In essence, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven used in chemistry to heat samples in a controlled and isolated environment. Its primary functions include the thermal decomposition of materials (ashing), heat-treating metals and ceramics, and preparing samples for further chemical analysis by ensuring that the heat source does not contaminate the material being studied.
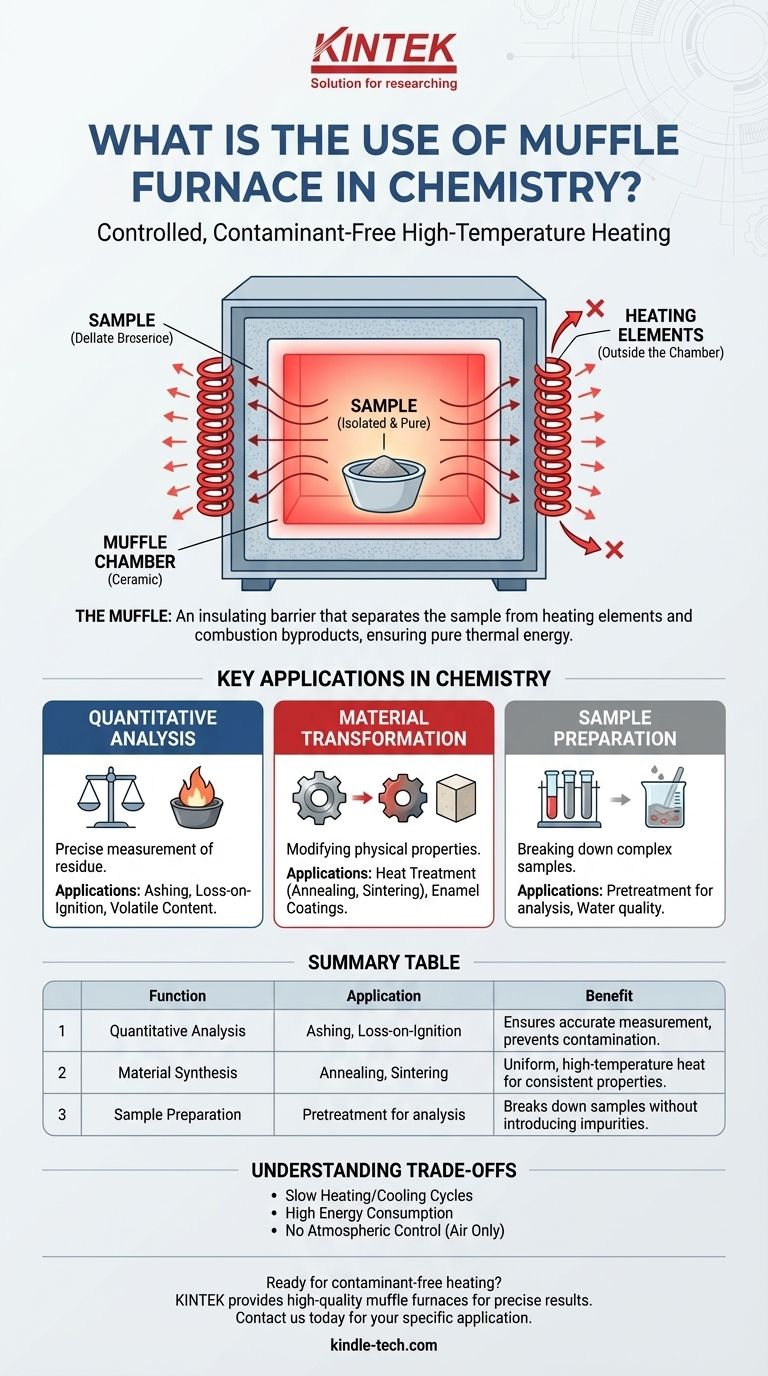
The core value of a muffle furnace is not simply its ability to generate high temperatures. Its defining feature is the "muffle"—an insulating chamber that separates the sample from the heating elements and their combustion byproducts, ensuring any changes to the sample are caused by heat alone.
The Core Principle: Controlled, Contaminant-Free Heating
A muffle furnace's design is key to its role in precise chemical work. Unlike a direct flame or a less-controlled oven, its purpose is to deliver pure thermal energy.
What is the "Muffle"?
