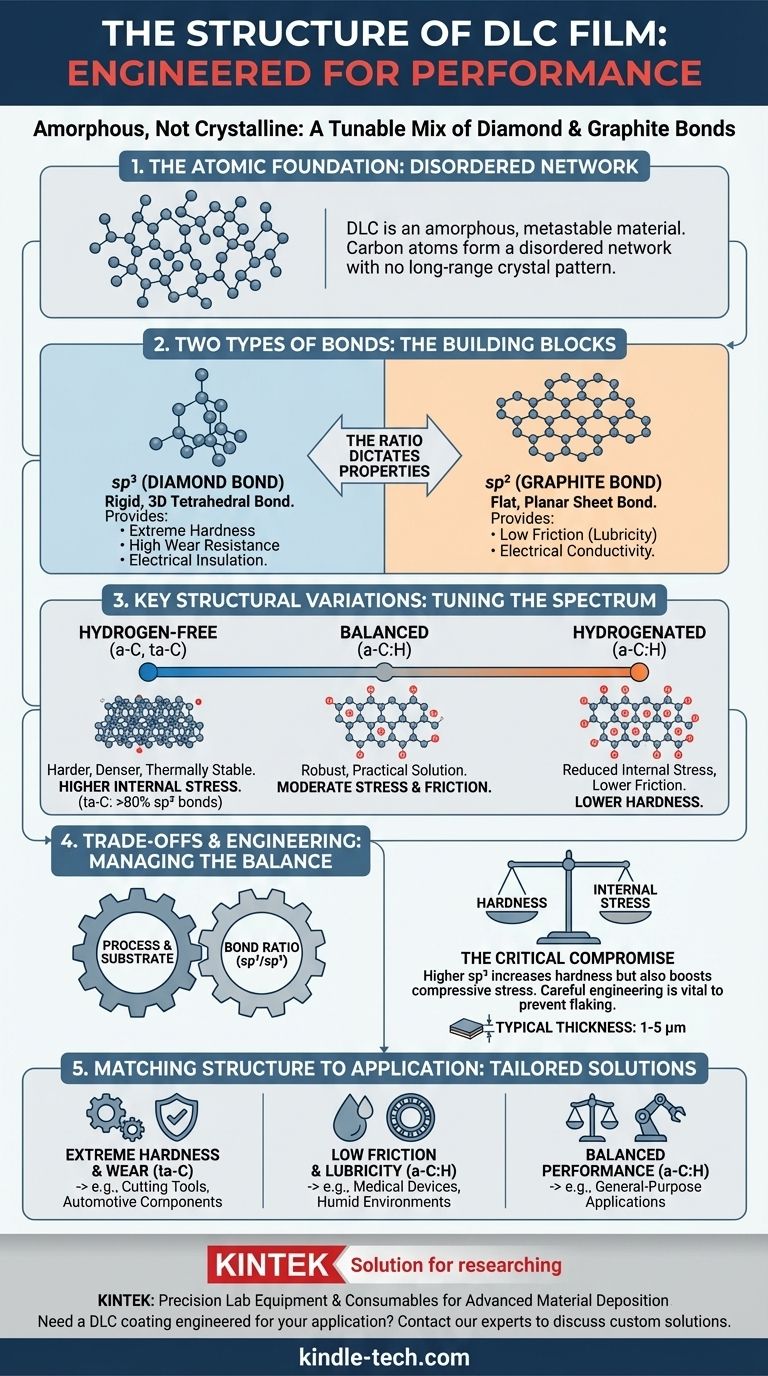
In short, a Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) film does not have a single, uniform crystal structure. Instead, it is an amorphous material, meaning its carbon atoms are arranged in a disordered network. The defining characteristic of this network is a mixture of two different types of atomic bonds: diamond-like (sp³) and graphite-like (sp²). The ratio of these two bonds, along with the potential inclusion of hydrogen, dictates the film's final properties.
The core concept to grasp is that DLC is not one material, but a tunable category of coatings. Its value comes from its amorphous, metastable structure—a controlled, disordered mix of hard diamond bonds and slick graphite bonds. This structure is intentionally engineered during deposition to achieve a specific outcome, such as extreme hardness or low friction.
The Atomic Foundation: sp² vs. sp³ Hybridization
To understand DLC, you must first understand the two fundamental ways carbon atoms can bond to each other. The interplay between these two bonding states within a single film is what gives DLC its unique identity.
The Diamond Bond (sp³)
The sp³ bond is the same three-dimensional tetrahedral bond found in natural diamond. Each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbon atoms.
