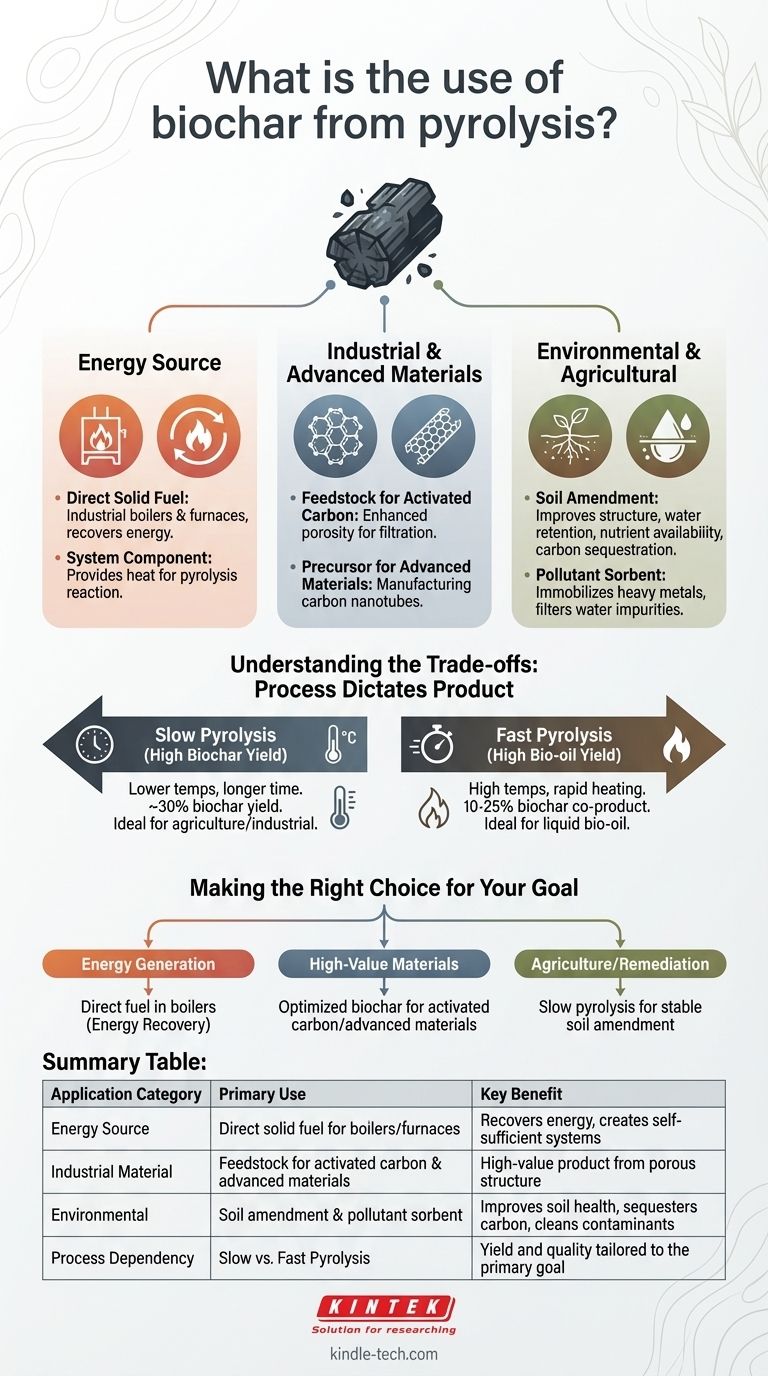
At its core, biochar produced from pyrolysis is a versatile, carbon-rich solid material, not merely a waste product. Its primary uses fall into three main categories: as a solid fuel, as a feedstock for advanced industrial materials, and as a powerful agent for environmental and agricultural improvement. The specific application depends heavily on the initial feedstock and the pyrolysis conditions used.
