Thermal evaporation is a Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) technique that uses heat to transform a solid source material into a vapor within a high-vacuum chamber. This vapor then travels and condenses onto a cooler substrate, methodically building a thin, solid film layer by layer. The process is one of the foundational methods for creating high-purity coatings due to its straightforward nature.
At its core, thermal evaporation is a process of controlled phase changes. It leverages high heat and a vacuum environment to convert a solid material directly into a vapor, which then re-solidifies as a highly uniform thin film on a target surface.
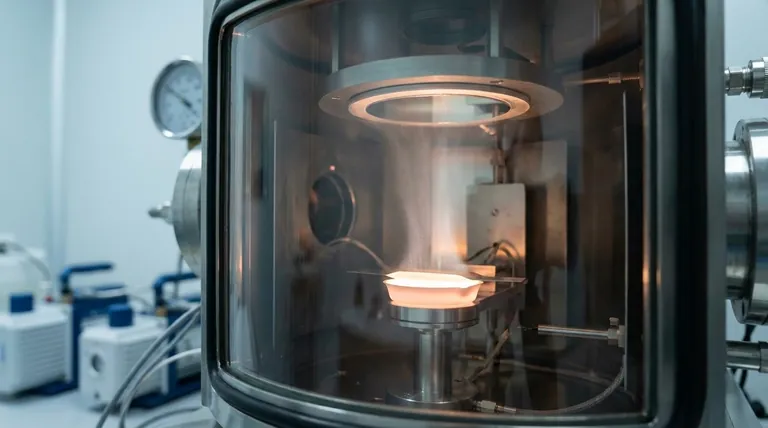

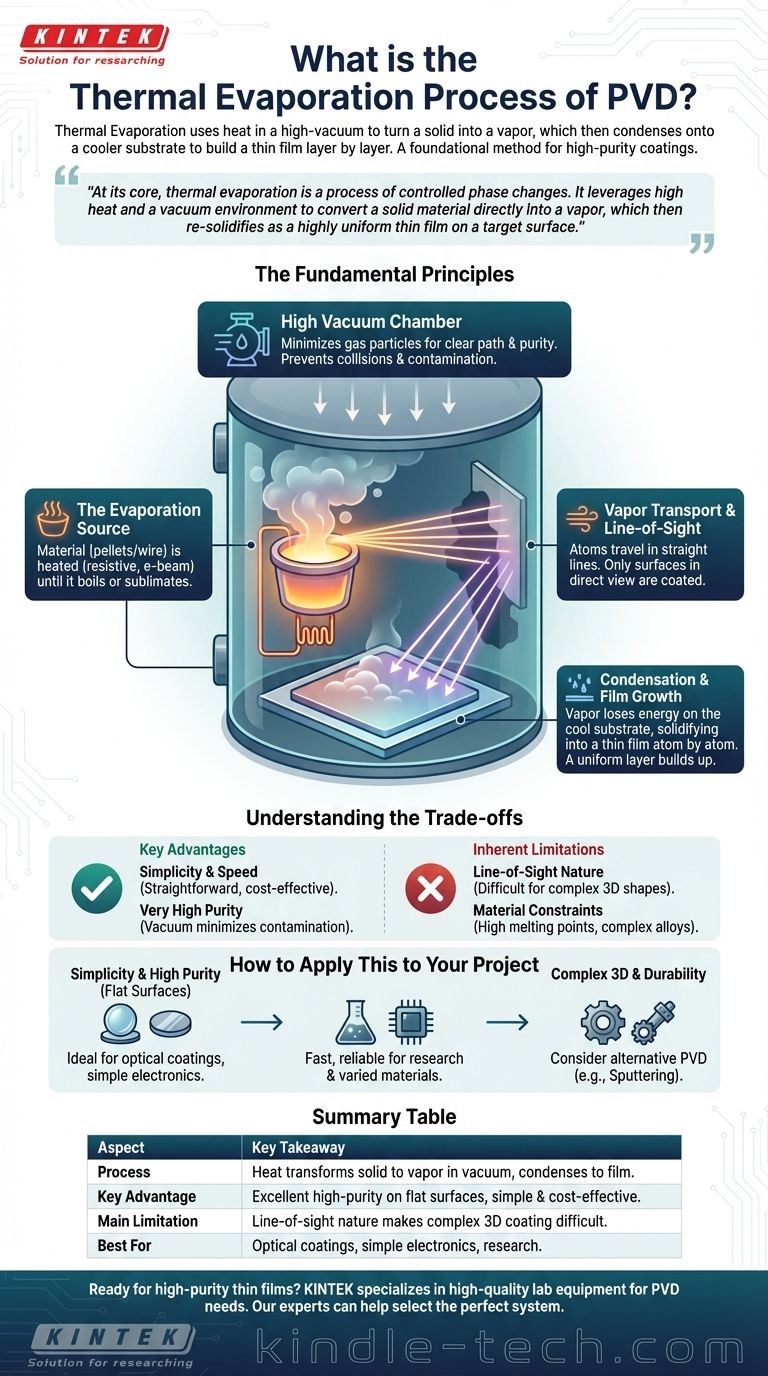
The Fundamental Principles of Thermal Evaporation
To understand thermal evaporation, it's best to break the process down into its critical stages. Each step is designed to control the material's state and ensure a clean, well-adhered final film.
