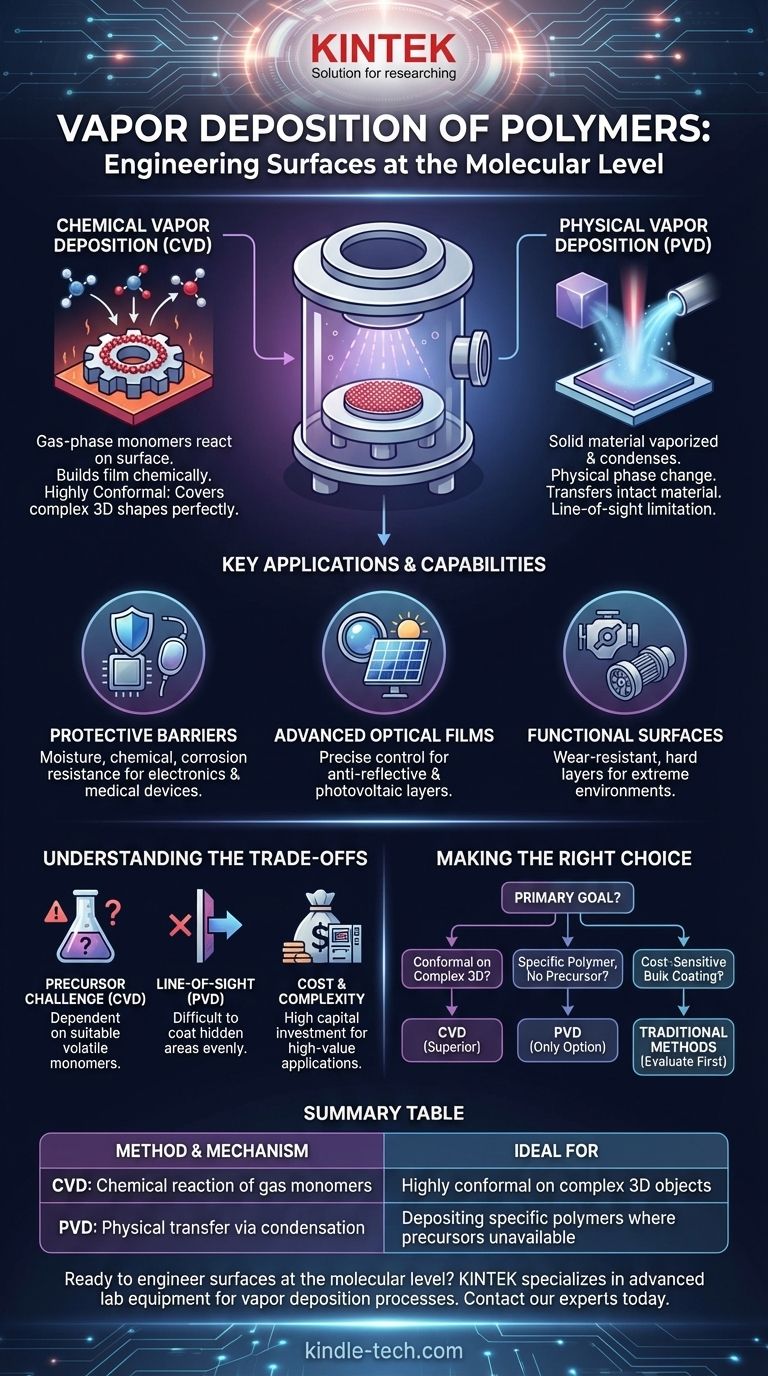
Vapor deposition of polymers is a family of advanced manufacturing techniques used to create ultra-thin, high-purity polymer films on a substrate. The process works by converting the polymer or its chemical precursors into a gaseous state within a vacuum chamber, which then deposits onto the target object's surface to form a solid, uniform coating. The two primary methods for this are Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
The core value of vapor deposition is not simply coating an object, but engineering a surface at the molecular level. This enables the creation of highly functional, conformal, and defect-free polymer layers that are impossible to achieve with traditional liquid-based methods like painting or spin-coating.