Biochar's true value is not in any single application, but in its adaptability. Viewing it as a co-product rather than a byproduct is essential to understanding the economic and environmental viability of any pyrolysis operation.

Biochar's Role as an Energy Source
The most direct application for biochar is leveraging the concentrated energy it contains from the original biomass. This makes it a straightforward substitute for traditional solid fuels.
A Direct Solid Fuel
Biochar can be burned directly in industrial boilers and furnaces. This process recovers a significant portion of the energy from the original feedstock, contributing to a more efficient and circular energy system.
A Component of the Pyrolysis System
In some integrated systems, a portion of the biochar produced is used to provide the heat required to sustain the pyrolysis reaction itself. This creates a self-sufficient process that reduces the need for external energy inputs.
Industrial and Advanced Material Applications
Biochar's unique physical and chemical properties make it a valuable precursor for creating higher-value industrial products. Its porous structure is key to these applications.
Feedstock for Activated Carbon
One of the most common industrial uses for biochar is as a feedstock for producing activated carbon. The inherent porosity of biochar is enhanced through an activation process, creating a material with an extremely high surface area ideal for filtration and purification processes.
Precursor for Advanced Materials
Research has also demonstrated biochar's potential as a raw material for manufacturing cutting-edge products like carbon nanotubes. This application transforms a relatively low-cost byproduct into a high-value advanced material.
Environmental and Agricultural Applications
Beyond energy and industry, biochar's most transformative uses are in environmental remediation and agriculture, where it can improve soil health and sequester carbon.
As a Soil Amendment
When added to soil, biochar can significantly improve soil structure, water retention, and nutrient availability. Its stable carbon structure resists decomposition, meaning it can benefit the soil for hundreds or even thousands of years.
As a Sorbent for Pollutants
The porous nature of biochar makes it an excellent sorbent for capturing pollutants. It can be used to immobilize heavy metals and other contaminants in soil or to filter impurities from water, acting as a powerful tool for environmental cleanup.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Process Dictates Product
The final characteristics and yield of biochar are not accidental; they are a direct result of the pyrolysis process parameters. Understanding this relationship is critical to producing a product fit for a specific purpose.
The Impact of Pyrolysis Speed
Slow pyrolysis is conducted at lower temperatures over a longer period, a process that maximizes the yield of biochar, often up to 30% by weight. This is the preferred method when high-quality biochar for agricultural or industrial use is the primary goal.
Fast pyrolysis, conversely, uses high temperatures and rapid heating to maximize the production of liquid bio-oil. In this case, biochar is a smaller co-product, with yields typically ranging from 10-25%.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine the best use of biochar, you must first define the primary objective of your pyrolysis system.
- If your primary focus is energy generation: Use the biochar directly as a solid fuel in boilers to maximize the energy recovery from your feedstock.
- If your primary focus is high-value materials: Optimize the pyrolysis process to create biochar with the specific properties needed to serve as a feedstock for activated carbon or other advanced materials.
- If your primary focus is agriculture or remediation: Employ slow pyrolysis to maximize the yield of stable, high-quality biochar for use as a long-term soil amendment or pollution sorbent.
Ultimately, understanding the potential applications of biochar is key to designing an effective and economically viable pyrolysis system.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Primary Use | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Direct solid fuel for boilers/furnaces | Recovers energy, creates self-sufficient systems |
| Industrial Material | Feedstock for activated carbon & advanced materials | High-value product from porous structure |
| Environmental | Soil amendment & pollutant sorbent | Improves soil health, sequesters carbon, cleans contaminants |
| Process Dependency | Slow Pyrolysis (maximizes biochar) vs. Fast Pyrolysis (maximizes bio-oil) | Yield and quality are tailored to the primary goal |
Ready to integrate biochar into your operations? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed to optimize your pyrolysis process and biochar analysis. Whether you're developing new materials, enhancing agricultural practices, or creating sustainable energy solutions, our expertise supports your goals. Contact our team today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior results with biochar.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas



















