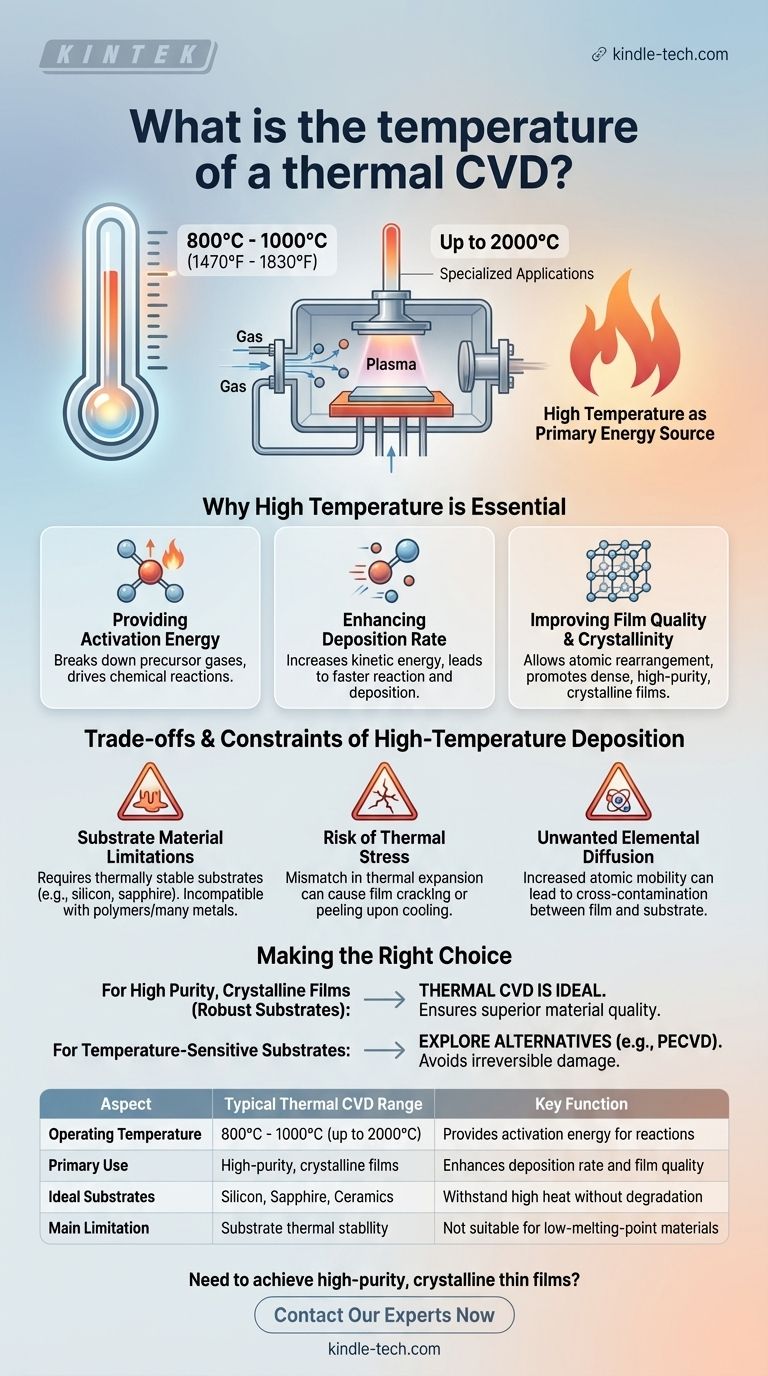
In a typical thermal Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process, operating temperatures are high, generally falling within the range of 800°C to 1000°C (1470°F to 1830°F). For more demanding or specialized applications, this range can extend significantly higher, sometimes reaching up to 2000°C.
The core principle of thermal CVD is its direct use of high temperature as the primary energy source. This heat is required to break down the precursor gases and drive the chemical reactions that form a solid, high-quality film on a substrate's surface.

Why Thermal CVD Relies on High Temperatures
The high-temperature environment is not an incidental detail; it is the fundamental mechanism that enables the entire process. It serves several critical functions that dictate the quality and characteristics of the final coating.
Providing Activation Energy
Every chemical reaction requires a minimum amount of energy to get started, known as activation energy. In thermal CVD, the intense heat provides this energy, allowing stable precursor gases to decompose and react near the substrate surface to form the desired solid material.
Enhancing Deposition Rate
Higher temperatures increase the kinetic energy of the gas molecules, leading to more frequent and energetic collisions. This directly accelerates the rate of the chemical reactions, resulting in a faster and more efficient deposition of the thin film.
Improving Film Quality and Crystallinity
Heat allows atoms on the surface to arrange themselves into a more ordered, stable, and crystalline structure. This thermal energy promotes the formation of dense, high-purity films with superior material properties, which is often impossible to achieve at lower temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs of High-Temperature Deposition
While essential for the process, the reliance on extreme heat introduces significant constraints and potential problems that must be carefully managed.
Substrate Material Limitations
The most significant drawback is the requirement for a thermally stable substrate. Materials that melt, warp, or degrade at high temperatures—such as polymers, many common metals, or complex integrated circuits—are incompatible with standard thermal CVD.
Risk of Thermal Stress
A large mismatch in the coefficient of thermal expansion between the substrate and the deposited film can cause significant problems. As the system cools down after deposition, this mismatch can introduce high levels of stress, leading to film cracking, peeling, or a warped substrate.
Unwanted Elemental Diffusion
At elevated temperatures, atoms become more mobile. This can lead to undesirable diffusion of elements from the substrate into the growing film, or vice versa. This cross-contamination can compromise the purity and performance of both the film and the substrate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition method requires balancing the need for film quality against the limitations of your substrate and application.
- If your primary focus is creating highly pure, dense, crystalline films on a robust substrate (like silicon, sapphire, or ceramics): Thermal CVD is often the ideal choice, as the high temperature ensures superior material quality that other methods struggle to match.
- If you are working with temperature-sensitive substrates or need to avoid thermal stress: You must explore alternative, lower-temperature deposition techniques, such as Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD), as conventional thermal CVD will likely cause irreversible damage.
Ultimately, understanding the role of temperature is the key to leveraging the power of CVD for your specific material and application.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Typical Thermal CVD Range | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | 800°C - 1000°C (up to 2000°C) | Provides activation energy for reactions |
| Primary Use | High-purity, crystalline films | Enhances deposition rate and film quality |
| Ideal Substrates | Silicon, Sapphire, Ceramics | Withstand high heat without degradation |
| Main Limitation | Substrate thermal stability | Not suitable for low-melting-point materials |
Need to achieve high-purity, crystalline thin films on robust substrates? The precise high-temperature control of a thermal CVD system is critical for your success. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment, including CVD systems, tailored to your specific research and production goals. Our experts can help you select the right furnace to ensure optimal film quality and deposition efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What function does CVD equipment serve in rhodium-modified coatings? Achieve Deep Diffusion and Microstructural Precision



















