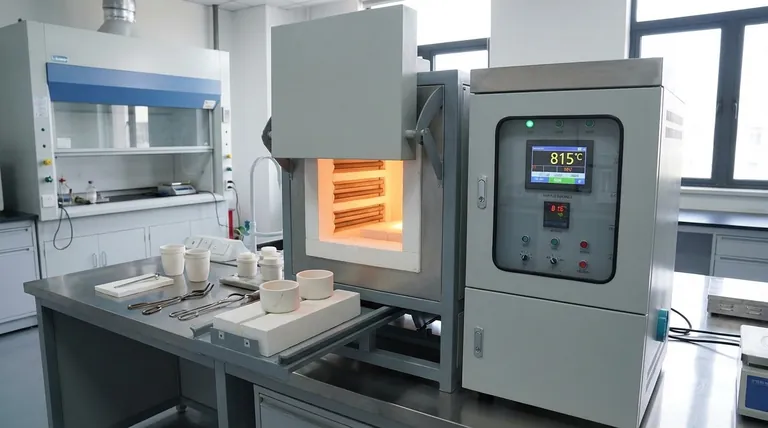
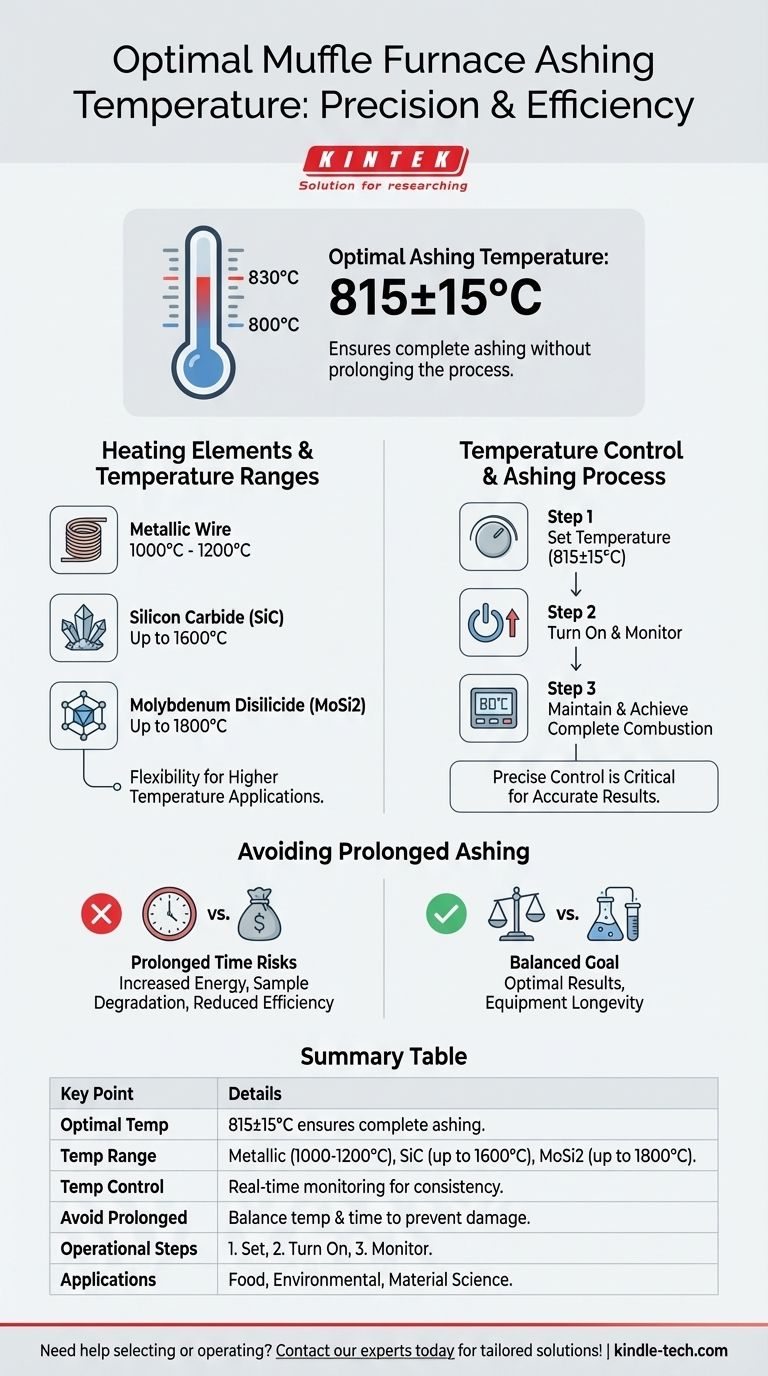
The temperature for ashing in a muffle furnace is typically set to 815±15°C, as this range ensures complete ashing of the sample without unnecessarily prolonging the process. Muffle furnaces are designed to handle a wide range of temperatures, depending on the heating elements used, with common models capable of reaching 1000°C to 1800°C. Proper operation involves setting the desired temperature, monitoring the real-time temperature display, and ensuring the furnace reaches and maintains the required temperature for effective ashing.