The "muffle" is a refractory ceramic chamber that contains the sample. The heating elements, typically electric coils, are positioned on the outside of this chamber.
This design creates a protective barrier. Heat radiates through the chamber walls to the sample, but any gases or particles shed by the heating elements themselves cannot enter the chamber and contaminate the sample.
Why Contamination Control is Critical
In many chemical processes, purity is paramount. For example, when determining the ash content of a substance, you must be certain that the final residue is only the non-combustible part of the original sample.
If byproducts from a flame or degrading heating elements were introduced, they would add mass to the residue, leading to inaccurate analytical results. The muffle furnace eliminates this variable.
Key Applications in Chemistry and Materials Science
The ability to provide clean, uniform heat makes the muffle furnace indispensable for several distinct tasks.
Quantitative Analysis (Measuring What's Left)
This is a classic use in analytical chemistry. The goal is to heat a sample until all volatile or combustible components are driven off, allowing for precise measurement of the remaining material.
Applications include ashing (burning off all organic matter to isolate the inorganic residue), loss-on-ignition analysis, and determining the volatile content of coal and other materials.
Material Transformation and Synthesis (Creating New Properties)
In materials science, heat is used to change a material's physical or chemical structure. The uniform and high temperatures of a muffle furnace are ideal for these transformations.
This includes heat treatment of metals like annealing (softening), hardening, and quenching. It is also essential for sintering (fusing ceramic or metal powders into a solid mass) and creating enamel coatings and technical ceramics.
Sample Preparation (Getting Samples Ready for Analysis)
Before complex samples can be analyzed by other instruments, they often need to be broken down. This is common in environmental and medical fields.
A muffle furnace can be used for the pretreatment of medical samples or the digestion of samples for water quality analysis, where high heat breaks down the complex organic matrix to simplify subsequent measurement.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a muffle furnace is not always the right tool. Understanding its limitations is crucial for proper experimental design.
Heating and Cooling Time
Due to their heavy insulation, muffle furnaces heat up and cool down very slowly. This can take several hours, making them inefficient for processes requiring rapid temperature changes.
Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining temperatures of 1000°C or higher requires a significant amount of electrical energy, making them costly to operate for long periods.
Atmospheric Control
A standard muffle furnace operates in an air atmosphere. If a process requires a specific inert (e.g., nitrogen, argon) or reactive atmosphere, a more specialized tube furnace is necessary. The muffle furnace cannot maintain a controlled gas environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To decide if a muffle furnace is appropriate, consider the primary objective of your heating process.
- If your primary focus is accurate quantitative analysis (e.g., ashing): The muffle furnace is the correct tool, as it provides complete, contaminant-free combustion essential for precise measurements.
- If your primary focus is modifying the physical properties of a material (e.g., annealing metal or sintering ceramics): The muffle furnace's uniform, high heat is ideal for achieving consistent and repeatable structural changes.
- If your primary focus is speed or requires a controlled gas atmosphere: The slow cycle time and air-only environment of a muffle furnace make it unsuitable; consider a tube furnace or a different heating method.
Ultimately, selecting a muffle furnace is a decision to prioritize sample purity and thermal uniformity above all other factors.

Summary Table:
| Key Function | Primary Application | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Quantitative Analysis | Ashing, Loss-on-Ignition | Ensures accurate measurement of residue by preventing contamination. |
| Material Synthesis | Annealing, Sintering | Provides uniform, high-temperature heat for consistent material properties. |
| Sample Preparation | Pretreatment for analysis | Breaks down complex samples for further testing without introducing impurities. |
Ready to achieve contaminant-free heating and precise results in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory equipment, including reliable muffle furnaces designed for the demanding needs of chemistry and materials science. Our furnaces provide the uniform heat and sample purity essential for accurate quantitative analysis and material synthesis.
Contact us today to find the perfect muffle furnace for your specific application and enhance the accuracy of your work. Get in touch →
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does heat treatment affect surface roughness? Minimize Surface Degradation for Precision Parts
- What is a muffle furnace used for? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing
- What is the relationship between sintering temperature and melting temperature? Key Differences for Material Engineers
- What are the 3 types of heat transfer? Master Conduction, Convection & Radiation for Your Lab
- What is a muffle furnace in the environment? Achieve Clean, Contaminant-Free Heating



















