In essence, a vacuum sintering furnace is a highly specialized industrial oven that heats materials in a controlled, low-pressure environment instead of in open air. Its primary function is to fuse powdered materials into a solid mass at high temperatures without allowing them to react with oxygen or other atmospheric gases. This process prevents contamination and oxidation, resulting in materials with superior purity, density, and performance characteristics.
The critical takeaway is that a vacuum furnace isn't just about heat; it's about absolute atmospheric control. By removing the air, you eliminate unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation, enabling the creation of advanced materials that would be impossible to produce in a conventional furnace.
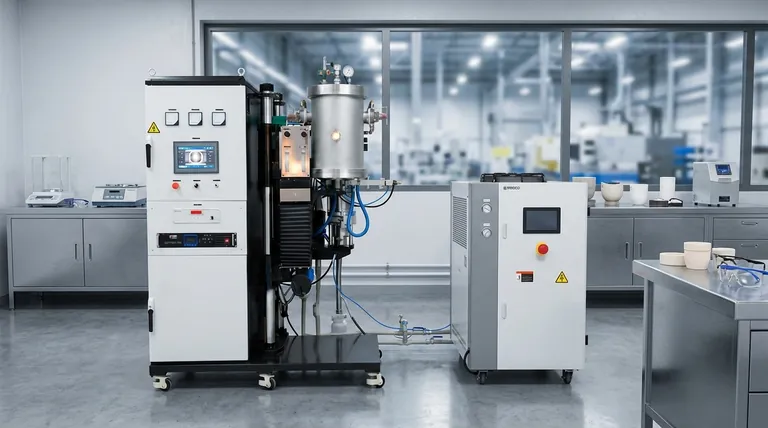

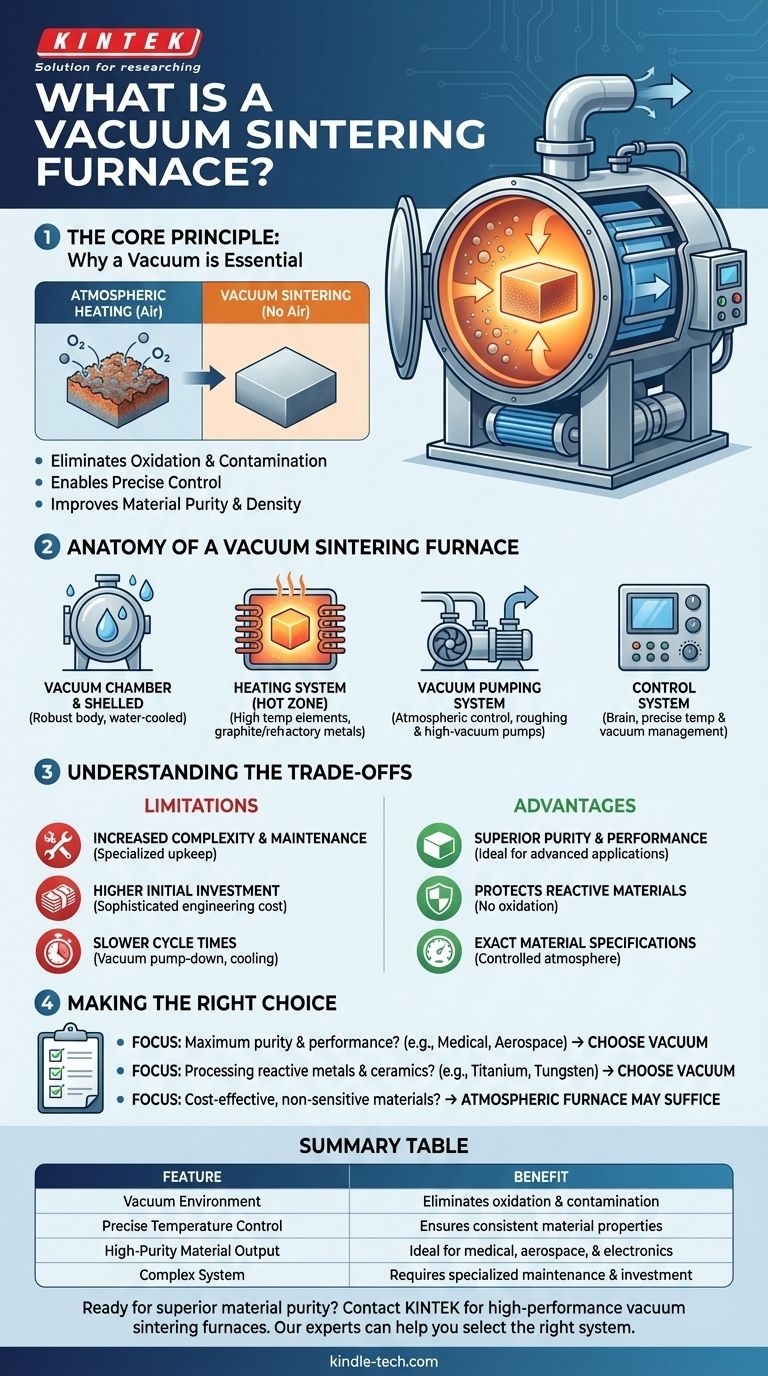
The Core Principle: Why a Vacuum is Essential
The defining feature of this technology is the vacuum. At the high temperatures required for sintering, most materials become highly reactive. The vacuum environment directly addresses this fundamental challenge.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
In a normal atmosphere, heating a material causes it to react with oxygen, forming an oxide layer. This oxidation can weaken the final product or change its properties entirely. By evacuating the chamber, the furnace removes virtually all oxygen and other reactive gases, preserving the material's chemical integrity.
