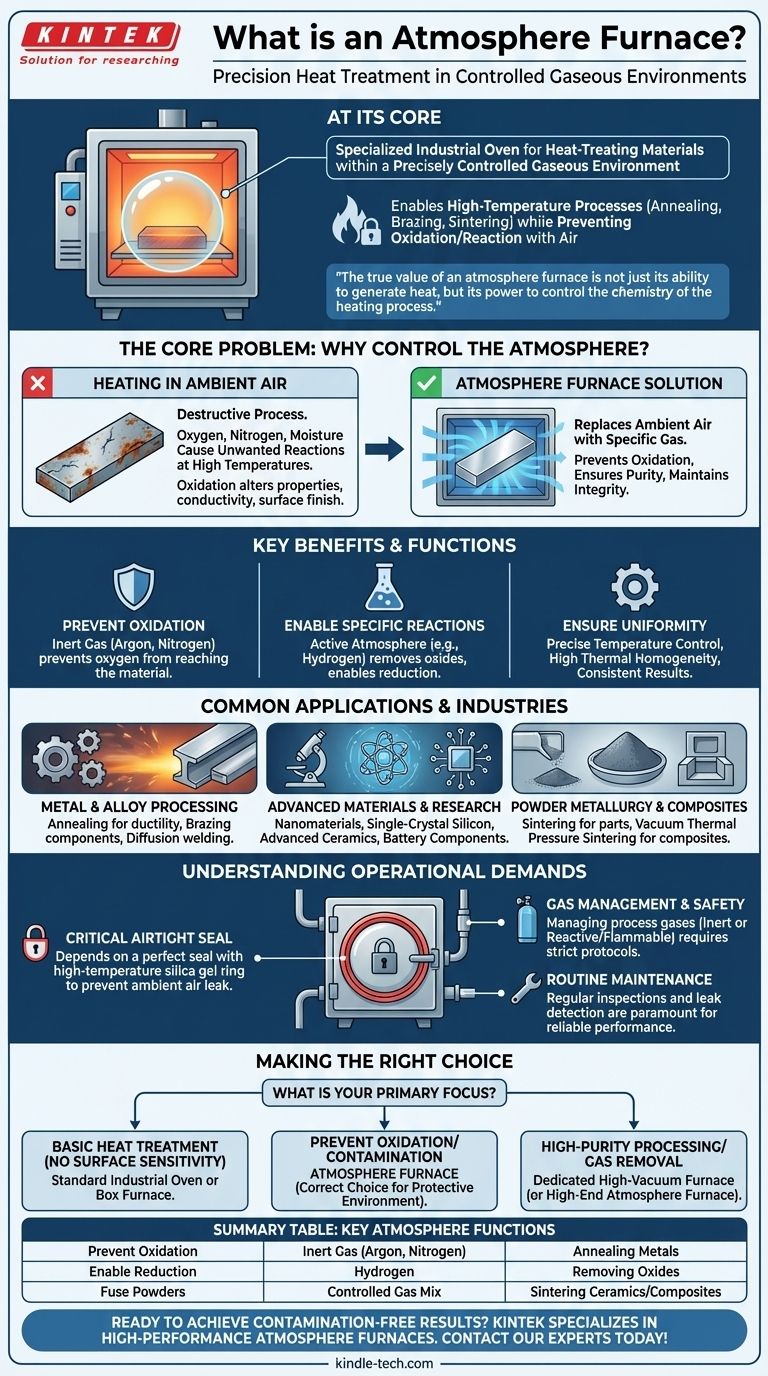
At its core, an atmosphere furnace is a specialized industrial oven used for heat-treating materials within a precisely controlled gaseous environment. Its primary function is to enable high-temperature processes like annealing, brazing, and sintering while preventing the material from reacting with oxygen or other elements present in the air. This control is essential for materials prone to oxidation, ensuring a clean finish and preserving their desired properties.
The true value of an atmosphere furnace is not just its ability to generate heat, but its power to control the chemistry of the heating process. It creates a protective bubble, allowing materials to be transformed by temperature without being degraded by their environment.

The Core Problem: Why Control the Atmosphere?
