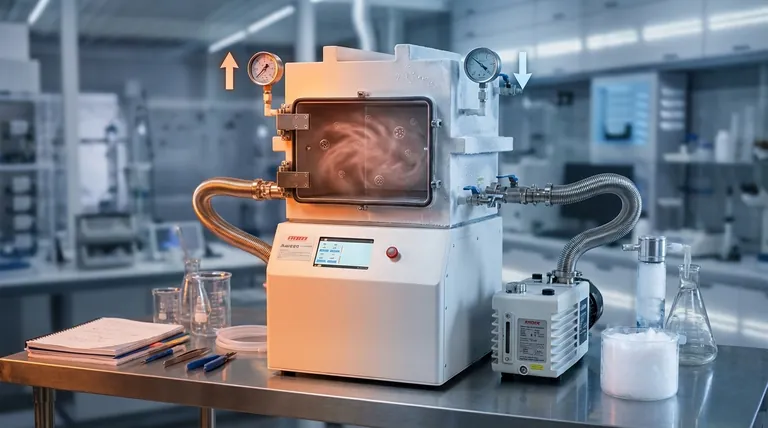
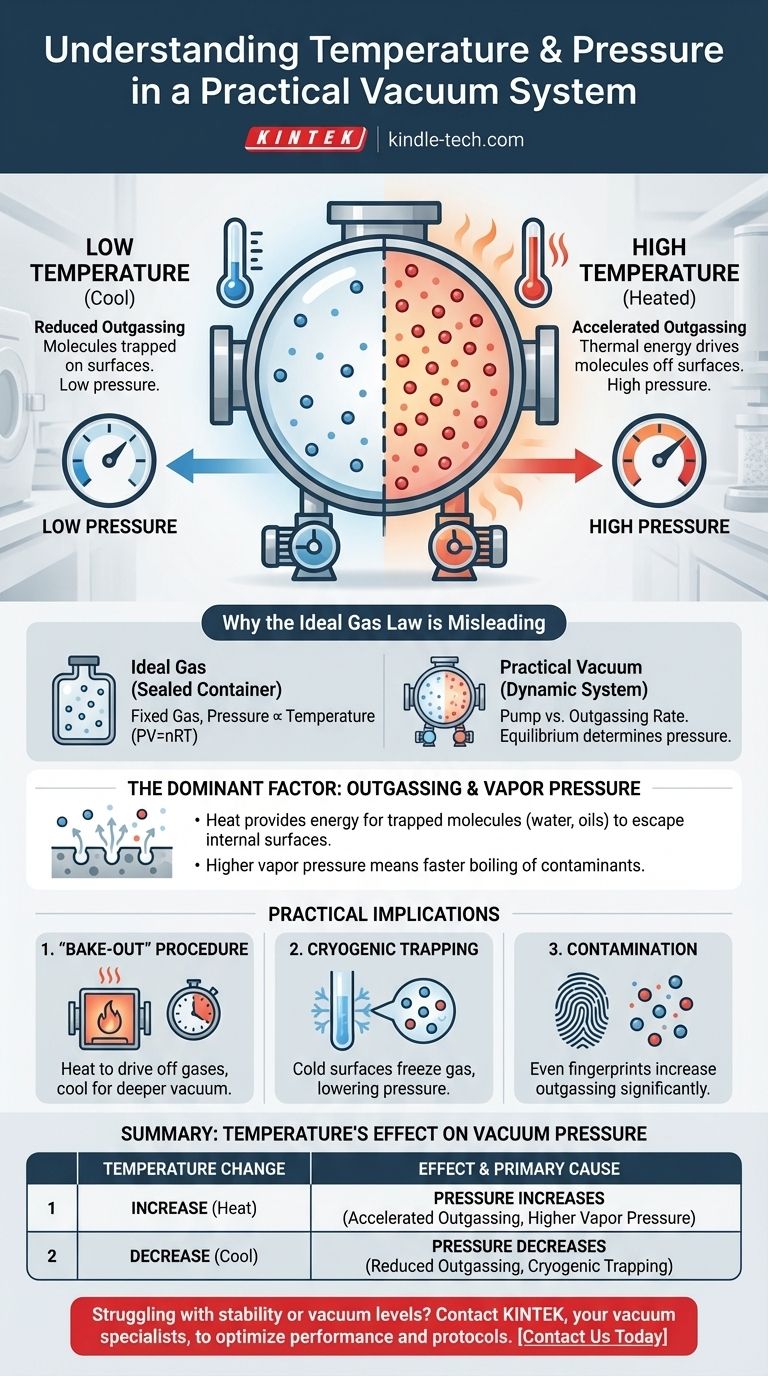
In a practical vacuum system, the relationship is direct: increasing the system's temperature will increase the pressure, thereby degrading the quality of the vacuum. This occurs because heat provides the energy for molecules trapped on the chamber's internal surfaces to escape into the vacuum space. This process, known as outgassing, is the dominant source of pressure in high-vacuum environments.
