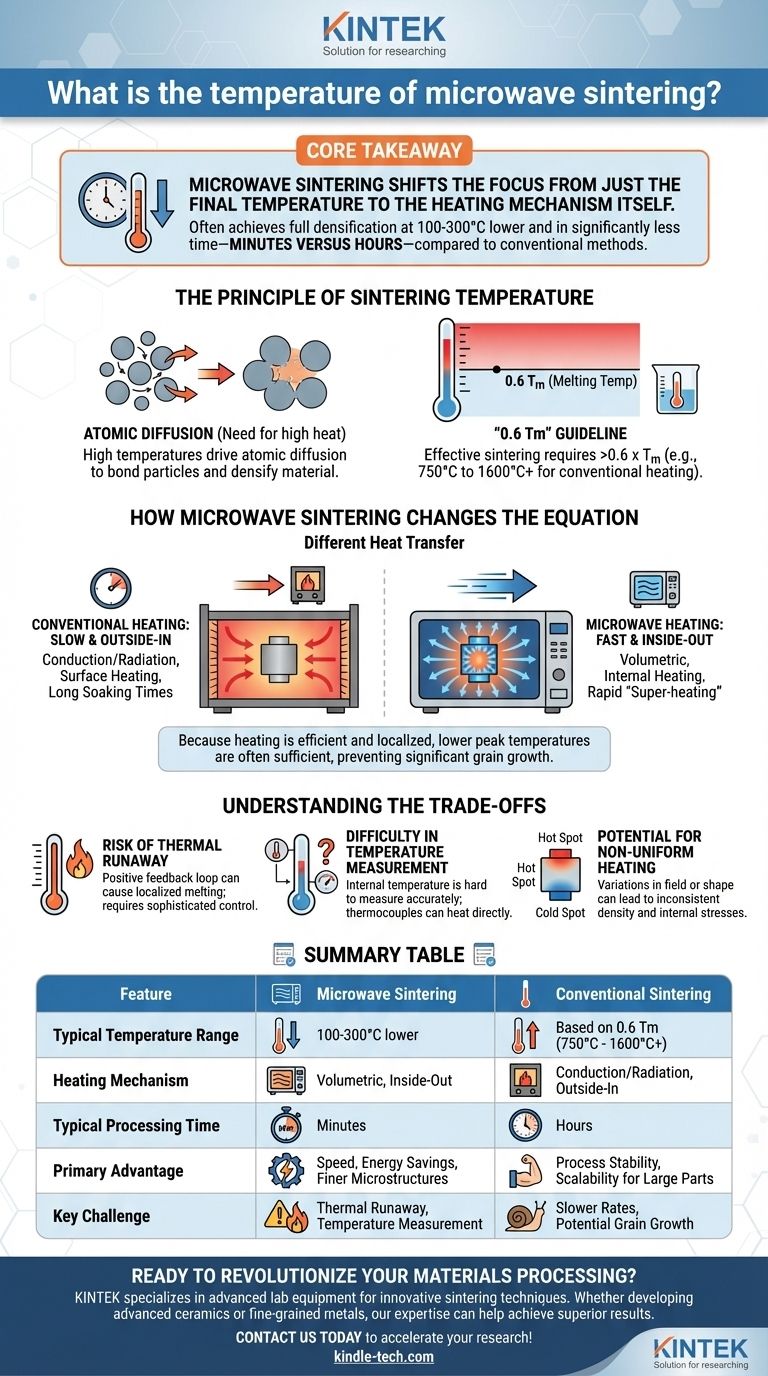
The temperature for microwave sintering is not a single value; it is entirely dependent on the specific material being processed. However, a primary advantage of the microwave technique is that it often achieves full densification at temperatures 100-300°C lower and in significantly less time—minutes versus hours—compared to conventional sintering methods for the same material.
The core takeaway is that microwave sintering shifts the focus from just the final temperature to the heating mechanism itself. By generating heat directly within the material, it accelerates the process and can reduce the required peak temperature, offering significant energy and time savings.

The Principle of Sintering Temperature
To understand the role of temperature in microwave sintering, we must first understand why high temperatures are required for any sintering process.
The Need for Atomic Diffusion
Sintering is the process of compacting a powder into a solid mass using heat. The driving force is the reduction of surface energy.
