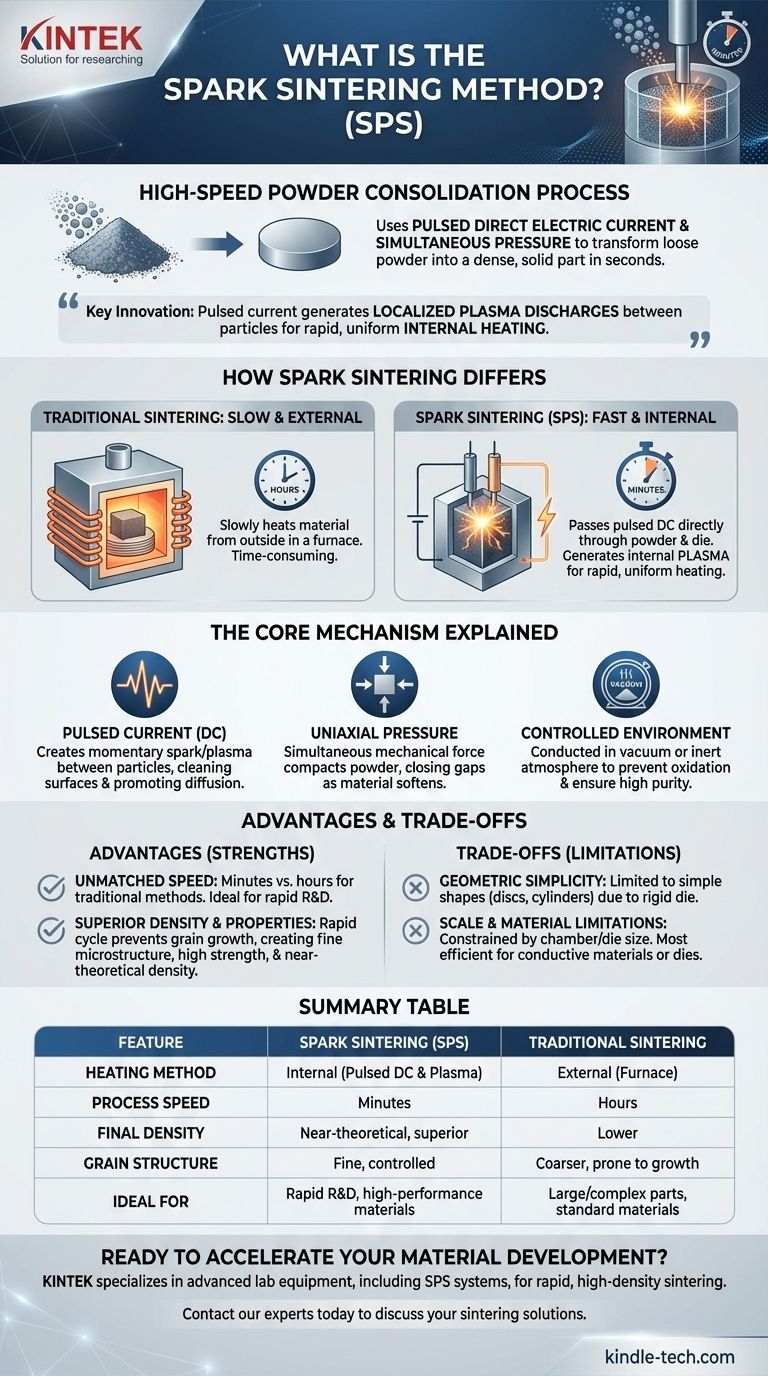
At its core, spark sintering is a high-speed powder consolidation process. Also known as Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS), it uses a powerful pulsed direct electric current and simultaneous mechanical pressure to transform loose powder into a dense, solid part in a matter of seconds. Unlike conventional methods that slowly heat a material from the outside, spark sintering heats the material internally, dramatically accelerating the process and improving the final material properties.
The fundamental innovation of spark sintering is its use of a pulsed electric current to generate localized plasma discharges between powder particles. This creates rapid, uniform, internal heating that, when combined with pressure, achieves densification far faster than traditional heat-only methods.

How Spark Sintering Fundamentally Differs
To understand the value of spark sintering, it's essential to first understand the conventional process it improves upon.
Traditional Sintering: Slow and External
Traditional sintering subjects loose powder to high temperatures and pressure in a furnace. The goal is to compact the material into a solid piece by reducing the porous spaces between particles, all without reaching the material's melting point.
