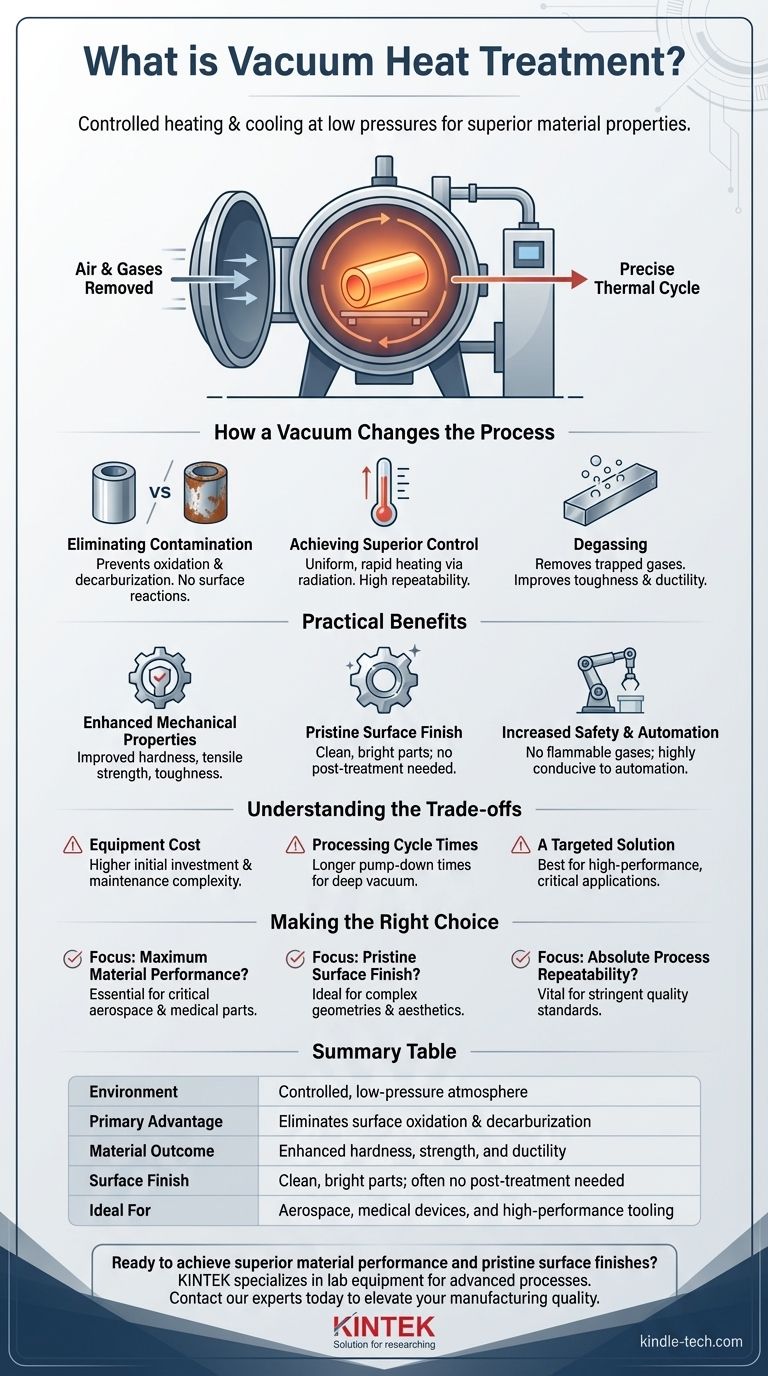
At its core, vacuum heat treatment is the process of heating and cooling metals in a controlled environment at pressures below atmospheric level. By removing air and other gases, this method prevents unwanted surface reactions like oxidation (rusting) and decarburization. This allows for precise manipulation of a material's properties—such as hardness, strength, and ductility—while producing a clean, bright part that often requires no further finishing.
The true value of vacuum heat treatment is not simply the absence of air; it is the unparalleled level of control and purity this environment provides, resulting in superior material properties, pristine surface finishes, and highly repeatable outcomes.

How a Vacuum Changes the Heat Treatment Process
To understand the benefits of this technology, it's essential to grasp how removing the atmosphere fundamentally alters the treatment environment. It is less a single technique and more a platform for achieving high-purity metallurgical results.
