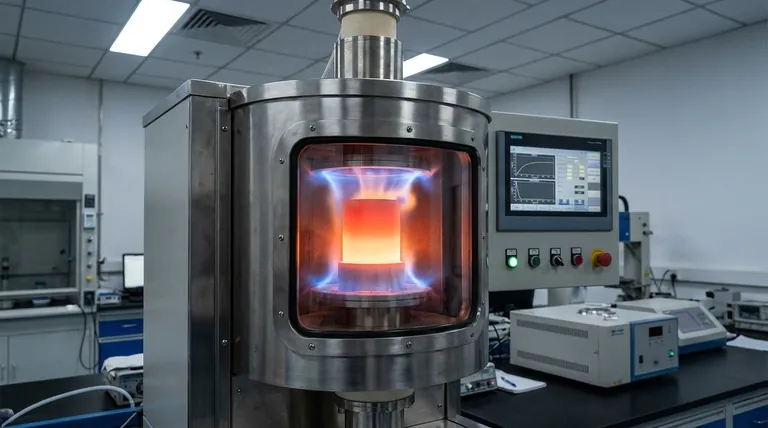
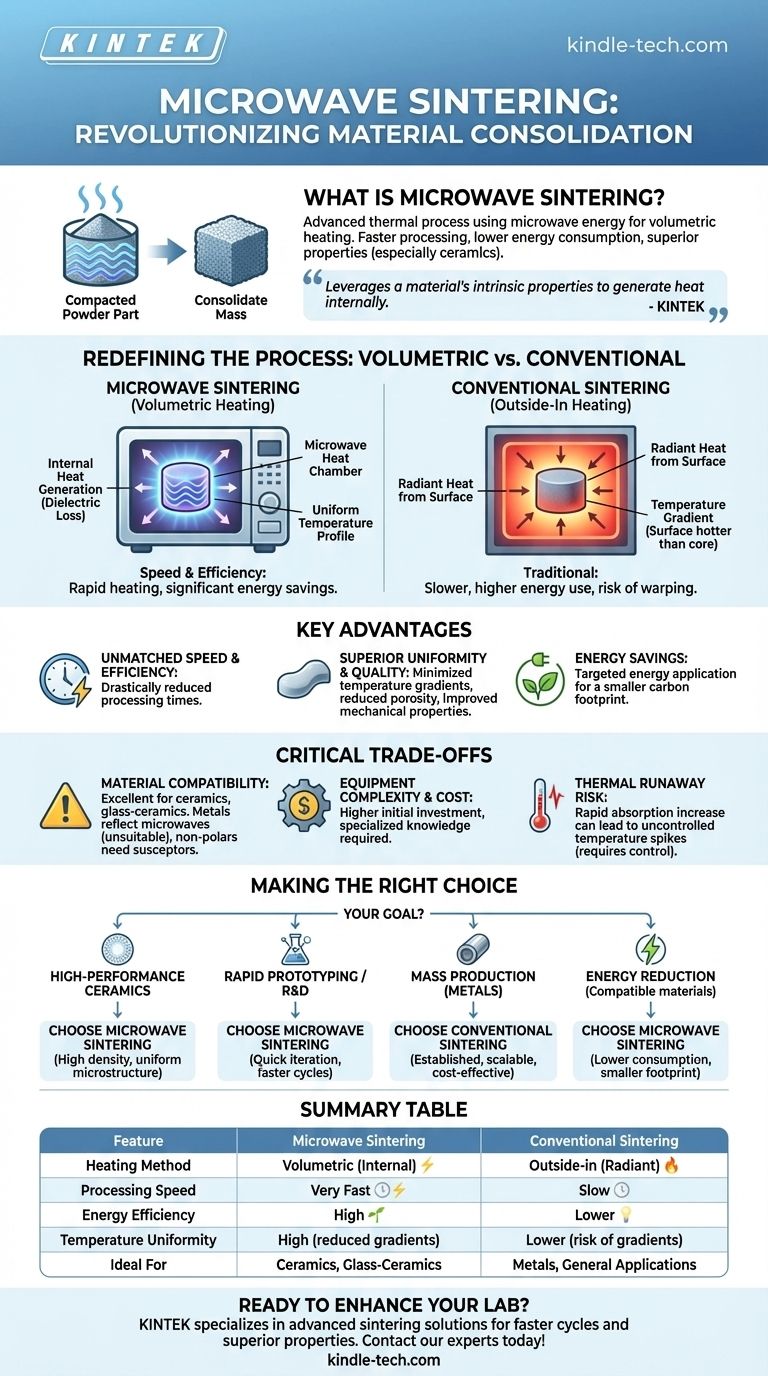
Microwave sintering is an advanced thermal process used to consolidate powdered materials into a solid, dense mass using microwave energy as the heat source. Unlike conventional ovens that heat from the outside in, this method heats the material volumetrically, resulting in significantly faster processing times, lower energy consumption, and often superior final properties, especially for ceramic materials.