This process relies on heat applied externally, which must slowly conduct through the material. This is often a time-consuming process, taking hours to complete.
Spark Sintering: Fast and Internal
Spark Sintering (SPS) revolutionizes this by passing a pulsed direct current (DC) directly through the powder and its conductive die (typically graphite).
This direct electrical contact creates two heating effects simultaneously. It heats the entire conductive die, which in turn heats the powder, but more importantly, it generates intense spark plasma discharges in the microscopic gaps between the powder particles.
This internal plasma generation cleans particle surfaces by burning away oxide films and provides extremely rapid and uniform heating throughout the material. This dual heating mechanism is the key to its incredible speed.
The Core Mechanism Explained
The SPS process is a precise combination of electrical, mechanical, and environmental controls.
The Role of Pulsed Current
The application of a pulsed DC, rather than a continuous current, is critical. This on-off application generates a unique electro-thermal environment.
Each pulse creates a momentary spark or plasma discharge between adjacent powder particles. This localized energy surge cleans the particle surfaces and promotes atomic diffusion, which is the mechanism that bonds the particles together.
The Importance of Uniaxial Pressure
While the current provides the heat, uniaxial pressure is applied simultaneously by the punches, which also act as the electrodes.
This constant mechanical force physically compacts the powder, closing the gaps between particles and aiding the consolidation process as the material softens from the intense heat.
The Controlled Environment
The entire process is conducted within a vacuum or a controlled inert atmosphere. This prevents oxidation of the powder, especially when working with reactive metals, ensuring high purity and superior properties in the final sintered component.
Understanding the Key Advantages & Trade-offs
SPS is a powerful technique, but its application is not universal. Understanding its strengths and weaknesses is crucial.
Advantage: Unmatched Speed
The primary advantage is speed. Heating rates are exceptionally fast, and the entire sintering cycle can be completed in minutes, compared to the hours required for conventional hot pressing. This makes it ideal for rapid material development and research.
Advantage: Superior Density and Properties
The rapid heating and cooling cycle helps prevent grain growth, which is common in slower, high-temperature processes. This results in materials with a very fine microstructure, leading to enhanced mechanical properties like strength and hardness.
The plasma discharge also has a cleaning effect on particle surfaces, promoting stronger bonds and achieving near-theoretical density.
Trade-off: Geometric Simplicity
SPS relies on a rigid die, typically made of graphite. This means the process is generally limited to producing simple shapes, such as discs, cylinders, or blocks. Complex, three-dimensional parts are not feasible with this method.
Trade-off: Scale and Material Limitations
The size of the final part is constrained by the size of the SPS chamber and the available die. Furthermore, while SPS can be used for non-conductive materials like ceramics, the process is most efficient when the material or the surrounding die is electrically conductive.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to use spark sintering depends entirely on your project's specific priorities.
- If your primary focus is rapid material development: Spark sintering is an unparalleled tool for quickly creating and testing new alloys or composite materials.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and fine grain structure: SPS is a leading method for producing high-performance components with superior mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is creating large or geometrically complex parts: You should consider alternative methods like traditional powder metallurgy, casting, or additive manufacturing.
This advanced technique fundamentally accelerates the creation of high-performance materials, opening new possibilities in material science and engineering.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Spark Sintering (SPS) | Traditional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Internal (Pulsed DC & Plasma) | External (Furnace) |
| Process Speed | Minutes | Hours |
| Final Density | Near-theoretical, superior | Lower |
| Grain Structure | Fine, controlled | Coarser, prone to growth |
| Ideal For | Rapid R&D, high-performance materials | Large/complex parts, standard materials |
Ready to accelerate your material development with Spark Plasma Sintering?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including SPS systems, to help you achieve rapid, high-density sintering for superior material properties. Our expertise supports researchers and engineers in developing next-generation alloys and composites.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our sintering solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and drive your projects forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the plasma sintering technique? Achieve Rapid, High-Density Material Fabrication
- What is the mechanism of SPS process? A Deep Dive into Rapid, Low-Temperature Sintering
- What are the parameters for spark plasma sintering? Master Speed, Pressure & Temperature Control
- What are the advantages of SPS? Achieve Superior Material Density and Performance
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts



















