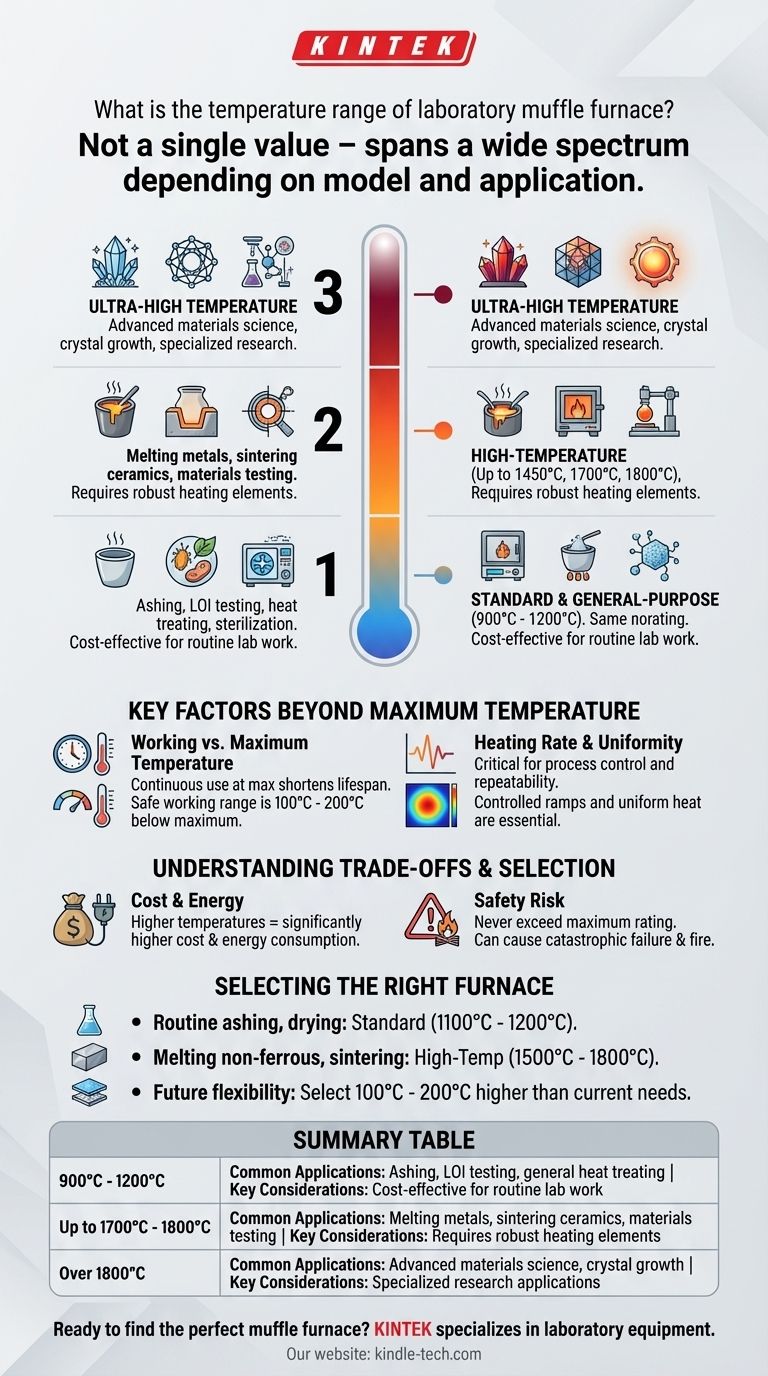
The temperature range of a laboratory muffle furnace is not a single value but spans a wide spectrum depending on the model and its intended application. While common furnaces operate in the 900°C to 1200°C range, more advanced units are widely available that can reach 1700°C, 1800°C, or even higher for specialized research.
The critical factor is not the broad range of all available furnaces, but rather selecting a specific model whose working temperature range safely exceeds the requirements of your intended application, from ashing and heat-treating to melting metals.

Deconstructing the Temperature Ranges
Different muffle furnaces are engineered with specific heating elements and insulation materials, which directly dictate their operational temperature capabilities. They are generally categorized into several tiers.
