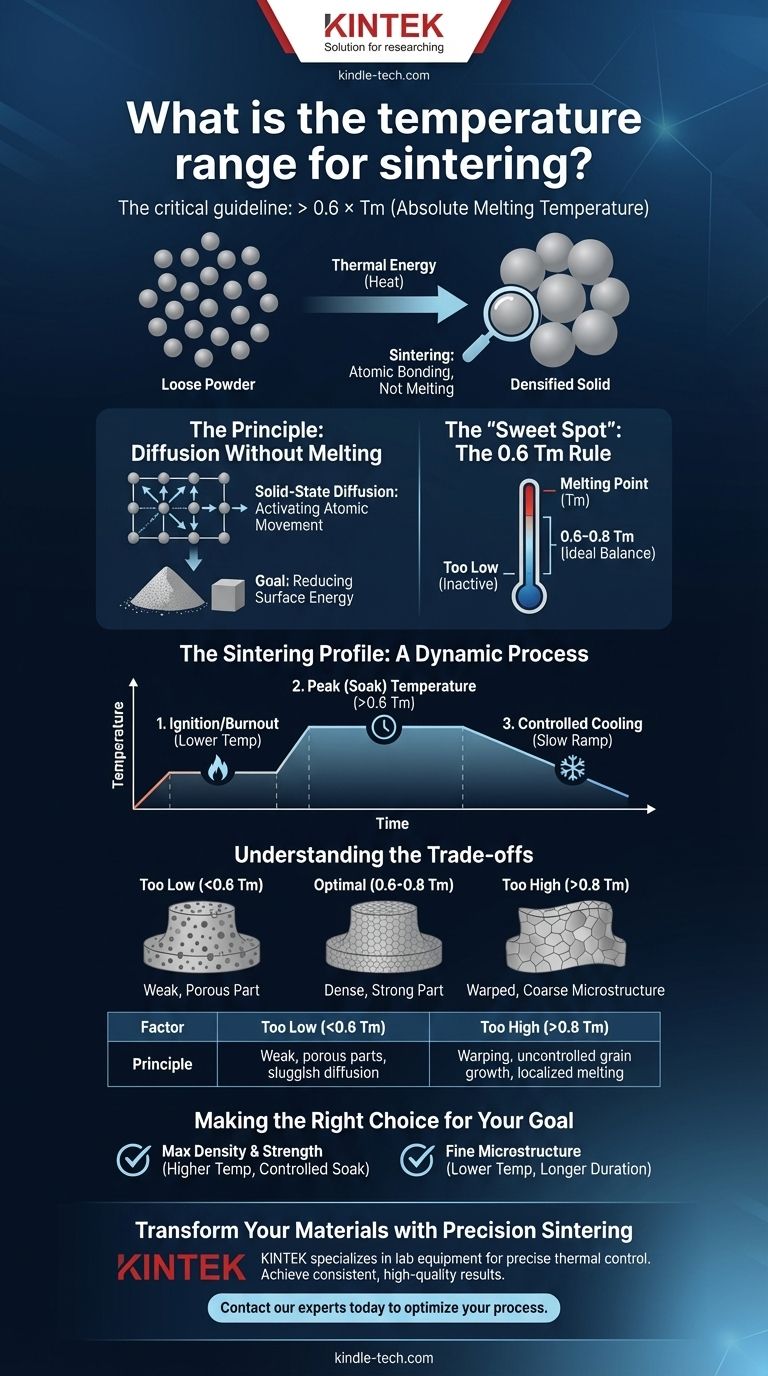
In materials science, there is no single temperature range for sintering, as it is entirely dependent on the specific material being processed. The critical guideline is that sintering occurs at a temperature greater than approximately 0.6 times the absolute melting temperature (Tm) of the material. This ensures the atoms are mobile enough to bond without the material turning into a liquid.
Sintering is not about melting. It is a thermal process that uses carefully controlled high temperatures to force solid particles to bond together, increasing density and strength by reducing the empty space between them. The correct temperature is the one that activates this atomic movement efficiently without causing deformation or liquefaction.
The Principle: Diffusion Without Melting
Sintering works by providing enough thermal energy to make atoms mobile. This allows them to move across the boundaries of individual powder particles, effectively welding them together on a microscopic scale.