This rigid, strong structure is responsible for the "diamond-like" properties of DLC:
- Extreme hardness
- High wear resistance
- Electrical insulation
The Graphite Bond (sp²)
The sp² bond is the two-dimensional planar bond found in graphite. Each carbon atom is bonded to three other atoms in flat, hexagonal sheets.
These sheets can slide easily over one another, imparting the "graphite-like" properties to the film:
- Low friction (lubricity)
- Electrical conductivity
A Disordered, Amorphous Network
Crucially, DLC is not a crystalline material like diamond or graphite. It has no long-range repeating pattern.
Instead, it is a random, jumbled network of sp² and sp³ bonded atoms. Think of it as a wall built from two different types of bricks (sp³ and sp²) mixed together randomly, creating a dense, solid, but non-uniform structure.
Key Structural Variations in DLC Films
The term "DLC" actually covers a family of coatings. The specific structure can be modified significantly during the manufacturing process to prioritize certain characteristics.
Hydrogenated vs. Hydrogen-Free (a-C:H vs. a-C)
One of the most common variations involves the incorporation of hydrogen.
Hydrogenated (a-C:H) films are produced in processes that use hydrocarbon gases. The hydrogen atoms terminate "dangling bonds" within the carbon network, which can reduce internal stress and significantly lower the coefficient of friction.
Hydrogen-Free (a-C) films are harder, denser, and often more thermally stable but can exhibit higher internal stress.
Tetrahedral Amorphous Carbon (ta-C)
This is a special, hydrogen-free sub-category of DLC that has a very high percentage of sp³ diamond bonds—often exceeding 80%.
This structure makes ta-C the hardest, stiffest, and most diamond-like form of DLC. Achieving this high sp³ fraction requires specialized deposition processes, like filtered cathodic vacuum arc (FCVA), that can deliver high-energy carbon ions to the surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The structure of a DLC film is a carefully engineered compromise. Optimizing for one property often means sacrificing another.
Hardness vs. Internal Stress
The most significant trade-off is between hardness and stress. As the percentage of sp³ bonds increases, the film becomes much harder, but the internal compressive stress also builds dramatically.
If this internal stress becomes too high, it can exceed the adhesion strength of the film, causing it to flake off or delaminate from the part it is coating.
The Influence of Process and Substrate
This is where factors like the substrate (the part being coated) and process parameters become critical. The energy of the deposition process directly controls the sp³/sp² ratio.
A well-prepared substrate with appropriate intermediate layers is essential for managing internal stress and ensuring the film adheres properly. This is why a DLC coating process that works for one material may fail on another—the entire system must be engineered to handle the stresses of the desired film structure.
Thickness Limitations
Due to this high internal stress, most DLC films are extremely thin, typically ranging from 1 to 5 micrometers. Attempting to deposit a thicker film often results in catastrophic stress failure.
Matching Structure to Application
The ideal DLC structure is determined entirely by the desired performance outcome. There is no single "best" type of DLC.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and wear resistance: You need a structure with the highest possible sp³ content, such as a hydrogen-free tetrahedral amorphous carbon (ta-C) film.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible friction, especially in humid environments: A hydrogenated amorphous carbon (a-C:H) film with a higher sp² content is typically the best choice.
- If your primary focus is balancing performance with manufacturability: A standard a-C:H film with a moderate sp³ content often provides the most robust and practical solution for general-purpose applications.
Understanding that DLC is a spectrum of engineered structures, not a single substance, is the key to leveraging its remarkable capabilities for your specific engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Structural Feature | Description | Key Property Influence |
|---|---|---|
| Amorphous Network | Disordered, non-crystalline arrangement of carbon atoms. | Enables a tunable blend of properties. |
| sp³ (Diamond) Bonds | Strong, tetrahedral bonds. | Provides extreme hardness and wear resistance. |
| sp² (Graphite) Bonds | Planar, sheet-like bonds. | Imparts low friction and lubricity. |
| Hydrogen Content (a-C:H) | Hydrogen atoms incorporated into the carbon network. | Reduces internal stress and friction. |
| High sp³ Content (ta-C) | A hydrogen-free DLC with >80% diamond bonds. | Maximizes hardness and stiffness. |
Need a DLC coating engineered for your specific application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision lab equipment and consumables for advanced material deposition. Our expertise in DLC coating processes allows us to help you tailor the sp³/sp² bond ratio to achieve the perfect balance of hardness, low friction, and adhesion for your components—whether for cutting tools, automotive parts, or medical devices.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your product's performance and durability with a custom DLC solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- What is diamond coating film? A Thin Layer of Diamond for Extreme Performance
- How thick is CVD diamond coating? Balancing Durability and Stress for Optimal Performance
- How are tools coated with diamond? Achieve Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Tools







