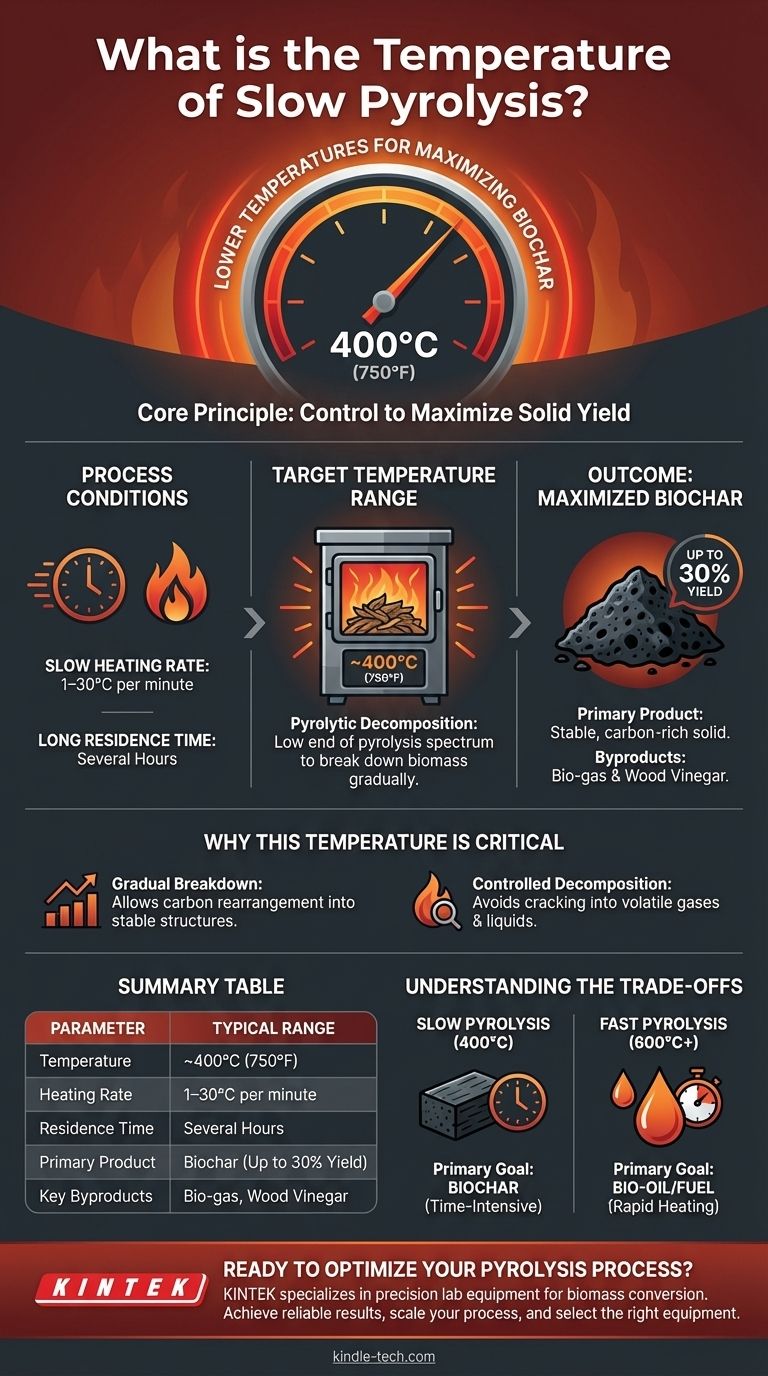
In short, slow pyrolysis operates at lower temperatures, typically around 400°C (approximately 750°F). This specific temperature, combined with a slow heating rate, is deliberately chosen to maximize the production of solid biochar from biomass.
The core principle of slow pyrolysis is control. By using a lower temperature (~400°C) and extending the process over several hours, it prioritizes the conversion of feedstock into a stable, carbon-rich solid (biochar) rather than liquid or gas products.

The Role of Temperature in Slow Pyrolysis
To understand slow pyrolysis, you must see temperature not as an isolated number, but as a critical lever that dictates the final outcome. It works in concert with the heating rate and duration to fundamentally change the chemical decomposition of the material.
