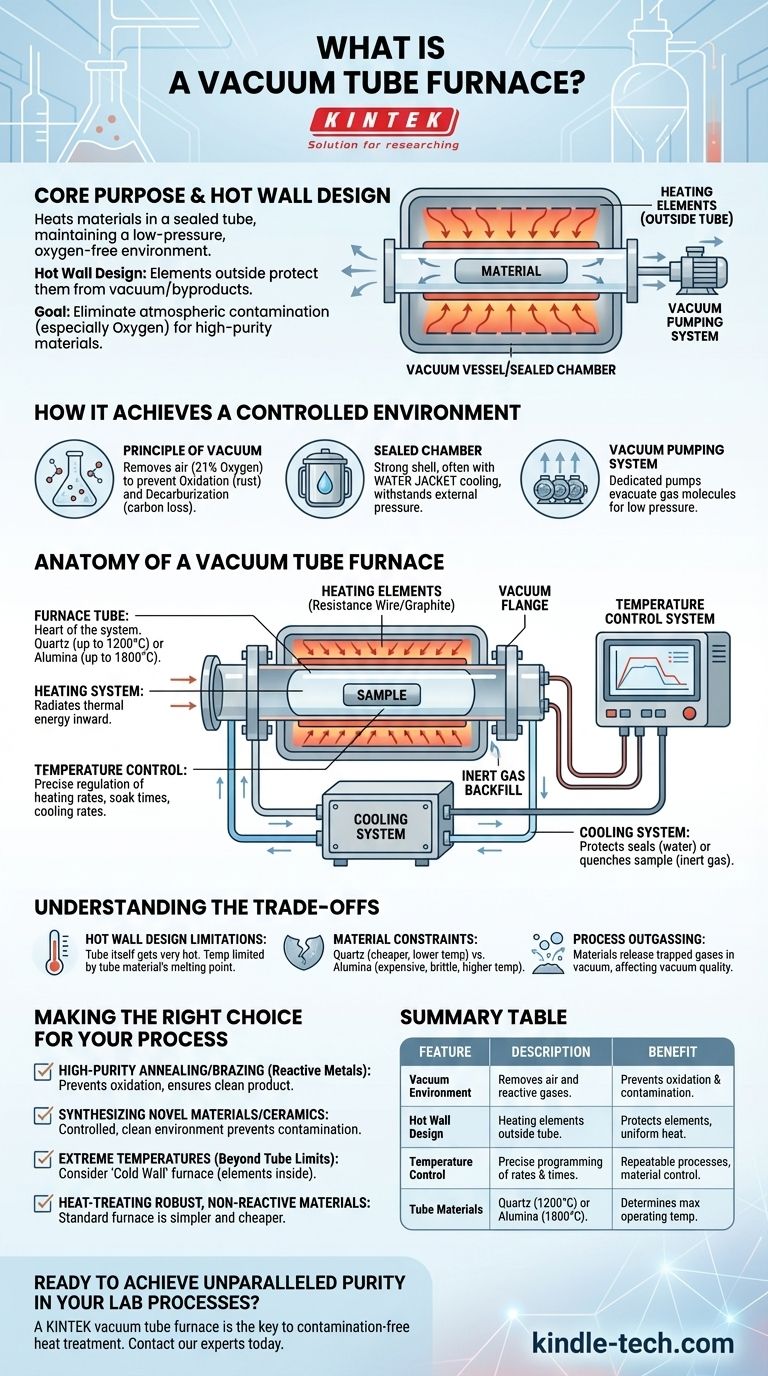
A vacuum tube furnace is a type of laboratory or industrial furnace that heats materials inside a sealed tube while maintaining a low-pressure, oxygen-free environment. Its defining feature is that the heating elements are located outside the tube, transferring thermal energy through the tube's walls to the sample within. This "hot wall" design protects the heating elements from the vacuum and any process byproducts.
The core purpose of a vacuum tube furnace is to eliminate atmospheric contamination, primarily oxygen, during high-temperature processing. This prevents unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation, allowing for the creation of higher-purity materials with precisely controlled properties.

How a Vacuum Furnace Achieves a Controlled Environment
A vacuum furnace's unique capabilities stem from its ability to manipulate the atmosphere surrounding the material being processed.
The Principle of Vacuum
The fundamental goal is to remove the air from the furnace chamber. Air contains approximately 21% oxygen and other reactive gases that can damage sensitive materials at high temperatures.
By creating a vacuum, these reactive gases are evacuated, preventing processes like oxidation (rusting or tarnishing) and decarburization (the loss of carbon content from steel).
The Role of the Sealed Chamber
The entire system is housed within a sealed furnace shell, also known as the vacuum vessel. This chamber must be robust enough to withstand the atmospheric pressure pushing in from the outside when a vacuum is pulled inside.