The pressure inside a real-world vacuum chamber is not governed by the Ideal Gas Law, but by the rate of outgassing from its internal surfaces. Higher temperatures increase this rate, releasing more gas molecules and thus increasing the overall pressure.

Why the Ideal Gas Law is Misleading Here
The Misconception of a "Contained Gas"
The familiar Ideal Gas Law (PV=nRT) describes the relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature for a fixed amount of gas in a sealed container. In that scenario, pressure is directly proportional to temperature.
A vacuum chamber, however, is not a sealed container with a fixed amount of gas. It is a dynamic system where a pump is actively removing molecules.
The Reality: A Dynamic Equilibrium
The pressure in a vacuum is determined by the balance between the rate at which the pump removes molecules and the rate at which new molecules enter the system. The primary source of these new molecules is the internal surfaces of the chamber itself.
The Dominant Factor: Outgassing and Vapor Pressure
What Is Outgassing?
All materials have gas molecules adsorbed (stuck to the surface) or absorbed (trapped within the material). In a vacuum, these molecules will gradually escape from the surfaces.
This process is called outgassing. The main culprit in most vacuum systems is water vapor, but oils, solvents, and gases trapped during manufacturing also contribute.
How Temperature Drives Outgassing
Heating the walls of the vacuum chamber transfers thermal energy to the trapped molecules. This increased energy allows them to overcome the forces holding them to the surface, causing them to be released into the vacuum.
A higher temperature means a significantly higher rate of outgassing, which leads directly to a higher pressure.
The Role of Vapor Pressure
For any condensed substance, like a droplet of water or a film of oil inside the chamber, there is a vapor pressure. This is the pressure at which the substance is in equilibrium with its own gas at a given temperature.
As temperature increases, the vapor pressure of these contaminants rises exponentially. If the vapor pressure of the contaminant exceeds the pressure in the chamber, it will rapidly boil away, causing a dramatic increase in pressure.
Understanding the Practical Implications
The "Bake-Out" Procedure
Engineers exploit this temperature-pressure relationship to achieve ultra-high vacuum (UHV). A system is heated, often to hundreds of degrees Celsius, for many hours or days while the pumps are running.
This "bake-out" dramatically accelerates outgassing, driving off trapped water and other contaminants so the pumps can remove them permanently. After the system is cooled back down, the outgassing rate is vastly lower, allowing for a much deeper vacuum.
The Impact of Cryogenics
The opposite effect is also used. Extremely cold surfaces, known as cryotraps or cryopumps, act as sinks for gas molecules.
When a molecule like water hits a very cold surface, it freezes instantly and its vapor pressure becomes negligible. This effectively removes it from the vacuum, dramatically lowering the system pressure.
The Problem of Contamination
This principle highlights why cleanliness is paramount in vacuum technology. A single fingerprint contains oils and water that will act as a significant source of outgassing, limiting the ultimate pressure a system can achieve, especially when heated.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To effectively manage a vacuum system, you must treat temperature as a primary control variable.
- If your primary focus is achieving the deepest possible vacuum: You must heat the chamber in a "bake-out" while pumping to force trapped gases out, then allow it to cool to achieve the target pressure.
- If your primary focus is maintaining a stable vacuum during a process: You must ensure precise temperature control, as even small thermal fluctuations will cause pressure changes due to shifting outgassing rates.
- If your primary focus is dealing with high-vapor-pressure substances: You may need to use cryogenic cooling (cold traps) to capture vapors and prevent them from overwhelming your pumps.
Ultimately, mastering the pressure in your vacuum system means mastering the thermal energy of its surfaces.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Change | Effect on Vacuum Pressure | Primary Cause |
|---|---|---|
| Increase | Pressure Increases | Accelerated outgassing and higher vapor pressure of contaminants. |
| Decrease | Pressure Decreases | Reduced outgassing rate; cryogenic surfaces can trap molecules. |
Struggling with pressure instability or unable to achieve your target vacuum level? The thermal management of your system is likely the key. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for precise vacuum applications. Our experts can help you select the right components and develop protocols for bake-out, temperature control, or cryogenic trapping to ensure your vacuum processes are reliable and repeatable. Contact our vacuum specialists today to optimize your system's performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic hot press play in rice husk-based composite boards? Achieve Structural Density
- What is the purpose of a hot pressing system following the reduction of iron powder in a fluidized bed? Stabilize DRI
- What is the function of a laboratory hydraulic hot press in the assembly of solid-state photoelectrochemical cells?
- What are the advantages of using hot-pressing sintering equipment? Maximize CoSb3 Performance and ZT Values
- What is the function of a laboratory high-temperature hydraulic press? Optimize MEA Fabrication for HCl Electrolysis



















