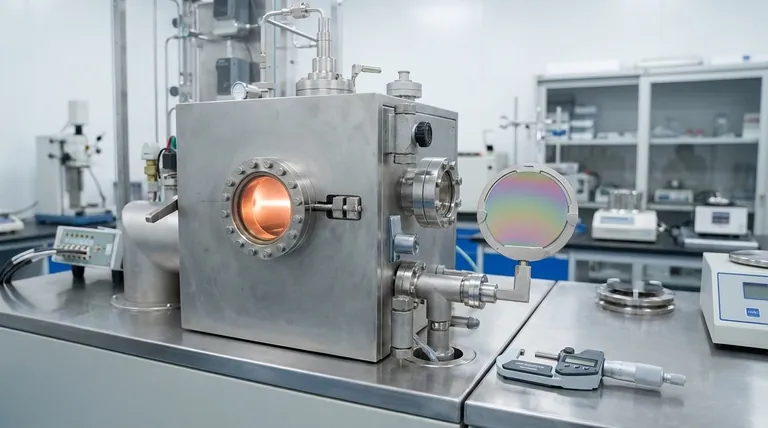
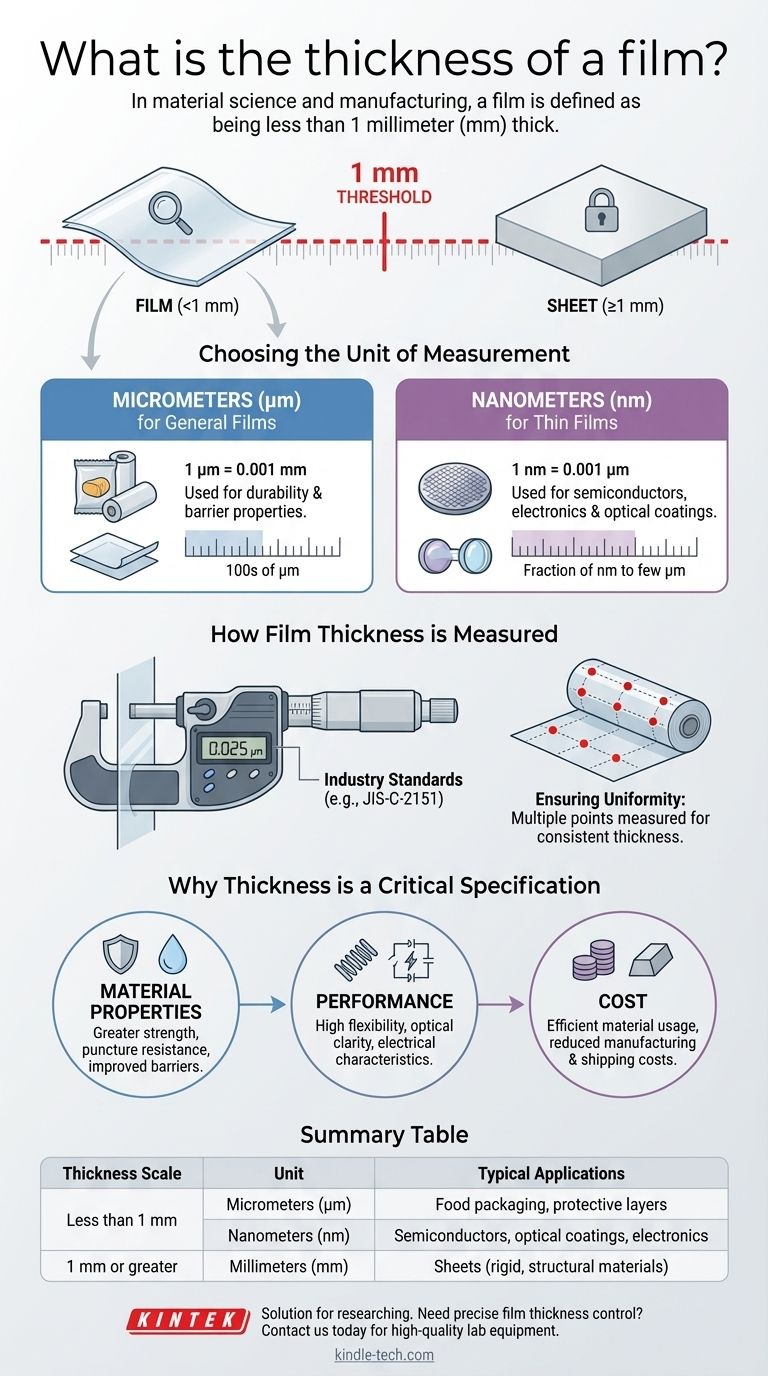
In material science and manufacturing, the thickness of a film is defined as being less than 1 millimeter (mm). This thickness can range from several micrometers (µm) for common applications down to fractions of a nanometer (nm) for highly specialized "thin films," such as those used in electronics or optics.
The term "film" fundamentally describes a material layer thinner than 1 mm, which distinguishes it from a thicker "sheet." The specific unit of measurement used—micrometers or nanometers—is determined entirely by the film's application and required precision.

Defining the Scale: Film vs. Sheet
The distinction between a film and a sheet is not arbitrary; it's a critical industry classification based on a simple threshold.
The 1 Millimeter Rule
The most important defining characteristic is the 1 mm threshold. Any material layer that is 1 mm or thicker is properly referred to as a sheet.
If the material is less than 1 mm thick, it is classified as a film. This rule provides a clear and universal standard for material specification.
Why This Distinction Matters
This classification directly impacts expectations about the material's properties. Films are expected to have a high degree of flexibility, while sheets are associated with rigidity and structural integrity.
Choosing the Right Unit of Measurement
The unit used to express a film's thickness communicates the scale and precision of the application.
Micrometers (µm) for General Films
For most industrial and commercial films, such as food packaging or protective layers, thickness is measured in micrometers (µm).
One micrometer is one-thousandth of a millimeter (0.001 mm). This unit provides the right level of granularity for applications where durability and barrier properties are key.
Nanometers (nm) for Thin Films
For advanced technological applications, the term "thin film" is used. These are layers of material ranging from a few micrometers down to a single layer of atoms.
The thickness of these highly engineered films is measured in nanometers (nm). One nanometer is one-thousandth of a micrometer (0.001 µm), making it the appropriate scale for semiconductors, optical coatings, and other precision surfaces.
How Film Thickness is Measured
Ensuring a film meets its specified thickness is a critical part of quality control.
The Micrometer Method
The most common method for measuring general film thickness is with a specialized instrument called a micrometer.
Industry standards, such as JIS-C-2151, outline the precise procedures for using this tool to get accurate and repeatable results.
Ensuring Uniformity
A single measurement is insufficient. To guarantee quality, technicians take measurements at multiple specified points across both the length and width of the film.
This process ensures the film has a consistent and uniform thickness, which is crucial for predictable performance.
Why Thickness is a Critical Specification
The thickness of a film is not just a number; it is a primary driver of its function, performance, and cost.
Impact on Material Properties
Thicker films generally provide greater tensile strength, puncture resistance, and improved barrier properties against moisture or gases.
Impact on Performance
Thinner films are often required for applications demanding high flexibility, optical clarity, or specific electrical characteristics. In electronics, the precise thickness of a thin film can determine a component's conductive or insulating properties.
Impact on Cost
Material usage is a primary cost driver. Producing a film that is thicker than necessary wastes raw material and increases manufacturing and shipping costs. Precise thickness control is essential for economic efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To interpret a specification correctly, you must consider the context of the application.
- If your primary focus is packaging or industrial materials: You will almost always be working with specifications in micrometers (µm).
- If your primary focus is electronics, optics, or semiconductors: You will be dealing with "thin films" where thickness is measured in the much finer scale of nanometers (nm).
- If your primary focus is differentiating from thicker materials: Remember the key threshold: anything 1 mm or thicker is classified as a "sheet," not a film.
Understanding these fundamental distinctions in scale and terminology is the first step to accurately specifying and evaluating material performance.
Summary Table:
| Thickness Scale | Unit | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Less than 1 mm | Micrometers (µm) | Food packaging, protective layers |
| Less than 1 mm | Nanometers (nm) | Semiconductors, optical coatings, electronics |
| 1 mm or greater | Millimeters (mm) | Sheets (rigid, structural materials) |
Need precise film thickness control for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for accurate material analysis and production. Whether you're developing thin films for electronics or require consistent packaging materials, our solutions ensure reliability and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Lab Blown Film Extrusion Three Layer Co-Extrusion Film Blowing Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the semiconductor materials for thin film? A Guide to Silicon, Compounds & Oxides
- What is the effect of sputtering gas pressure? Master Film Density, Stress, and Conformality
- What is thin film deposition metals? Enhance Your Substrate with Advanced Metal Coatings
- What size are sputtering targets? Custom Shapes & Sizes for Your Deposition System
- What is sputtering in thin film? A Guide to Atomic-Level Deposition
- What are the applications of semiconductor thin films? Powering the Core of Modern Electronics
- What are sputtering targets for semiconductors? Essential High-Purity Materials for Thin Film Deposition
- What is the use of RF sputtering? Essential for Depositing High-Quality Insulating Films
