The Two Core Pathways: CVD vs. PVD
Understanding the distinction between chemical and physical deposition is fundamental. The choice between them depends entirely on the material you are using and the properties you need in the final film.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Building a Film from Monomers
In CVD, volatile precursor molecules, known as monomers, are introduced into a reaction chamber in a gaseous state.
These gases interact with the heated surface of the substrate, triggering a chemical reaction. This reaction synthesizes the polymer directly on the surface, building the film molecule by molecule.
This process ensures an exceptionally conformal coating, meaning it can uniformly cover even highly complex, three-dimensional shapes without defects.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): Transferring an Intact Material
In PVD, the starting material is a solid polymer. This source material is vaporized inside a vacuum chamber, typically using heat (thermal evaporation) or an electron beam (e-beam evaporation).
The resulting polymer vapor then travels through the vacuum and condenses onto the cooler surface of the substrate, forming a thin film.
PVD is fundamentally a physical process of phase change—solid to gas to solid again. It does not involve a chemical reaction on the target surface.
Key Applications and Material Capabilities
The precision of vapor deposition enables performance characteristics that are critical in high-tech industries. It is used not for simple aesthetics, but for essential functionality.
Protective Barriers in Electronics and Medical Devices
The ultra-thin, pinhole-free films created by vapor deposition serve as excellent barriers against moisture, chemicals, and corrosion.
This is vital for protecting sensitive electronic components in packaging or encapsulating medical implants to ensure biocompatibility and prevent degradation.
Advanced Optical and Photovoltaic Films
Vapor deposition allows for precise control over a film's thickness, density, and refractive index.
This capability is used to create anti-reflective coatings, specialized layers in holographic displays, and thin-film photovoltaic materials for efficient solar cells.
Functional Surfaces for Automotive and Aerospace
In the automotive and aerospace industries, these coatings can impart critical surface properties.
They can create hard, wear-resistant layers on tools and components or apply dense, temperature-resistant coatings to parts that must endure extreme environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vapor deposition is not a universal solution. The technical requirements and costs necessitate a clear understanding of its limitations.
The Challenge of Precursor Materials
For polymer CVD, the process is entirely dependent on the availability of suitable monomer precursors that are volatile and react cleanly. Finding the right precursors for a specific polymer can be a significant research and development challenge.
The Limitation of Line-of-Sight (PVD)
Many PVD techniques are "line-of-sight," meaning the vaporized material travels in a straight line to the substrate. This can make it difficult to uniformly coat hidden areas or complex internal geometries.
Cost and Process Complexity
Vapor deposition systems require significant capital investment in vacuum chambers, gas handling systems, and power supplies. The processes are slower and more complex than simple painting or dipping, making them best suited for high-value applications where performance is non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate deposition strategy requires matching the technique's strengths to your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is a highly conformal, pinhole-free coating on a complex 3D object: CVD is likely the superior choice because the gas-phase precursors can reach and react on all exposed surfaces.
- If your primary focus is depositing a specific, complex polymer that lacks a suitable chemical precursor: PVD may be your only option, as it physically transfers the source material without needing to synthesize it on the surface.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive bulk coating on simple shapes: You should first evaluate traditional liquid-based methods, as vapor deposition is a high-performance, higher-cost solution reserved for demanding applications.
Ultimately, vapor deposition empowers you to engineer polymer surfaces with a level of precision that unlocks new technological capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Mechanism | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Chemical reaction of gas-phase monomers on the substrate surface. | Highly conformal, pinhole-free coatings on complex 3D objects. |
| Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) | Physical transfer of vaporized polymer via condensation. | Depositing specific polymers where chemical precursors are unavailable. |
Ready to engineer surfaces at the molecular level?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment for vapor deposition processes. Whether you are developing protective barriers for medical devices, optical films for photovoltaics, or wear-resistant coatings for aerospace components, our solutions empower your R&D and production.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our polymer deposition systems can bring precision and high performance to your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the floating catalyst method? A Guide to High-Yield CNT Production
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques
- What are the advantages of industrial CVD for solid boriding? Superior Process Control and Material Integrity
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition



