The Role of High Vacuum
The entire process is performed inside a high-vacuum chamber. This environment is not optional; it is essential for success.
A vacuum minimizes the presence of ambient gas molecules, which accomplishes two critical goals. First, it prevents the vaporized source material from colliding with air particles, allowing it to travel a clear path to the substrate. Second, it reduces the risk of unwanted chemical reactions and contamination, ensuring the purity of the deposited film.
The Evaporation Source
The source material, often in the form of pellets or wire, is heated until it either boils or sublimates (transitions directly from solid to gas).
This heating is achieved through several methods. The most common is resistive heating, where a current is passed through a refractory boat or filament holding the source material. Other advanced methods include using electron beams or lasers to precisely heat the material.
Vapor Transport and Line-of-Sight
Once the material becomes a vapor, its atoms travel in straight lines away from the source. This is known as line-of-sight deposition.
This characteristic means that the process coats everything in its direct path, much like a spray paint can. Any surface not directly "visible" to the evaporation source will not receive a coating.
Condensation and Film Growth
When the vapor stream reaches the comparatively cool substrate, the atoms lose their thermal energy and condense back into a solid state.
This condensation builds up atom by atom, forming a thin, solid film. The temperature of the substrate itself is often controlled to influence the film's properties, such as its structure and adhesion.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any technical process, thermal evaporation has distinct advantages and limitations that make it suitable for some applications but not others.
Key Advantages
The primary advantage of thermal evaporation is its simplicity and speed. It does not require complex gases or high voltages, making it a relatively straightforward and cost-effective method.
It is also capable of producing very high-purity films, as the vacuum environment minimizes contamination and the process itself is a form of distillation.
Inherent Limitations
The most significant drawback is its line-of-sight nature. This makes it difficult to coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with uniform thickness, as surfaces not directly facing the source will be shadowed.
Additionally, some materials are difficult to deposit. High-melting-point materials require a large amount of energy, and complex alloys can decompose or evaporate at different rates, changing the composition of the final film.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing the right deposition method depends entirely on your project's specific requirements. Thermal evaporation is an excellent tool when used for the right task.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and high purity for flat surfaces: Thermal evaporation is an ideal choice for applications like optical coatings or simple electronic contacts.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective prototyping or research: This method provides a fast and reliable way to deposit a wide range of materials without complex equipment.
- If your primary focus is coating complex 3D geometries or durable mechanical parts: You should consider alternative PVD methods like sputtering, which do not have the same line-of-sight limitations.
Understanding these core principles allows you to leverage thermal evaporation's simplicity and purity for applications where a direct, clean coating is paramount.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Process | Heat transforms a solid into vapor in a vacuum, which condenses into a thin film on a substrate. |
| Key Advantage | Excellent for achieving high-purity coatings on flat surfaces simply and cost-effectively. |
| Main Limitation | Line-of-sight nature makes uniform coating of complex 3D shapes difficult. |
| Best For | Applications requiring high purity on flat surfaces, like optical coatings, simple electronics, and research. |
Ready to achieve high-purity thin films for your lab?
Thermal evaporation is a powerful tool for depositing clean, uniform coatings. Whether you're developing new optical layers, creating electronic components, or conducting materials research, having the right equipment is crucial for success.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your PVD and thin film deposition needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect thermal evaporation system to enhance your project's efficiency and results.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum thermal evaporation? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between sputtering and thermal evaporation? Choose the Right PVD Method for Your Thin Film
- What is thermal evaporation used to deposit? A Guide to Metals, Compounds, and Key Applications
- What is the widely used boat made of in thermal evaporation? Choosing the Right Material for High-Purity Deposition
- What is the thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition for Your Lab



