While traditional sintering relies on external heat transfer, microwave sintering leverages a material's intrinsic properties to generate heat internally. This fundamental difference allows for faster, more uniform, and more efficient processing, making it a powerful tool for developing advanced materials.

How Microwave Sintering Redefines the Process
Conventional sintering works by placing a compacted part (a "green body") into a furnace. Heat radiates from the furnace walls, slowly penetrating the material from the surface inward. Microwave sintering fundamentally changes this dynamic.
The Principle: Volumetric Heating
Microwave sintering uses an electromagnetic field to induce heat directly within the material itself. This occurs through a phenomenon called dielectric loss, where the rapidly oscillating electric field causes molecules and ions within the material to vibrate and rotate, generating thermal energy.
This is analogous to how a microwave oven heats food. The energy doesn't just warm the surface; it penetrates and heats the entire volume simultaneously.
The Result: Speed and Efficiency
Because the material heats itself from within, the process is incredibly fast. Heating rates can be orders of magnitude higher than in a conventional furnace, drastically reducing the total time required to reach sintering temperature.
This speed, combined with the targeted application of energy, leads to significant energy savings and improved production efficiency compared to heating a large, poorly insulated furnace for hours.
The Advantage: Uniformity and Quality
Traditional "outside-in" heating creates a temperature gradient, where the surface is much hotter than the core. This can cause internal stresses, warping, and inconsistent densification throughout the part.
Microwave sintering's volumetric heating minimizes these gradients. The core and surface heat up at nearly the same rate, resulting in a more uniform microstructure, reduced porosity, and improved mechanical properties in the final product.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
While powerful, microwave sintering is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is dependent on specific factors that create important trade-offs compared to established conventional methods.
Material Compatibility is Key
The process relies on a material's ability to absorb microwave energy (its dielectric properties). It is exceptionally effective for many ceramics, porcelain, and glass-ceramics.
However, highly conductive materials like most metals will simply reflect microwaves, making them unsuitable for this process. Non-polar materials that do not absorb microwave energy also cannot be processed this way without special additives called susceptors.
Equipment Complexity and Cost
Microwave sintering systems are more technologically complex than traditional resistance-heated furnaces. This often translates to a higher initial capital investment and may require more specialized knowledge for operation and maintenance.
Challenges with Thermal Runaway
Some materials exhibit a rapid increase in microwave absorption as they get hotter. If not properly controlled, this can lead to thermal runaway, where the temperature spikes uncontrollably, potentially damaging the material or the equipment. Sophisticated control systems are required to manage this risk.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate sintering method depends entirely on your material, budget, and performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-performance ceramics: Microwave sintering is a superior choice for achieving high density and a uniform microstructure in less time.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping or R&D: The dramatic reduction in cycle time makes microwave sintering ideal for iterating on new materials and designs quickly.
- If your primary focus is mass production of standard metal parts: Conventional powder metallurgy and furnace sintering remain the most established, scalable, and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is energy reduction: For compatible materials, microwave sintering offers a clear path to lower energy consumption and a smaller carbon footprint per part.
By understanding the fundamental heating mechanism, you can select the most effective sintering technology for your specific material and production goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Microwave Sintering | Conventional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Volumetric (internal) | Outside-in (radiant) |
| Processing Speed | Very Fast | Slow |
| Energy Efficiency | High | Lower |
| Temperature Uniformity | High (reduced gradients) | Lower (risk of gradients) |
| Ideal For | Ceramics, Glass-Ceramics | Metals, General Applications |
Ready to enhance your lab's material processing capabilities? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including sintering solutions. Our expertise can help you achieve faster cycle times, superior material properties, and significant energy savings for your ceramic and advanced material projects. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific R&D or production goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control



