Defining the Process Conditions
Slow pyrolysis is a thermal decomposition process conducted in an oxygen-free or oxygen-limited environment. The defining characteristics are a slow heating rate (typically 1–30°C per minute) and a long residence time, often lasting several hours.
The Target Temperature Range
The pyrolytic decomposition occurs at approximately 400°C. This places it at the low end of the overall pyrolysis spectrum, which can range up to 900°C for other methods like fast pyrolysis. This lower heat input is a deliberate choice.
Why This Temperature is Critical
At around 400°C, the organic materials in the feedstock, such as wood, break down gradually. This controlled decomposition allows carbon atoms to rearrange into stable, aromatic structures, forming biochar. Higher temperatures would cause these structures to crack further into volatile gases and liquids.
How Process Conditions Dictate the Outcome
The goal of slow pyrolysis is fundamentally different from other pyrolysis methods. The objective is not energy in the form of gas or liquid fuel, but rather a solid material with specific properties.
The Primary Product: Biochar
The main output of slow pyrolysis is a solid char, also known as biochar or biocoal. Yields of this solid product can be as high as 30% of the initial dry feedstock weight.
The Byproducts
While biochar is the primary goal, the process also creates two major byproducts. The first is a combustible bio-gas, which can be captured and burned to provide the energy needed to sustain the pyrolysis process. The second is an aqueous liquid often called wood vinegar.
Maximizing Solid Yield
The combination of low temperature and long duration is what maximizes the biochar yield. It gives the feedstock time to decompose completely without aggressively vaporizing the valuable carbon into the gas and liquid phases.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing slow pyrolysis involves accepting a clear set of compromises. The process is optimized for one specific output at the expense of others.
Time vs. Product
The most significant trade-off is speed. Slow pyrolysis is, by definition, a time-intensive process that takes hours to complete. This is a direct contrast to fast pyrolysis, which occurs in seconds.
Biochar vs. Bio-oil
This process is designed to maximize biochar. Consequently, it minimizes the yield of bio-oil (the primary target of fast pyrolysis) and volatile gases. If your goal is liquid fuel, this is the wrong method.
Feedstock Dependency
The final properties of the biochar and other products are highly dependent on the initial feedstock and precise process conditions. This variability can make it challenging to produce a perfectly consistent product without strict controls.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal temperature and process depend entirely on your desired end product. Pyrolysis is not a single method but a range of techniques tailored to different outcomes.
- If your primary focus is maximizing high-quality biochar: Slow pyrolysis at a lower temperature of around 400°C is the correct approach.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid bio-oil or fuel gas: A different method, such as fast pyrolysis, which uses much higher temperatures (often over 600°C) and rapid heating, would be necessary.
Ultimately, selecting the right temperature is about defining your goal and choosing the thermal process that reliably achieves it.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Typical Range for Slow Pyrolysis |
|---|---|
| Temperature | ~400°C (750°F) |
| Heating Rate | 1–30°C per minute |
| Residence Time | Several hours |
| Primary Product | Biochar (up to 30% yield) |
| Key Byproducts | Bio-gas, Wood Vinegar |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process for maximum biochar yield?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision lab equipment for biomass conversion and thermal processing. Whether you're developing a new pyrolysis method or scaling up production, our reactors and control systems are designed to deliver the precise temperature control and process consistency you need.
We help you:
- Achieve reliable, repeatable results with precise temperature management.
- Scale your process from lab research to pilot production.
- Select the right equipment for your specific feedstock and product goals.
Let's discuss your project. Contact our experts today to find the perfect pyrolysis solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a rotary heat type furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Uniform Heating & Mixing
- How do tube furnaces or muffle furnaces ensure stoichiometric accuracy during synthesis? Mastering Li4GeO4 & Li4VO4
- At what temperature does wood pyrolysis begin? Control the Process for Biochar, Bio-Oil, or Syngas
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process
- What is the process of zirconium production? From Ore to High-Performance Metal & Ceramic



