Key Points Explained:
-
Optimal Ashing Temperature:
- The standard temperature for ashing in a muffle furnace is 815±15°C. This range is chosen to ensure the sample is fully ashed while avoiding excessive time exposure, which could lead to unnecessary energy consumption or potential damage to the sample or furnace.
-
Temperature Range of Muffle Furnaces:
- Muffle furnaces are available with varying maximum temperatures, depending on the heating elements used:
- Metallic wire heating elements: Typically allow temperatures up to 1000°C to 1200°C.
- Silicon carbide heating elements: Can achieve temperatures up to 1600°C.
- Molybdenum disilicide heating elements: Can reach temperatures up to 1800°C.
- These options provide flexibility for applications requiring higher temperatures beyond standard ashing.
- Muffle furnaces are available with varying maximum temperatures, depending on the heating elements used:
-
Importance of Temperature Control:
- Precise temperature control is critical for effective ashing. The furnace must reach and maintain the target temperature (815±15°C) to ensure complete combustion of organic materials in the sample.
- Modern muffle furnaces feature control panels that display real-time temperature, input current, voltage, and output power, allowing users to monitor and adjust the process as needed.
-
Avoiding Prolonged Ashing Time:
- While the temperature is crucial, the duration of ashing should also be carefully managed. Prolonged ashing times can lead to:
- Increased energy consumption.
- Potential degradation of the sample or furnace components.
- Reduced efficiency in laboratory workflows.
- The goal is to balance temperature and time to achieve complete ashing without unnecessary delays.
- While the temperature is crucial, the duration of ashing should also be carefully managed. Prolonged ashing times can lead to:
-
Operational Steps for Ashing:
- Set the temperature: Adjust the furnace to the required working temperature (815±15°C).
- Turn on the power: Activate the furnace and monitor the control panel for real-time temperature updates.
- Monitor the process: Ensure the furnace reaches and maintains the target temperature, indicating proper operation.
-
Applications and Considerations:
- Ashing is commonly used in industries such as food testing, environmental analysis, and material science to determine the inorganic residue content of samples.
- Selecting the appropriate furnace with the right temperature range and heating elements is essential for achieving accurate and consistent results.
By understanding these key points, users can effectively operate a muffle furnace for ashing, ensuring optimal results while maintaining equipment longevity and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Optimal Ashing Temperature | 815±15°C ensures complete ashing without unnecessary energy consumption. |
| Temperature Range | - Metallic wire: 1000–1200°C - Silicon carbide: up to 1600°C - Molybdenum disilicide: up to 1800°C |
| Temperature Control | Real-time monitoring ensures precise ashing for consistent results. |
| Avoid Prolonged Ashing | Balance temperature and time to prevent sample or furnace damage. |
| Operational Steps | 1. Set temperature 2. Turn on power 3. Monitor real-time temperature. |
| Applications | Food testing, environmental analysis, material science. |
Need help selecting or operating a muffle furnace? Contact our experts today for tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the use of muffle oven in laboratory? For Clean, High-Temperature Material Processing
- What is the muffle furnace method? A Guide to Clean, High-Temperature Processing
- What is a muffle furnace test? Achieve Precise, Contamination-Free Heating for Your Lab
- What is the principle of muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Precise High-Temperature Heating
- How do you adjust the temperature on a muffle furnace? Master Precise Control for Your Lab



















