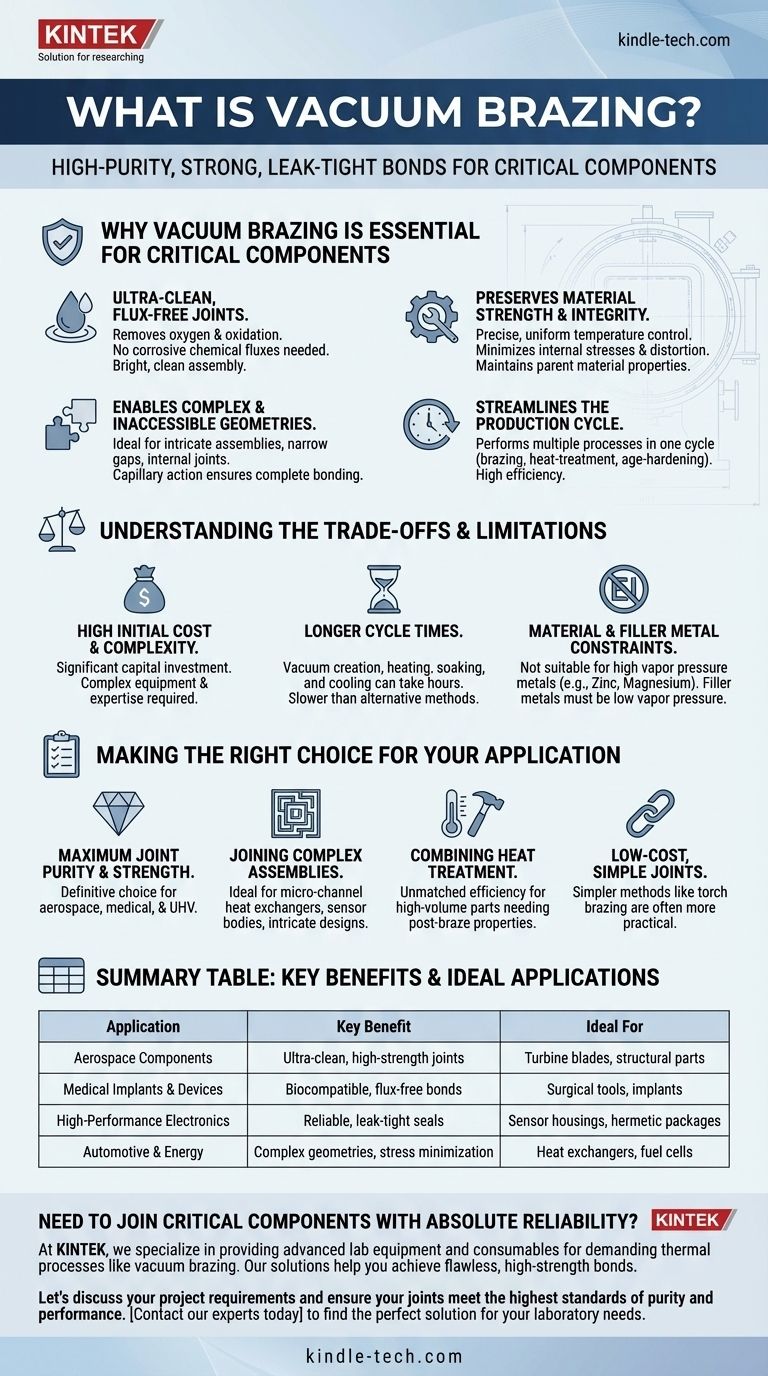
At its core, vacuum brazing is a high-purity material joining process used to create exceptionally strong, clean, and leak-tight bonds between metal components. It is the preferred method for manufacturing critical parts in demanding industries like aerospace, medical, automotive, and high-end electronics where performance and reliability are non-negotiable.
Vacuum brazing is chosen not just for joining parts, but for doing so in a highly controlled, contaminant-free environment. This process protects the integrity of the base materials and produces a finished joint that is often stronger and cleaner than what can be achieved with other methods.