Enabling Precise Control
The vacuum environment provides a clean, neutral baseline. This allows operators to maintain a pure vacuum or to intentionally introduce specific, high-purity inert gases like argon. This level of control is crucial for achieving exact material specifications.
Improving Material Purity and Density
Without the interference of atmospheric gases, material particles can bond more effectively. This results in a final product that is denser, stronger, and free from the microscopic voids and impurities that can form during atmospheric heating.
Anatomy of a Vacuum Sintering Furnace
A vacuum furnace is a complex system where several key components work in concert to manage temperature and pressure with extreme precision.
The Vacuum Chamber and Shell
This is the sealed, robust body of the furnace. It is engineered to withstand both the intense internal heat and the powerful external pressure created by the vacuum. A water-cooling system is typically integrated into the shell to prevent it from overheating.
The Heating System (Hot Zone)
Located inside the chamber, the hot zone contains the heating elements that generate the required high temperatures. These elements can be made of graphite or refractory metals and use methods like electrical resistance or induction to heat the material.
The Vacuum Pumping System
This is the heart of the furnace's atmospheric control. It typically consists of a series of pumps—often a roughing pump paired with a high-vacuum pump (like a diffusion or turbomolecular pump)—that work together to evacuate air from the chamber and achieve the target low-pressure state.
The Control System
The furnace's brain is a sophisticated electronic system that manages every stage of the process. It precisely controls the heating rates, holds the material at a specific temperature (known as "soaking"), controls the cooling rates, and maintains the vacuum level.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, vacuum sintering is not the solution for every application. Its advantages come with specific trade-offs that are critical to understand.
Increased Complexity and Maintenance
The combination of high-temperature, high-vacuum, and electronic control systems makes these furnaces complex. Components like vacuum pumps and hot zones require regular, specialized maintenance to ensure reliable operation.
Higher Initial Investment
The sophisticated engineering and materials required to build a furnace that can safely handle extreme temperatures and pressures result in a significantly higher upfront cost compared to conventional atmospheric furnaces.
Slower Cycle Times
Achieving a deep vacuum is not instantaneous. The time required to pump down the chamber before heating and to safely cool the material before venting adds to the overall cycle time, potentially limiting throughput.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use this technology depends entirely on your material and final performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and performance: For applications like medical implants, aerospace components, or advanced electronics, the clean environment of a vacuum furnace is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive metals and ceramics: Materials like titanium, tungsten, and certain advanced ceramics will be ruined by oxidation, making a vacuum furnace the only viable option.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of non-sensitive materials: For basic ceramics or metals that are not harmed by air exposure, a conventional atmospheric furnace is a far more practical and economical choice.
Ultimately, understanding the furnace's core function—precise atmospheric control—is the key to leveraging its power for advanced material innovation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Environment | Eliminates oxidation and contamination |
| Precise Temperature Control | Ensures consistent material properties |
| High-Purity Material Output | Ideal for medical, aerospace, and electronics |
| Complex System | Requires specialized maintenance and investment |
Ready to achieve superior material purity and performance? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including vacuum sintering furnaces designed for critical applications in medical, aerospace, and advanced ceramics. Our experts will help you select the right system to meet your precise material specifications. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can support your innovation goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why must green bodies produced via binder jetting undergo treatment in a vacuum sintering furnace?
- Does sintering use diffusion? The Atomic Mechanism for Building Stronger Materials
- How does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace facilitate the post-treatment of Zirconia coatings?
- Why is a high vacuum environment necessary in sintering equipment for TiAl alloys? Ensure High-Purity Metal Bonding
- What is sintering reaction? Transform Powders into Dense Solids Without Melting



