Standard and General-Purpose Furnaces
Most standard laboratory models are designed for a maximum temperature of 900°C to 1200°C.
These are the workhorses for common applications like loss-on-ignition (LOI) testing, ashing organic samples, general heat treating, and sterilizing equipment.
High-Temperature Furnaces
For more demanding processes, high-temperature models are available that operate reliably up to 1450°C, 1700°C, or 1800°C.
These furnaces use more robust heating elements (like silicon carbide or molybdenum disilicide) and advanced insulation. They are necessary for applications in metallurgy, ceramics research, and testing high-performance materials.
Ultra-High Temperature Models
Specialized research furnaces can push beyond 1800°C, with some models capable of reaching over 2000°C.
These are highly specialized instruments used for advanced materials science, crystal growth, and experimental research where extreme thermal conditions are required.
Key Factors Beyond Maximum Temperature
The maximum temperature is the headline specification, but for professional use, other performance factors are equally important.
Working vs. Maximum Temperature
It's crucial to distinguish between a furnace's maximum temperature and its continuous working temperature. The maximum temperature is often a peak rating that should only be held for short periods.
Consistently operating a furnace at its absolute maximum will significantly shorten the lifespan of its heating elements and insulation. A safe working temperature is typically 100°C to 200°C below the listed maximum.
Heating Rate and Uniformity
The rate at which the furnace reaches its target temperature (ramp rate) and the uniformity of temperature throughout the chamber are critical for process control and repeatability.
Some applications require slow, controlled ramps to prevent thermal shock to the sample, while others demand excellent uniformity to ensure every part of a sample is treated equally.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Choosing the right furnace involves balancing capability with practical constraints.
The Cost of Higher Temperatures
As the maximum operating temperature increases, the cost of the furnace rises significantly. This is due to the more exotic and durable materials required for heating elements, thermocouples, and insulation to withstand extreme heat.
Energy Consumption
Higher temperatures demand exponentially more electrical power to achieve and maintain. A furnace rated for 1800°C will consume far more energy than a 1200°C model, impacting operational costs.
Never Exceed the Maximum Rating
Operating a furnace beyond its maximum rated temperature is a critical safety risk. It can lead to catastrophic failure of the heating elements, damage to the insulation, and potentially create a fire hazard. Always adhere to the manufacturer's specified limits.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Application
Your choice should be dictated by your most demanding current and near-future processes.
- If your primary focus is routine ashing, drying, or basic heat treating: A standard furnace with a maximum temperature between 1100°C and 1200°C is sufficient and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is melting non-ferrous metals, sintering ceramics, or materials testing: You require a high-temperature furnace rated for at least 1500°C to 1800°C.
- If your primary focus is ensuring flexibility for future projects: Select a furnace with a maximum temperature that is 100°C to 200°C higher than your most demanding known application.
Ultimately, matching the furnace's capabilities to your specific material and process requirements is the key to achieving reliable and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Common Applications | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| 900°C - 1200°C | Ashing, LOI testing, general heat treating | Cost-effective for routine lab work |
| Up to 1700°C - 1800°C | Melting metals, sintering ceramics, materials testing | Requires robust heating elements |
| Over 1800°C | Advanced materials science, crystal growth | Specialized research applications |
Ready to find the perfect muffle furnace for your lab's needs? KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables, offering a wide range of muffle furnaces tailored to your specific temperature requirements and applications. Our experts can help you select a model that provides the precise temperature control, uniformity, and durability your research demands. Contact us today for a personalized consultation and enhance your lab's capabilities with the right equipment from KINTEK!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the safety precautions for heat experiment? Essential Steps to Prevent Lab Burns and Accidents
- What is a muffle furnace used in determination of? Precise Ash Content and Material Composition
- What are the precautions for heat in the laboratory? Essential Safety Rules to Prevent Burns and Fires
- What is the main function of the muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Heating Without Contamination
- What precautions should you take while using a muffle furnace? Ensure Safe High-Temperature Processing in Your Lab



















