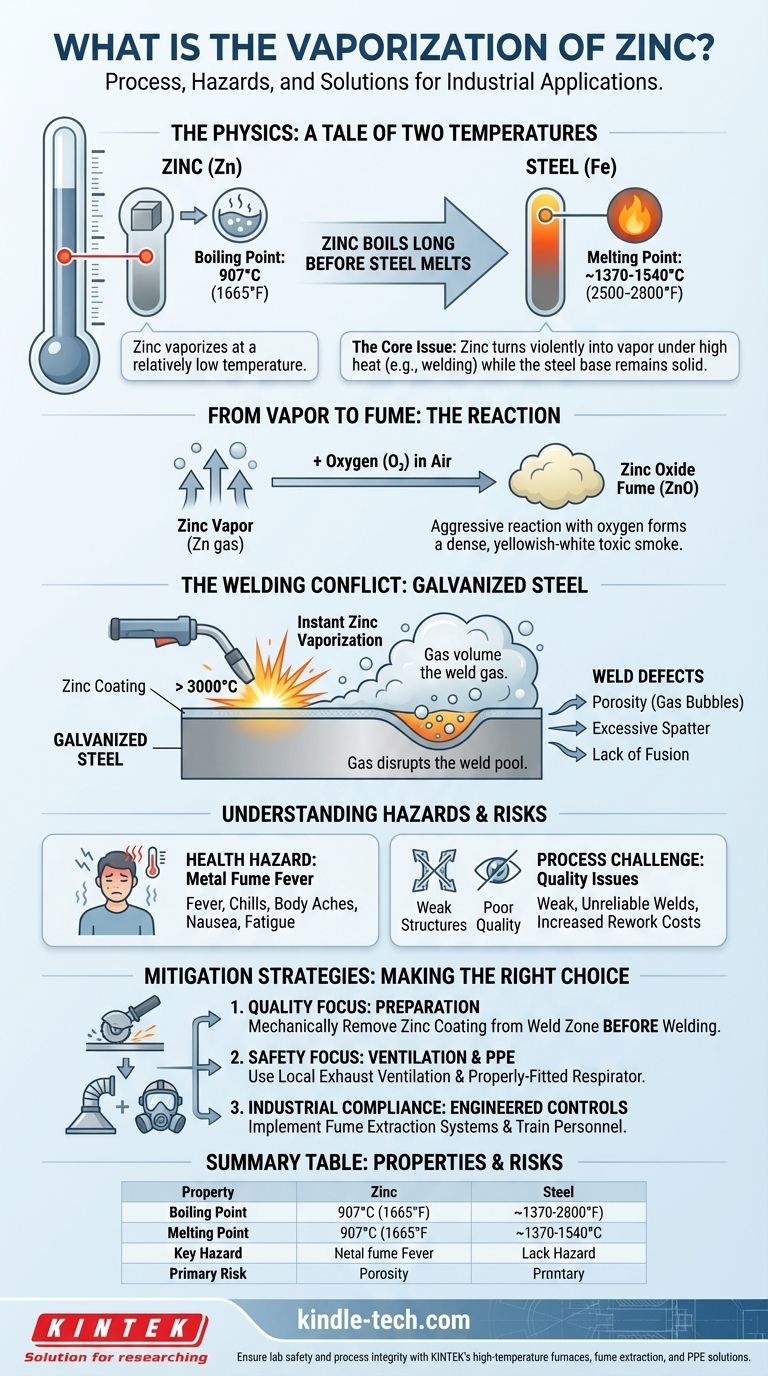
In essence, the vaporization of zinc is the physical process where the metal transforms from a solid or liquid state into a gaseous vapor. This occurs when zinc is heated to its boiling point of 907°C (1665°F). Critically, this temperature is significantly lower than the melting point of steel, which is the primary reason this phenomenon is a major concern in industrial applications like welding.
The core issue with zinc vaporization is its low boiling point relative to other common metals, especially steel. This disparity means that in high-heat processes, a protective zinc coating will violently turn into a toxic fume long before the base metal even begins to melt, creating profound safety and quality challenges.

The Physics Driving the Problem
The practical implications of zinc vaporization are rooted in a fundamental mismatch of material properties. Understanding this conflict is the first step to managing it.
A Tale of Two Temperatures
The entire challenge can be summarized by comparing two numbers.
