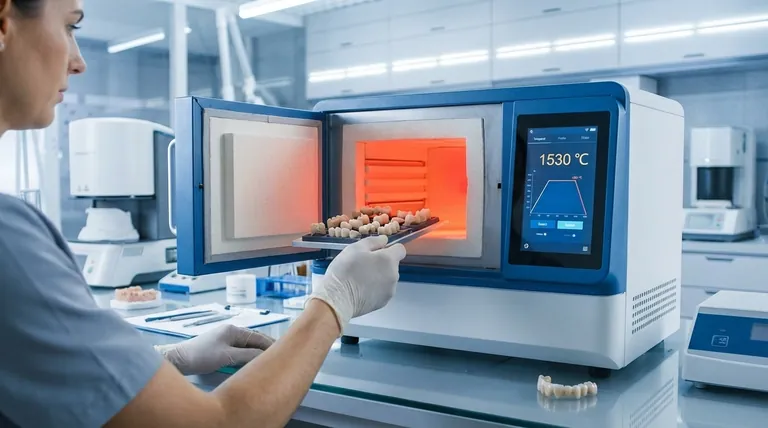
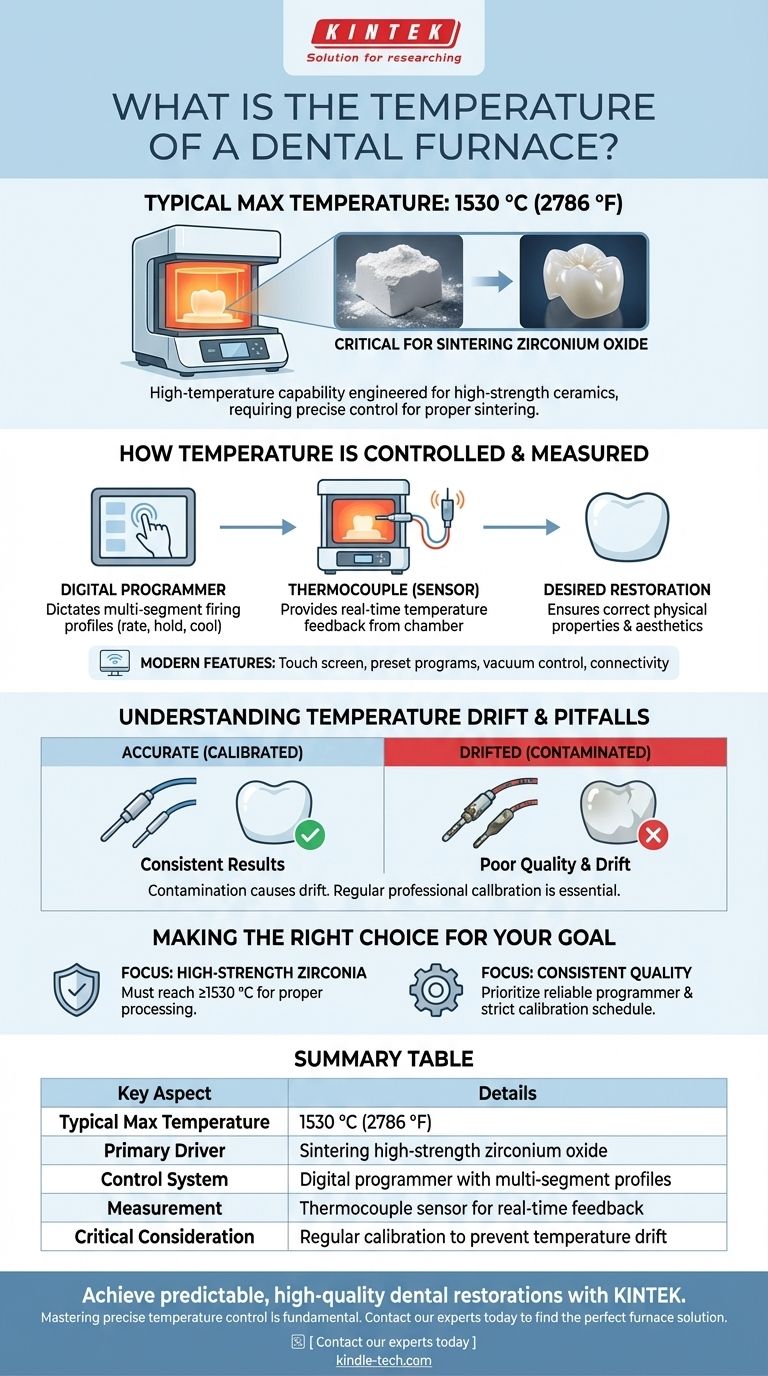
A modern dental furnace can typically reach a maximum temperature of 1530 °C (2786 °F). This high-temperature capability is specifically engineered to process the majority of commercially available dental materials, most notably high-strength ceramics like zirconium oxide, which require such heat for proper sintering.