These shells are typically constructed from steel plates and often feature a double-layer "water jacket" structure for active cooling, which protects seals and the integrity of the chamber.
The Vacuum Pumping System
A dedicated vacuum system, consisting of one or more pumps, is responsible for evacuating the air from the sealed tube. This system removes gas molecules to achieve the low-pressure environment required for the process.
The Anatomy of a Vacuum Tube Furnace
While designs vary, all vacuum tube furnaces share a common set of essential components that work together.
The Furnace Tube
This is the heart of the system. The material to be heated is placed inside this tube. The tube's material—commonly quartz or a ceramic like alumina—is the primary factor determining the furnace's maximum operating temperature. The ends of the tube are sealed with vacuum flanges to maintain the low-pressure environment.
The Heating System
Heating elements, typically a form of resistance wire or graphite heater, are positioned around the exterior of the furnace tube. An electrical current is passed through these elements, causing them to heat up and radiate thermal energy inward through the tube walls.
The Temperature Control System
This is the brain of the furnace. A sophisticated control system manages the power supplied to the heating elements, allowing for precise regulation of the temperature. It enables operators to program specific heating rates, soak times (holding at a peak temperature), and cooling rates.
The Cooling System
Cooling is just as critical as heating. Many furnaces use a water cooling system to circulate water through the furnace shell and around the vacuum flanges. This prevents the rubber O-ring seals from overheating and failing.
For rapidly cooling the material itself (a process called quenching), the system can be backfilled with a high-pressure inert gas, such as argon or nitrogen, which absorbs heat and circulates it away.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum tube furnaces have specific characteristics that make them suitable for some tasks but not others.
Hot Wall Design Limitations
In a vacuum tube furnace, the tube itself gets extremely hot. This is known as a hot wall design. The main limitation is that the process temperature can never exceed the melting or softening point of the tube material.
Material Constraints
The choice of tube material dictates the furnace's performance. Quartz is common and relatively inexpensive but is typically limited to around 1100-1200°C. High-purity alumina tubes can reach much higher temperatures (e.g., 1700-1800°C) but are more expensive and brittle.
Process Outgassing
When materials are heated in a vacuum, they can release trapped gases, a phenomenon called outgassing. This can degrade the quality of the vacuum during a process and must be managed by the pumping system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Use these guidelines to determine if a vacuum tube furnace fits your objective.
- If your primary focus is high-purity annealing or brazing of reactive metals: A vacuum furnace is essential to prevent oxidation and ensure a clean, strong final product.
- If you are synthesizing novel materials or firing ceramics where contamination is a concern: The controlled, clean environment of a vacuum furnace is a significant advantage.
- If your process requires temperatures beyond the limits of available tube materials: You may need to investigate a "cold wall" furnace, where the heating elements are located inside the vacuum chamber itself.
- If you are simply heat-treating robust, non-reactive materials in air: A standard, non-vacuum atmosphere furnace is a much simpler and more cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, a vacuum tube furnace provides an unparalleled level of atmospheric control, enabling processes that are impossible to achieve in a conventional furnace.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Environment | Removes air and reactive gases from the sealed tube. | Prevents oxidation and contamination of sensitive materials. |
| Hot Wall Design | Heating elements are located outside the furnace tube. | Protects heating elements and allows for uniform heat transfer. |
| Temperature Control | Precise programming of heating rates, soak times, and cooling. | Enables repeatable processes and exact material property control. |
| Tube Materials | Typically quartz (up to 1200°C) or alumina (up to 1800°C). | Determines maximum operating temperature and process compatibility. |
Ready to achieve unparalleled purity in your lab processes? A vacuum tube furnace from KINTEK is the key to contamination-free heat treatment, sintering, and materials synthesis. Our expertise in lab equipment ensures you get the right solution for your specific needs, whether you're working with reactive metals, advanced ceramics, or novel materials. Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK vacuum furnace can enhance your research and production outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of tubular furnace? Precision Heating for Research & Small-Batch Production
- What role does a tube furnace play in LLZTO sintering? Master Phase Purity and Densification in Solid Electrolytes
- What is the allowable stress for a quartz tube? Understanding Its Brittle Nature and Practical Limits
- What role do high-temperature sintering or tube furnaces play in biomass catalysts? Engineering the Carbon Skeleton
- How hot does a quartz test tube get? Unlock Superior Heat Resistance for Your Lab
- What is the high temperature of a tube furnace? Unlock the Right Model for Your Application
- What is the role of tube furnaces and TGA in biomass torrefaction? Optimize Your Fuel Research Parameters
- What are the primary functions of high-temperature tube furnaces? Master Iron Oxide Nanoparticle Synthesis



