Zinc boils at 907°C (1665°F).
Steel melts around 1370-1540°C (2500-2800°F).
This means that any process designed to melt steel, like welding, will supply more than enough energy to violently boil off any zinc present in the immediate area.
From Vapor to Fume
Once zinc turns into a gas, it doesn't remain as an invisible vapor for long. The hot zinc gas immediately and aggressively reacts with oxygen in the surrounding air.
This reaction forms zinc oxide (ZnO), a fine particulate that manifests as a dense, yellowish-white smoke. This fume is the primary source of both health risks and process complications.
The Most Common Scenario: Welding Galvanized Steel
While zinc vaporization is relevant in metal refining and casting, its most frequent and problematic appearance is in the welding of galvanized steel.
What is Galvanization?
Galvanization is the process of applying a protective zinc coating to steel or iron. This coating acts as a sacrificial barrier, preventing the underlying steel from rusting.
The Welding Conflict
When a welding arc, which can exceed 3000°C, strikes galvanized steel, the zinc coating underneath is instantly vaporized.
This sudden conversion from a thin solid layer to a large volume of gas creates enormous pressure within the molten weld pool. The gas disrupts the stability of the arc and contaminates the weld itself.
The Impact on Weld Quality
The escaping zinc vapor is directly responsible for severe weld defects.
These include porosity (gas bubbles trapped in the solidified weld), excessive weld spatter, and lack of fusion. The resulting weld is often structurally weak, unreliable, and visually poor.
Understanding the Hazards and Trade-offs
Simply "welding through" a zinc coating is not a viable strategy. The trade-offs in safety and quality are severe and must be addressed with proper procedure.
The Health Hazard: Metal Fume Fever
Inhaling the zinc oxide fume is a serious occupational hazard. It can cause an acute condition known as Metal Fume Fever.
Symptoms typically appear several hours after exposure and mimic the flu: fever, chills, body aches, nausea, and fatigue. While the illness is usually temporary, repeated exposure can have cumulative effects and should always be avoided.
The Process Challenge: Preparation is Non-Negotiable
The only way to guarantee a high-quality weld is to prevent the zinc from entering the weld pool in the first place.
This requires mechanically removing the zinc coating from the weld zone before starting. Methods like grinding, sanding, or using a flap disc are common. This adds a significant preparation step, increasing time and labor costs.
The Control Imperative: Ventilation and PPE
Because some fume generation is often unavoidable, proper safety controls are critical.
This includes using local exhaust ventilation (fume extractors) to capture the smoke at its source and wearing appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), especially a respirator rated for metal fumes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to managing zinc vaporization must be dictated by your primary objective, whether it's personal safety, project quality, or industrial compliance.
- If your primary focus is weld quality: You must mechanically remove the zinc coating from the weld zone and surrounding areas before you begin welding.
- If your primary focus is personal safety: Always prioritize ventilation, work in an open or well-ventilated area, and wear a properly-fitted respirator rated for metal fumes.
- If your primary focus is industrial compliance: Implement engineered controls like fume extraction systems and ensure all personnel are trained on the hazards and equipped with the correct PPE.
Understanding that zinc will always vaporize under welding heat is the key to anticipating its effects and ensuring both personal safety and structural integrity in your work.
Summary Table:
| Property | Zinc | Steel (for comparison) |
|---|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 907°C (1665°F) | N/A |
| Melting Point | 420°C (787°F) | ~1370-1540°C (2500-2800°F) |
| Key Hazard | Forms toxic zinc oxide (ZnO) fume | N/A |
| Primary Risk | Metal Fume Fever, weld defects | N/A |
Ensure your lab's safety and process integrity when working with metals like zinc. The risks of toxic fume exposure and material failure are real. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with high-temperature furnaces, fume extraction systems, and PPE to protect your team and your work. Don't compromise on safety—contact our experts today to find the right solution for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of vacuum furnace? Achieve Unmatched Material Purity and Performance
- What are the advantages of vacuum hardening? Achieve Superior Precision and Cleanliness for Critical Components
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? Selecting the Right Hot Zone for Your Process
- What does a vacuum furnace do? Achieve High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Components
- What is the maximum temperature in a vacuum furnace? It Depends on Your Materials and Process Needs



