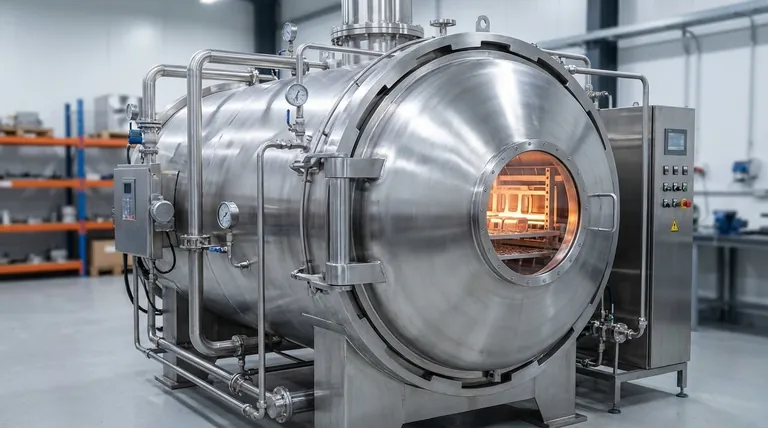

Why Vacuum Brazing is Essential for Critical Components
The "why" behind choosing vacuum brazing lies in its unique advantages, which stem from performing the process inside a vacuum furnace. This environment fundamentally changes the nature of the joining process.
It Creates Ultra-Clean, Flux-Free Joints
The primary function of the vacuum is to remove oxygen and other atmospheric gases that cause oxidation at brazing temperatures.
This eliminates the need for corrosive chemical fluxes, which are typically required in other brazing processes to clean the metal surfaces. The result is a bright, clean assembly with no risk of flux entrapment or post-braze corrosion.
It Preserves Material Strength and Integrity
Vacuum furnaces allow for precise and uniform temperature control across the entire part, regardless of its complexity.
This slow, even heating and cooling cycle minimizes internal stresses and distortion, preserving the mechanical and thermal properties of the parent materials. The low heating temperature, relative to welding, ensures the base metal's core structure is minimally affected.
It Enables Complex and Inaccessible Geometries
Vacuum brazing is ideal for joining intricate assemblies, parts with very narrow gaps, or components with internal joints that would be impossible to reach with a torch.
Because the entire assembly is heated uniformly, the brazing filler metal can flow into tight capillaries and complex pathways via capillary action, ensuring a complete and robust joint throughout the part.
It Streamlines the Production Cycle
Modern vacuum furnaces can perform multiple thermal processes in a single, uninterrupted cycle.
This means that parts can be brazed, heat-treated, and age-hardened in one run. This consolidation is a significant advantage for high-volume production, improving efficiency and ensuring consistent quality from part to part.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, vacuum brazing is not the solution for every application. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
High Initial Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment. The equipment and the expertise required to operate it are far more complex and costly than those for simpler methods like torch or induction brazing.
Longer Cycle Times
The process of creating a vacuum, slowly heating to temperature, soaking, and then carefully cooling the parts can take several hours. While this controlled cycle is a benefit for part quality, it is slower than many alternative joining methods.
Material and Filler Metal Constraints
The vacuum environment is not suitable for all materials. Metals with high vapor pressures, such as zinc, cadmium, or magnesium, can outgas during the cycle, contaminating both the furnace and the component. Filler metals must also be selected carefully to have a low vapor pressure at the brazing temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing vacuum brazing depends entirely on your project's specific requirements for performance, quality, and cost.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint purity and strength: Vacuum brazing is the definitive choice for mission-critical parts like aerospace turbine blades, medical implants, or UHV scientific instruments.
- If your primary focus is joining complex assemblies: This process is ideal for micro-channel heat exchangers, sensor bodies, or any design with intricate, inaccessible joints.
- If your primary focus is combining heat treatment with joining: Vacuum brazing offers unmatched efficiency for high-volume parts that require specific post-braze hardness and strength properties.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, simple joints: Simpler methods like torch brazing or soldering are often more practical and cost-effective for applications where absolute cleanliness and minimal internal stress are not critical requirements.
Ultimately, vacuum brazing is the engineering solution for when the integrity of the joint and the performance of the final assembly cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace Components | Ultra-clean, high-strength joints | Turbine blades, structural parts |
| Medical Implants & Devices | Biocompatible, flux-free bonds | Surgical tools, implants |
| High-Performance Electronics | Reliable, leak-tight seals | Sensor housings, hermetic packages |
| Automotive & Energy | Complex geometries, stress minimization | Heat exchangers, fuel cells |
Need to join critical components with absolute reliability?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for demanding thermal processes like vacuum brazing. Our solutions help you achieve the flawless, high-strength bonds required for aerospace, medical, and electronics applications.
Let's discuss your project requirements and ensure your joints meet the highest standards of purity and performance.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Which element made stainless steel difficult to brazed? It's Chromium's Oxide Layer
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy
- What are some applications of brazing? Join Dissimilar Metals with Strong, Leak-Proof Bonds
- What are the factors that affect the strength of a brazed joint? Master the 4 Keys to a Perfect Bond



