The specific temperature of a dental furnace is not a single value but a precisely controlled profile over time. The maximum temperature capability is driven by the demands of advanced materials, while its accuracy depends on careful measurement and consistent maintenance.

How Temperature is Controlled and Measured
Achieving the correct temperature is not a simple matter of heating an element. It involves a sophisticated system of control and feedback to ensure the final dental restoration has the desired physical properties and aesthetics.
The Role of the Programmer
Modern dental furnaces are governed by a digital programmer. This controller allows technicians to run specific firing programs, often with multiple segments, that dictate the rate of temperature increase, the holding time at specific temperatures, and the cooling rate.
Precision Measurement
To maintain accuracy, the furnace relies on a thermocouple, which is a sensor typically placed in the upper part of the firing chamber near the ceramic object. This provides real-time temperature feedback to the controller. Some advanced systems may also use thermal imaging to measure the temperature directly on the restoration itself.
Integration and Modern Features
Contemporary furnaces often feature touch screen controls with preset programs for common materials. They also manage the vacuum level within the chamber and may offer internet connectivity for program updates and remote diagnostics.
Why 1530 °C is a Critical Benchmark
The maximum temperature is not an arbitrary number; it is dictated by the materials used in modern dentistry.
Sintering Zirconium Oxide
The primary driver for high-temperature furnaces is the sintering of zirconium oxide (zirconia). This process transforms the milled, chalk-like zirconia into a dense, strong, and translucent final restoration. Reaching temperatures up to 1530 °C is essential for this transformation to occur correctly.
Versatility for Other Materials
While zirconia sets the upper limit, the furnace's ability to precisely control temperatures at lower levels makes it versatile. It can process a wide range of other materials, including various ceramics, alloys, and soldering materials, each with its own unique firing schedule.
Understanding the Key Pitfall: Temperature Drift
The most significant challenge in furnace operation is maintaining its initial accuracy over time. A furnace that is not firing at the correct temperature will produce poor-quality restorations.
The Impact of Contamination
Over time, the furnace's internal environment changes. Soiling and chemical deposits from the materials being fired—such as ceramics and alloys—can accumulate within the chamber and on the thermocouple.
The Need for Regular Calibration
These deposits and other physical influences cause the furnace's temperature control to drift from its factory settings. What the display reads may no longer be the true temperature inside the chamber, making regular calibration essential to ensure consistent and predictable results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the role of temperature allows you to evaluate equipment and processes based on your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is high-strength zirconia: A furnace with a verified maximum temperature of at least 1530 °C is non-negotiable for proper material processing.
- If your primary focus is consistent, high-quality results: Prioritize a furnace with a reliable programmer and commit to a strict schedule of cleaning and professional calibration to counteract temperature drift.
Ultimately, mastering temperature control is fundamental to achieving predictable excellence in dental fabrication.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Typical Max Temperature | 1530 °C (2786 °F) |
| Primary Driver | Sintering high-strength zirconium oxide |
| Control System | Digital programmer with multi-segment firing profiles |
| Measurement | Thermocouple sensor for real-time feedback |
| Critical Consideration | Regular calibration to prevent temperature drift |
Achieve predictable, high-quality dental restorations with KINTEK.
Mastering precise temperature control is the foundation of excellent dental fabrication. Whether your primary focus is high-strength zirconia sintering or consistent results with other ceramics, the right equipment and support are crucial.
KINTEK specializes in reliable lab equipment and consumables for dental laboratories. We provide the durable, high-performance dental furnaces and expert guidance you need to ensure your furnace operates at peak accuracy, batch after batch.
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and find the perfect furnace solution for your goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?
- What is the primary advantage of using a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature and Atmosphere Control
- What is the function of alumina tubes and alumina wool in a pyrolysis furnace? Optimize Your Biochar Production Quality
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning













