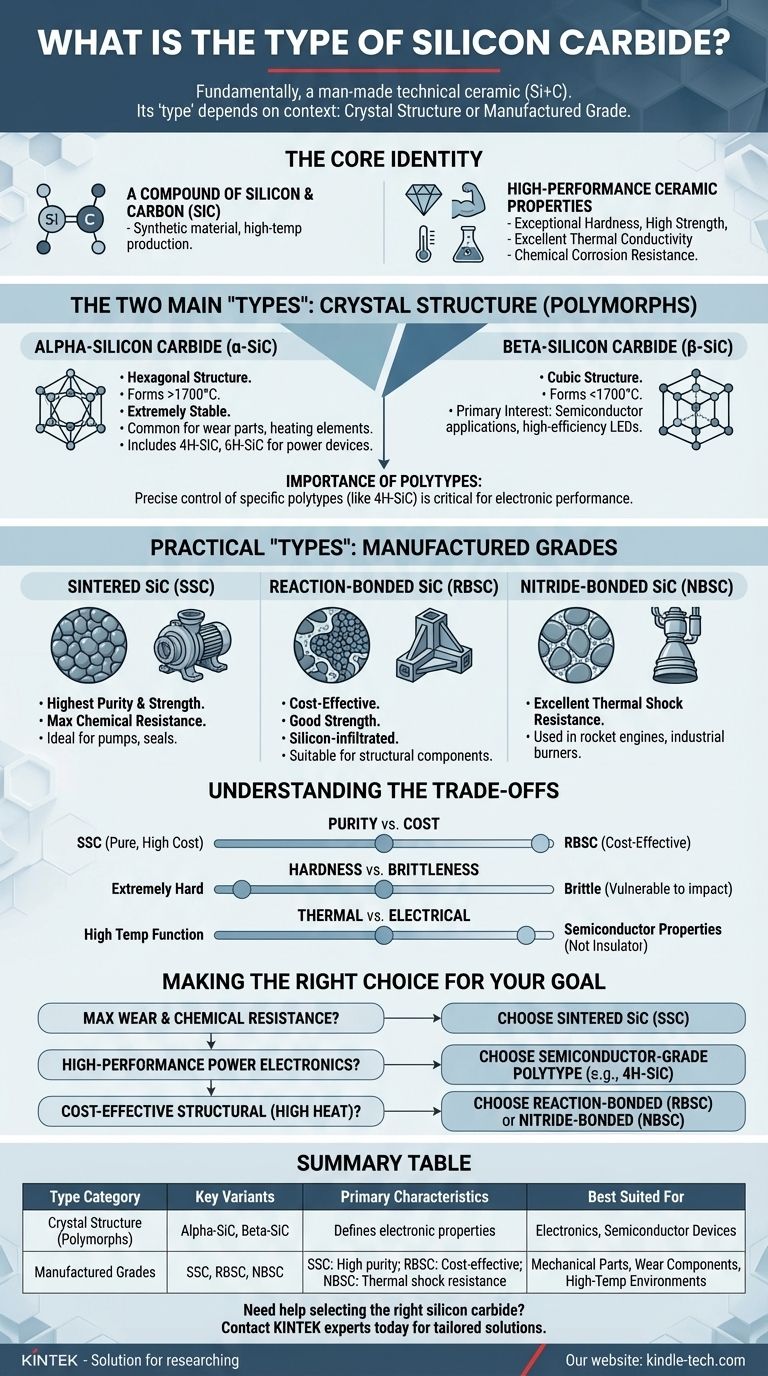
Fundamentally, silicon carbide (SiC) is a man-made technical ceramic composed of silicon and carbon. Its "type" isn't a single answer, as it refers to both its underlying crystal structure and the method by which it is manufactured into a usable product. Both of these factors determine its final properties and suitability for a specific application.
The most critical takeaway is that asking for the "type" of silicon carbide requires you to specify your context. Are you interested in the fundamental crystal structure (polymorphs like Alpha-SiC vs. Beta-SiC) for electronic properties, or the commercial grade (like Sintered vs. Reaction-Bonded) for mechanical performance?

The Core Identity: A Technical Ceramic
A Compound of Silicon and Carbon
Silicon carbide is a synthetic material with the chemical formula SiC. It is produced in furnaces at very high temperatures by combining silicon and carbon sources.
Properties of a High-Performance Ceramic
Unlike metals, SiC does not melt at normal pressures but instead sublimes at extremely high temperatures (around 2700°C). It is valued for its exceptional hardness, high strength, excellent thermal conductivity, and resistance to chemical corrosion.