Activating Atomic Movement
Heat gives the atoms within the material's crystal lattice the energy they need to "jump" from one position to another. This process, known as solid-state diffusion, is the fundamental mechanism behind sintering. Without sufficient heat, atoms remain locked in place, and no bonding occurs.
The Goal: Reducing Surface Energy
A pile of fine powder has an enormous amount of surface area. All systems in nature, including this powder compact, seek a lower energy state. By bonding together and reducing the gaps between them, the particles dramatically decrease their total surface area, achieving a more stable, lower-energy configuration as a dense solid.
The "Sweet Spot": The 0.6 Tm Rule
The rule of thumb to use a temperature of at least 0.6 Tm (often ranging up to 0.8 Tm) represents the ideal balance. It is hot enough to enable rapid atomic diffusion but remains safely below the melting point, ensuring the component holds its shape while it densifies.
Beyond a Single Temperature: The Sintering Profile
In industrial and laboratory settings, sintering is not a single, static temperature. It is a dynamic thermal profile with several key control points to ensure a high-quality final product.
Ignition or Burnout Temperature
In many processes, the initial heating phase serves to burn off binders, lubricants, or other organic additives mixed with the powder. This must be done slowly and at a lower temperature to prevent defects in the final part. For some materials, like ore, this is the "ignition temperature" that starts the process.
Peak (Soak) Temperature
This is the main sintering temperature—the ">0.6 Tm" phase—where the component is held for a specific duration. During this "soaking" period, the majority of the diffusion, bonding, and densification takes place. The exact temperature and time determine the final density of the part.
Controlled Cooling
The rate of cooling is just as critical as the heating. Cooling too quickly can induce thermal shock, causing cracks and internal stresses. A controlled cooling ramp helps ensure the final part is stable and strong. This is why factors like "end temperature" and "exhaust gas temperature" are monitored in continuous industrial furnaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong temperature has direct and significant consequences on the final product. Precision is not optional; it is essential for success.
Sintering Too Low
If the temperature is too low (e.g., below 0.5 Tm), atomic diffusion will be sluggish and incomplete. This results in poor consolidation, leaving a porous and mechanically weak part that fails to meet performance specifications.
Sintering Too High
Exceeding the optimal temperature, even if it's below the full melting point, is dangerous. It can lead to uncontrolled grain growth, where smaller grains are consumed by larger ones, creating a coarse microstructure that is often brittle. In the worst case, you can get localized melting, causing the part to slump, warp, or lose its intended shape entirely.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal sintering temperature is a function of your material and your desired outcome. Use the following principles as your guide.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and strength: You must operate near the upper end of the material's sintering range, carefully controlling the soak time to achieve full consolidation without causing excessive grain growth.
- If your primary focus is preserving a fine-grained microstructure for specific properties (like hardness): A lower soak temperature for a longer duration may be the better strategy, balancing densification with the prevention of grain coarsening.
- If you are working with a new or composite material: Begin with the 0.6-0.8 * Tm rule of thumb for the primary component and conduct systematic experiments to map out the ideal temperature profile for your specific goals.
Mastering the thermal profile is the key to transforming loose powder into a high-performance engineered component.

Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Consideration |
|---|---|
| Fundamental Principle | Sintering occurs at 0.6 to 0.8 Tm (absolute melting temperature). |
| Too Low (<0.6 Tm) | Results in weak, porous parts due to insufficient atomic diffusion. |
| Too High (>0.8 Tm) | Risks part warping, uncontrolled grain growth, or localized melting. |
| Process Goal | Max Strength/Density: Higher temperature. Fine Microstructure: Lower temperature/longer time. |
Transform Your Materials with Precision Sintering
Choosing the correct sintering temperature profile is critical for achieving the desired density, strength, and microstructure in your components. The difference between success and failure often comes down to precise thermal control.
KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables needed to master this process. Our furnaces and expertise help you:
- Precisely control temperature ramps, soak times, and cooling rates.
- Experiment efficiently to determine the ideal sintering profile for new materials.
- Achieve consistent, high-quality results batch after batch.
Ready to optimize your sintering process and create stronger, more reliable parts? Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss your specific material and application goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What is the primary advantage of using a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature and Atmosphere Control
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis



