High temperatures are critical because they give atoms the energy they need to move, or diffuse. This atomic movement allows individual powder particles to bond, eliminating the pores between them and causing the material to densify.
The "0.6 Tm" Guideline
As a general rule, effective sintering requires a temperature greater than approximately 0.6 times the material's absolute melting temperature (Tm).
For many industrial metals and ceramics, this places the required temperature in a range of 750°C to over 1600°C for conventional furnace heating, depending on the alloy and desired properties.
How Microwave Sintering Changes the Equation
The key difference between microwave and conventional sintering is not the final temperature, but how the material reaches that temperature. This fundamental difference in heat transfer is what allows for lower temperatures and faster processing.
Conventional Heating: Slow and From the Outside-In
A conventional furnace heats a part through conduction, convection, and radiation. The heat is applied to the surface of the component and must slowly travel toward the core.
This process is inefficient and requires long "soaking" times at high temperatures to ensure the entire part is uniformly heated and densified.
Microwave Heating: Fast and From the Inside-Out
Microwave sintering generates heat volumetrically. The microwaves penetrate the material and directly excite its molecules, causing it to heat from within.
This internal heating is much more rapid and efficient. Because the heat doesn't need to creep in from the surface, the part can reach the necessary sintering temperature in a fraction of the time. This rapid heating rate is often called "super-heating."
The Impact on Temperature
Because the heating is so efficient and localized where it's needed (at the atomic level), the overall process can often be completed at a lower peak temperature. The material densifies quickly before significant grain growth—a common side effect of long exposure to high heat—can occur.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, microwave sintering introduces unique challenges that are not as prevalent in conventional methods.
The Risk of Thermal Runaway
A material's ability to absorb microwave energy often increases with temperature. This can create a positive feedback loop where the hotter the material gets, the faster it heats, leading to a thermal runaway that can cause localized melting or damage. This requires highly sophisticated temperature control.
Difficulty in Temperature Measurement
Measuring the true internal temperature of a material during microwave heating is notoriously difficult. Thermocouples can be heated directly by the microwaves, giving false readings, while infrared pyrometers only measure the surface temperature, which may be significantly cooler than the core.
Potential for Non-Uniform Heating
Although microwave heating is volumetric, it is not always perfectly uniform. Variations in the microwave field or the shape of the component can create "hot spots" and "cold spots," leading to inconsistent density and internal stresses within the final part.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a sintering method depends entirely on your material and project objectives.
- If your primary focus is speed and energy savings: Microwave sintering is an excellent choice for materials with good dielectric properties, as it can drastically cut processing time from hours to minutes.
- If you are developing advanced or fine-grained materials: The lower temperatures and shorter times of microwave sintering can help achieve high density while preventing unwanted grain growth.
- If your primary focus is process stability and scalability for large parts: Conventional sintering is a more mature and predictable technology that generally provides more uniform heating for large or geometrically complex components.
- If you are working with metallic powders that reflect microwaves: A hybrid heating approach (microwave-assisted conventional sintering) or a purely conventional process is necessary.
Ultimately, understanding the principles of heat transfer is key to choosing the sintering process that best serves your material and your goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Microwave Sintering | Conventional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Temperature Range | 100-300°C lower than conventional | Based on 0.6 Tm (e.g., 750°C to 1600°C+) |
| Heating Mechanism | Volumetric, from the inside-out | Conduction/Radiation, from the outside-in |
| Typical Processing Time | Minutes | Hours |
| Primary Advantage | Speed, energy savings, finer microstructures | Process stability, scalability for large parts |
| Key Challenge | Risk of thermal runaway; temperature measurement | Slower heating rates; potential for grain growth |
Ready to revolutionize your materials processing with faster, more efficient sintering?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including solutions for innovative sintering techniques. Whether you are developing advanced ceramics, fine-grained metals, or seeking significant energy and time savings, our expertise can help you achieve superior results.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs and accelerate your research. Get in touch via our contact form to speak with an expert!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the most important factor influencing the strength of the brazed joint? Master Joint Clearance for Maximum Strength
- What are the advantages of brazing compared to welding? Achieve Clean, Low-Distortion Metal Joining
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- How is the greatest joint strength obtained in brazing? Master the 3 Keys to Superior Metallurgical Bonds
- Does brazing require heat? Yes, it's the catalyst for creating strong, permanent bonds.



