The Two Main "Types": Understanding Crystal Structure (Polymorphs)
The atoms in silicon carbide can arrange themselves into different crystal structures, known as polymorphs or polytypes. This is the most important distinction at a scientific level and is critical for electronic applications.
Alpha-Silicon Carbide (α-SiC)
This is the most common polymorph, characterized by a hexagonal crystal structure. It is formed at temperatures above 1700°C and is extremely stable. Most of the structural SiC used for wear parts and heating elements, as mentioned for industrial furnaces, is alpha-SiC.
Beta-Silicon Carbide (β-SiC)
This polymorph has a cubic crystal structure and forms at lower temperatures (below 1700°C). Beta-SiC is of primary interest in semiconductor applications, as its specific electronic properties are essential for creating devices like the high-efficiency LEDs noted in its modern uses.
The Importance of Polytypes
Within these two main forms, over 250 variations, or polytypes, exist. In electronics, the specific polytype (such as 4H-SiC or 6H-SiC, both forms of alpha-SiC) is precisely controlled to achieve the desired semiconductor performance for power devices and substrates.
Practical "Types": Understanding Manufactured Grades
For mechanical and structural uses, the "type" of SiC more often refers to how the SiC powder is consolidated into a dense, solid part.
Sintered Silicon Carbide (SSC)
This is a very pure form of SiC, produced by pressing SiC powder at high temperatures until the grains fuse together. It offers the highest strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for pump components and seals in chemically aggressive environments.
Reaction-Bonded Silicon Carbide (RBSC)
Also known as silicon-infiltrated SiC, this grade is made by infiltrating molten silicon into a porous preform of SiC and carbon. While very strong and hard, the presence of free silicon makes it less suitable for the most extreme temperatures or chemically corrosive applications compared to SSC.
Nitride-Bonded Silicon Carbide (NBSC)
In this type, silicon carbide grains are held together by a silicon nitride binder. This material offers excellent thermal shock resistance and is often used to make components for rocket engines and industrial burners.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a type of silicon carbide involves balancing performance requirements with practical limitations.
Purity vs. Cost
Sintered SiC (SSC) is the purest and highest-performing grade for mechanical applications, but it is also the most expensive to produce. Reaction-Bonded SiC (RBSC) offers a more cost-effective solution with excellent properties, but its performance ceiling is limited by the free silicon in its structure.
Hardness vs. Brittleness
Silicon carbide is one of the hardest materials available, which is why it excels in wear-resistant applications. However, like most ceramics, it is brittle. It can withstand immense compressive force but may fracture under sharp, direct impact.
Thermal vs. Electrical Properties
Its ability to function at extreme temperatures makes it perfect for heating elements and furnace parts. Simultaneously, its unique semiconductor properties make it a key material for next-generation electronics, but this means it is not an electrical insulator, a factor that must be considered in component design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct type of silicon carbide, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear and chemical resistance: Your best choice is Sintered Silicon Carbide (SSC) for its purity and density.
- If your primary focus is high-performance power electronics: You must specify a semiconductor-grade polytype, such as 4H-SiC, grown as a single crystal.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective structural components for high heat: Reaction-Bonded (RBSC) or Nitride-Bonded (NBSC) SiC often provide the best balance of performance and cost.
Understanding these distinctions is the key to leveraging the remarkable capabilities of this versatile material.
Summary Table:
| Type Category | Key Variants | Primary Characteristics | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal Structure (Polymorphs) | Alpha-SiC (α-SiC), Beta-SiC (β-SiC) | Defines electronic properties; Alpha is stable & common, Beta is for semiconductors | Electronics, Semiconductor Devices |
| Manufactured Grades | Sintered (SSC), Reaction-Bonded (RBSC), Nitride-Bonded (NBSC) | SSC: High purity & strength; RBSC: Cost-effective; NBSC: Thermal shock resistance | Mechanical Parts, Wear Components, High-Temperature Environments |
Need help selecting the right silicon carbide for your project? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and materials, including silicon carbide components tailored for demanding applications. Whether you require sintered SiC for superior corrosion resistance or a specific polytype for electronic applications, our experts can guide you to the optimal solution. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK's precision materials can enhance your laboratory's performance and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
- Thin-Layer Spectral Electrolysis Electrochemical Cell
- High Shear Homogenizer for Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature for a SiC heating element? Unlock the Key to Longevity and Performance
- What kind of metal is used in heating elements? A Guide to Materials for Every Temperature & Atmosphere
- What is SiC elements? The Ultimate High-Temperature Heating Solution
- What is the maximum temperature for silicon carbide heating element? The Real Limit for Your High-Temp Furnace
- What material is used for making heating element? Choose the Right Alloy for Your Application



