Eliminating Atmospheric Contamination
In a conventional furnace, the oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor in the air react with the hot metal surface. This can lead to oxidation (scaling) and decarburization (loss of carbon from the surface), both of which degrade the part's performance and appearance.
A vacuum chamber removes these reactive gases. This preserves the material's original surface chemistry and luster, eliminating the need for costly and time-consuming post-treatment cleaning processes like sandblasting or acid pickling.
Achieving Superior Process Control
The vacuum environment allows for extremely uniform and rapid heating and cooling. Without air to transfer heat unpredictably, thermal energy is applied more directly and evenly, typically through radiation.
This high degree of control ensures that every part in a batch, and every batch over time, receives the exact same treatment. This repeatability is critical for industries like aerospace and medical devices where consistency is non-negotiable.
Degassing for Internal Material Integrity
Many metals contain dissolved gases, such as hydrogen, which can cause internal defects and lead to embrittlement. The low-pressure environment of a vacuum furnace effectively pulls these trapped gases out of the metal.
This degassing effect significantly improves the material's toughness, ductility, and fatigue resistance, leading to a longer and more reliable service life for the finished component.
The Practical Benefits of a Vacuum Environment
The precise, clean, and controlled nature of vacuum heat treatment translates directly into tangible advantages for manufactured components.
Enhanced Mechanical Properties
By preventing negative surface reactions and removing harmful internal gases, the process allows the material to achieve its full potential. The result is improved hardness, tensile strength, toughness, and overall functionality.
Pristine Surface Finish
Components treated in a vacuum emerge from the furnace clean, bright, and free of discoloration or scale. This is especially valuable for parts where the final surface finish is critical or for complex geometries that are difficult to clean after treatment.
Increased Safety and Automation
Vacuum furnaces do not use flammable or explosive gases as part of their standard operation, creating a much safer work environment. The entire process is also highly conducive to automation, ensuring precise execution and reducing the potential for human error.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum heat treatment is not the ideal solution for every application. Acknowledging its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Equipment Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are technologically sophisticated and represent a significantly higher capital investment than traditional atmospheric furnaces. The pumps, seals, and control systems required add to both the initial cost and ongoing maintenance complexity.
Processing Cycle Times
Achieving a deep vacuum requires time to pump down the chamber before the heating cycle can even begin. This can result in longer overall cycle times compared to continuous atmospheric furnaces, making it better suited for batch production rather than high-volume, low-margin parts.
A Targeted Solution
For many common applications where a small amount of surface oxidation is acceptable or will be removed by subsequent machining, the precision of vacuum treatment may be unnecessary. It is an investment best reserved for materials and components that demand the highest level of quality and performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the decision to use vacuum heat treatment depends entirely on the requirements of your final product.
- If your primary focus is maximum material performance: The degassing and contamination prevention of a vacuum process is essential for critical components in aerospace, medical, and high-performance tooling.
- If your primary focus is a pristine, ready-to-use surface: Vacuum treatment eliminates the need for post-processing cleaning, making it ideal for finished goods with complex geometries or aesthetic requirements.
- If your primary focus is absolute process repeatability: The precise control over temperature and environment ensures that parts are produced with exceptional consistency, vital for meeting stringent quality standards.
Choosing vacuum heat treatment is an investment in control, purity, and predictable, high-quality results.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Environment | Controlled, low-pressure atmosphere |
| Primary Advantage | Eliminates surface oxidation and decarburization |
| Material Outcome | Enhanced hardness, strength, and ductility |
| Surface Finish | Clean, bright parts; often no post-treatment needed |
| Ideal For | Aerospace, medical devices, and high-performance tooling |
Ready to achieve superior material performance and pristine surface finishes?
KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables that power advanced processes like vacuum heat treatment. Our expertise ensures you have the right tools for unparalleled control, purity, and repeatable results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs and elevate your manufacturing quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Hot Zone Materials and Processed Metals
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What does a vacuum furnace do? Achieve High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Components
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? Selecting the Right Hot Zone for Your Process
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost



