Heating many materials in ambient air is a destructive process. The oxygen, nitrogen, and moisture in the air can cause unwanted chemical reactions at high temperatures. An atmosphere furnace is designed to solve this fundamental problem.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
Many metals and alloys form an oxide layer when heated. This oxidation can alter a material's mechanical properties, electrical conductivity, and surface finish.
An atmosphere furnace replaces the ambient air with a specific gas, such as an inert gas like argon or nitrogen. This protective atmosphere prevents oxygen from reaching the material, ensuring its purity and integrity are maintained.
Enabling Specific Chemical Reactions
Beyond simply being protective, the atmosphere can be an active part of the process. For example, a hydrogen atmosphere can be used to actively remove oxides from a material's surface, a process known as reduction.
Other processes, like sintering, rely on a controlled atmosphere to fuse powder materials together without melting them, which is critical for manufacturing advanced ceramics and composite materials.
Ensuring Uniformity and Precision
Atmosphere furnaces are engineered for exceptional thermal performance. They provide precise temperature control and high thermal homogeneity, meaning the temperature is consistent throughout the entire heating chamber.
This uniformity is crucial for achieving stable, repeatable results, especially in sensitive applications like manufacturing semiconductors, batteries, and other advanced materials.
Common Applications and Industries
The ability to control both heat and chemistry makes atmosphere furnaces indispensable in various high-value sectors.
Metal and Alloy Processing
These furnaces are heavily used for the annealing of metals to increase their ductility, the brazing of components to create strong joints, and the diffusion welding of dissimilar metals.
Advanced Materials and Research
University labs, research institutions, and high-tech industries use atmosphere furnaces for developing and processing a wide range of materials. This includes nanomaterials, single-crystal silicon, advanced ceramics, and next-generation battery components.
Powder Metallurgy and Composites
The furnace is essential for creating parts from powder materials. It allows for sintering and vacuum thermal pressure sintering, which are foundational processes for manufacturing composite materials, powder-based alloys, and structural ceramics.
Understanding the Operational Demands
While powerful, an atmosphere furnace is not a simple "set and forget" piece of equipment. Its effectiveness depends entirely on its operational integrity.
The Criticality of a Perfect Seal
The entire system relies on an airtight seal. The furnace door is typically fitted with a high-temperature resistant silica gel ring to prevent any ambient air from leaking into the chamber.
Even a minor leak can compromise the controlled atmosphere, negate the benefits of the process, and lead to product defects.
Gas Management and Safety
Operating the furnace requires managing a supply of process gases. This can range from simple inert gases like argon to reactive or flammable gases like hydrogen, which demand strict safety protocols and handling procedures.
Routine Maintenance and Leak Detection
To ensure reliable performance, routine preventative maintenance is not optional. This includes regular visual inspections and, most importantly, periodic leak detection tests. Identifying and repairing any source of a leak is paramount to maintaining the integrity of the controlled atmosphere.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating equipment depends entirely on the chemical sensitivity of your material and the desired outcome of your process.
- If your primary focus is basic heat treatment without surface sensitivity: A standard industrial oven or box furnace may be sufficient and more cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is preventing any oxidation or surface contamination: An atmosphere furnace is the correct choice, as it provides the necessary protective environment.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing or removing all gases: You may need to consider a dedicated high-vacuum furnace, though many atmosphere furnaces can pull a sufficient vacuum for a wide range of applications.
Ultimately, choosing an atmosphere furnace is a decision to invest in precise control over your material's final quality and performance.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Atmosphere Type | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Prevent Oxidation | Inert Gas (Argon, Nitrogen) | Annealing Metals |
| Enable Reduction | Hydrogen | Removing Oxides |
| Fuse Powders | Controlled Gas Mix | Sintering Ceramics/Composites |
Ready to achieve contamination-free results in your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-performance atmosphere furnaces for precise annealing, brazing, and sintering. Our equipment ensures the uniform heating and airtight seals your R&D or production needs demand. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your materials processing!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- Why nitrogen is used in annealing furnace? To prevent oxidation and decarburization for superior metal quality
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- What is the purpose of inert atmosphere? A Guide to Protecting Your Materials and Processes
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2



















