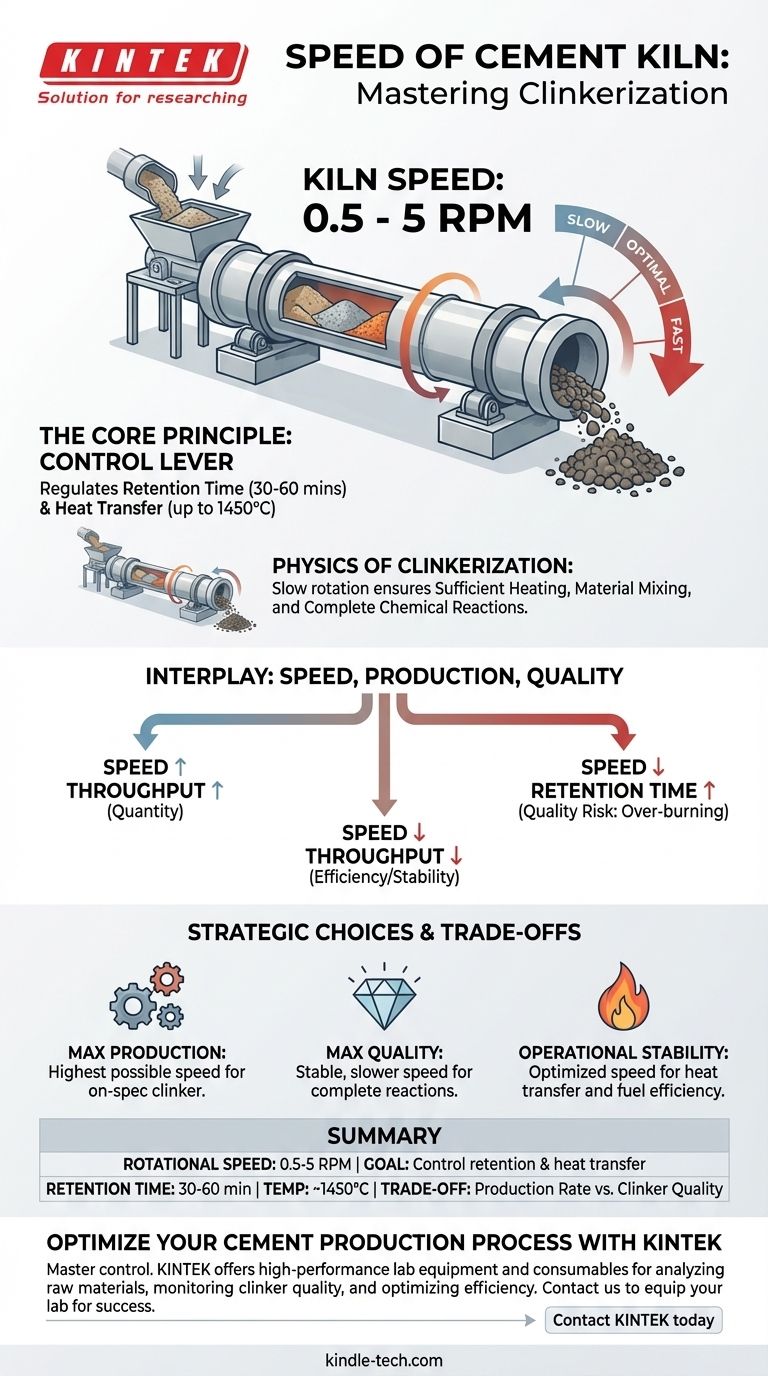
The rotational speed of a cement kiln is deliberately slow, typically operating between 0.5 and 5 revolutions per minute (RPM). This speed is not a fixed constant but a critical process variable that plant operators carefully adjust. The goal is not to move material quickly, but to precisely control the chemical reactions that transform raw materials into cement clinker.
The core principle to understand is that kiln speed is a control lever for retention time and heat transfer. It dictates how long the material is exposed to extreme heat, which directly determines the quality of the final product and the efficiency of the entire operation.

