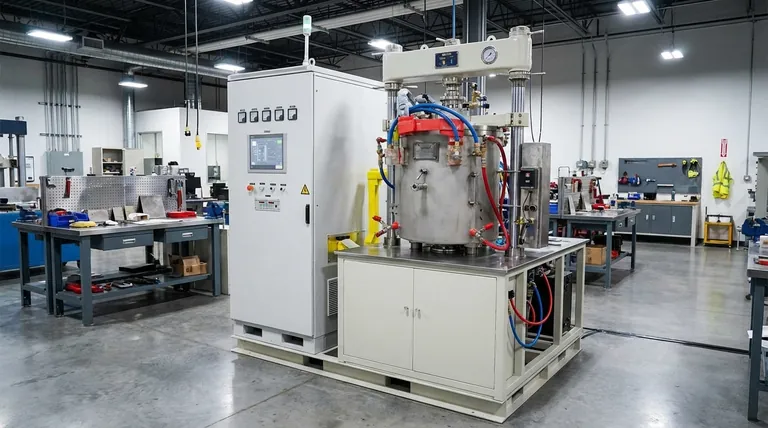

The Core Economic and Operational Hurdles
The most immediate drawbacks of hot pressing relate to its speed, cost, and the human expertise required to run it effectively. These factors often make it non-viable for many manufacturing scenarios.
Low Productivity and Throughput
The nature of the process, which involves carefully heating and pressing a single part or a very small batch within a die, makes it inherently slow. This results in extremely low production rates compared to other sintering or manufacturing methods.
High Associated Costs
Costs accumulate from multiple sources. The specialized molds and dies are expensive to fabricate and have a short service life due to the extreme heat and pressure. Furthermore, the process can be energy-intensive.
Demanding Operational Skill
Hot pressing is not a "set and forget" operation. It requires highly skilled operators to manage the delicate interplay of temperature, pressure, and heating/cooling speeds. Poor control over these variables can easily lead to product defects or complete failure.
Limitations in Material and Geometric Design
Beyond the economic factors, hot pressing imposes significant physical and material constraints that limit its application.
Constrained Product Geometry
The process is limited by the shape of the die. It is best suited for producing simple geometries, such as cylinders or flat discs. Creating complex, non-symmetrical shapes is often impractical or impossible.
The Challenge of Scale
While the process can produce large-diameter parts, producing large or thick components is challenging. Thermal stress during the heating and cooling cycles can easily cause large billets to crack, requiring exceptionally stable and uniform equipment.
Inconsistent Microstructure and Properties
The unidirectional pressure applied during hot pressing can create an anisotropic microstructure. This means the material's mechanical properties, like strength, may be different in one direction compared to another, which is unacceptable for many high-performance applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Quality vs. Consistency
The core trade-off with hot pressing is achieving high density at the cost of uniformity. The very forces that create density can also introduce inconsistencies and defects.
Uneven Pressure Distribution
Pressure is typically applied from one direction, which can lead to density variations within the part. The areas directly under the press will be denser than those near the edges, leading to an inhomogeneous final product.
Material-Specific Surface Issues
The combination of heat and pressure can cause certain elements within an alloy to be "squeezed out." For example, cobalt can be extruded from the surface of some products, causing material loss and resulting in a rough surface that is difficult to process further.
Risk of Contamination and Defects
At high temperatures, the die material can sometimes react with the part material, leading to contamination. For sensitive materials like ITO targets, this process can also create an uneven distribution of oxygen content, which directly impacts the performance of the final product.
Is Hot Pressing the Right Choice for Your Application?
Choosing this method requires a clear understanding of your project's primary goal. The decision hinges on whether you prioritize density and performance over cost, speed, and geometric complexity.
- If your primary focus is mass production or cost-efficiency: Hot pressing is almost certainly the wrong choice due to its inherently low throughput and high operational costs.
- If your primary focus is creating complex shapes: The limitations of the die make hot pressing unsuitable; consider methods like additive manufacturing or metal injection molding.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density in a simple, high-value component: Hot pressing is a strong contender, provided you are prepared to invest in the process control and skilled operation required to manage its inherent challenges.
Ultimately, understanding these limitations is the key to leveraging hot pressing for its intended purpose: creating highly dense, specialized materials where precision outweighs productivity.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage Category | Key Challenges |
|---|---|
| Economic & Operational | Low productivity & throughput, High equipment & energy costs, Requires highly skilled operators |
| Design & Material | Limited to simple geometries (e.g., discs), Risk of anisotropic properties, Challenging to scale for large parts |
| Quality & Consistency | Uneven pressure distribution, Potential for surface defects & contamination, Risk of inconsistent microstructure |
Unsure if hot pressing is the right method for your materials? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in lab equipment and consumables, providing the precise tools and expert advice you need to optimize your processes. Let us help you navigate the trade-offs between density, cost, and complexity to achieve your specific goals.
Contact KINTEL today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Touchscreen Automatic Vacuum Heat Press
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
People Also Ask
- What is the primary role of a vacuum hot press furnace? Optimize Cd2SnO4 Transparent Conductive Target Production
- What is the principle of hot pressing? Achieve Superior Density for High-Performance Components
- What is the necessity of pre-pressing composite powders? Enhance Stability in Vacuum Hot-Pressing Sintering
- What are the advantages of hot pressing for PEO electrolytes? Achieve superior density and solvent-free performance.
- How do the long holding times and high vacuum of hot pressing improve diamond/aluminum bonding? Key Mechanisms Revealed
- Who manufactures spark plasma sintering? Discover Leading SPS Equipment Suppliers
- What does hot-pressing do? Transform Materials with High-Temperature, High-Pressure Densification
- What is a vacuum hot press? Achieve Superior Material Densification and Bonding



