Why Such a Slow Rotation? The Physics of Clinkerization
A rotary kiln's primary job is to heat a finely ground mixture of limestone, clay, and other materials to approximately 1450°C (2640°F). This process, called clinkerization, involves a series of complex chemical reactions that must occur over a specific duration.
Defining Retention Time
Retention time is the total time a particle of raw material spends traveling from the kiln's inlet to its outlet. The slow rotation, combined with the slight downward angle of the kiln, ensures this journey takes the required amount of time, typically around 30-60 minutes.
The Need for Sufficient Heating
The chemical transformation into cement clinker cannot be rushed. Slower speeds increase the retention time, giving the material adequate time to absorb heat and for the necessary chemical bonds to break and reform into the desired crystalline structures.
Ensuring Material Mixing
The slow tumbling action is also essential for homogenization. It continuously exposes new surfaces of the material bed to the hot gases and radiant heat from the flame, ensuring a uniform and complete reaction throughout the entire volume of material.
The Interplay Between Speed, Production, and Quality
Kiln speed is a constant balancing act between three competing factors: the quality of the clinker, the rate of production, and the overall efficiency of the system.
Speed and Material Throughput
In the simplest sense, a faster rotation speed pushes more material through the kiln, increasing the potential production rate (measured in tons per day). This is the "quantity" part of the equation.
The Quality vs. Quantity Balance
However, increasing speed reduces retention time. If the material moves through the kiln too quickly, the clinkerization process will be incomplete. This results in a poor-quality product with undesirable chemical properties, such as high free lime, which weakens the final cement.
Impact on Heat Transfer
The speed also affects how efficiently heat is transferred from the flame and hot gas stream to the material. As the kiln rotates, it lifts material, which then tumbles down through the hot gases. The right speed optimizes this "curtain" of material for maximum heat absorption.
Understanding the Trade-offs
There is no single "best" speed. The optimal RPM is dynamic and depends on the specific kiln design, fuel type, and the chemical composition of the raw materials. Operators must constantly adjust the speed to navigate critical trade-offs.
The Risk of Running Too Fast
Pushing the kiln too fast directly risks incomplete combustion and clinkerization. This not only produces substandard clinker but can also lead to process instability, damage to the protective coating inside the kiln, and wasted fuel.
The Risk of Running Too Slow
Running the kiln too slowly can over-burn the clinker. This creates large, dense nodules that are difficult to grind in the subsequent cement mill, consuming excess energy. It also unnecessarily reduces the plant's production rate, making the operation less economical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The target kiln speed is always a strategic decision based on the primary objective of the plant at any given moment.
- If your primary focus is maximizing production output: You will operate at the highest possible speed that still allows for the production of on-spec, high-quality clinker.
- If your primary focus is ensuring maximum clinker quality: You will prioritize a stable and slightly slower speed to guarantee complete chemical reactions and ideal crystal growth.
- If your primary focus is operational stability and fuel efficiency: You will find a steady, optimized speed that maintains a healthy internal kiln coating and maximizes heat transfer, avoiding drastic changes.
Ultimately, controlling the kiln's slow rotation is the art of balancing chemistry, thermodynamics, and economics at the very heart of cement manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Typical Range / Importance |
|---|---|
| Rotational Speed | 0.5 - 5 RPM |
| Primary Goal | Control retention time & heat transfer |
| Typical Retention Time | 30 - 60 minutes |
| Clinkerization Temperature | ~1450°C (2640°F) |
| Key Trade-off | Production Rate vs. Clinker Quality |
Optimize Your Cement Production Process with KINTEK
Mastering the precise control of your kiln's rotation is just one part of achieving peak efficiency and product quality. KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance laboratory equipment and consumables essential for analyzing raw materials, monitoring clinker quality, and optimizing your entire manufacturing process.
Whether you are focused on maximizing output, ensuring superior clinker quality, or improving fuel efficiency, having the right analytical tools is critical. Let our experts help you equip your lab for success.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our solutions can support your cement production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing



















