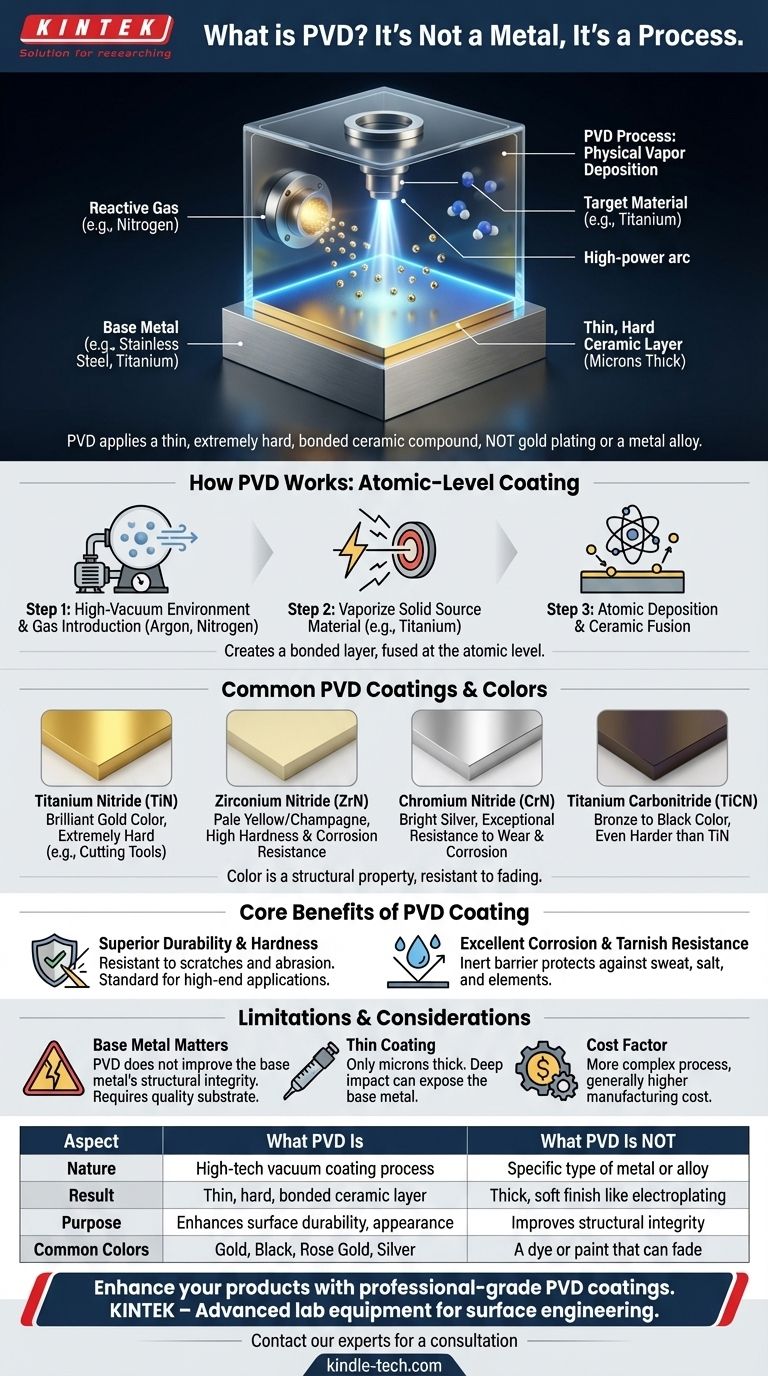
Contrary to a common misconception, PVD is not a type of metal. Instead, PVD—which stands for Physical Vapor Deposition—is a high-tech vacuum coating process. It applies a very thin, but extremely hard and durable, layer of a ceramic compound onto the surface of a base metal, like stainless steel or titanium.
The crucial takeaway is that PVD is not a material itself, but an advanced manufacturing process that fundamentally enhances the durability, wear resistance, and appearance of the metal it is applied to. The quality of a PVD-coated product depends on both the coating and the quality of the underlying base metal.

What is PVD? A Deeper Look
Not a Metal, But a Process
PVD is a method for producing a metal vapor that can be deposited on electrically conductive materials. It is not an alloy or a specific element but a sophisticated technique for surface engineering.
This process is fundamentally different from older methods like electroplating or powder coating, which often result in thicker, softer, and less durable finishes.
How PVD Works: The Science Simplified
The PVD process is like atomic-level spray painting and takes place inside a high-vacuum chamber.
First, the item to be coated is placed in the chamber, and the air is pumped out to create a near-perfect vacuum. A small amount of a specific gas, like argon, is introduced.
Next, a high-power electric arc is used to vaporize a solid source material (the "target"). This target is made of the material that will form the final coating, such as titanium.
The vaporized metal atoms then react with a gas (like nitrogen) inside the chamber and are deposited onto the product, molecule by molecule. This creates a bonded, ceramic layer that is atomically fused to the surface of the base metal.
The "PVD Metal" You're Actually Seeing
When you see a product advertised with a gold, black, or rose gold "PVD finish," you are not seeing gold plating. You are seeing a thin layer of a specific ceramic compound.
- Titanium Nitride (TiN): This is the most common PVD coating. It produces a brilliant gold-like color and is extremely hard, often used on cutting tools and drill bits.
- Zirconium Nitride (ZrN): Produces a pale yellow or champagne gold color, also known for its high hardness and excellent corrosion resistance.
- Chromium Nitride (CrN): Offers a bright, metallic silver color with exceptional resistance to wear and corrosion.
- Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN): Can produce colors from bronze to violet to black, depending on the composition. It is even harder than TiN.
The color of the PVD coating is a structural property of the material being deposited, not a dye, which is why it is so resistant to fading.
The Core Benefits of PVD Coating
Superior Durability and Hardness
PVD coatings are exceptionally hard and highly resistant to scratches and abrasion. This is why PVD is the standard for high-end watch bracelets, premium faucets, and industrial tools.
A PVD finish is significantly more durable than traditional electroplating, which can easily flake or wear away with use.
Excellent Corrosion and Tarnish Resistance
The ceramic layer created by PVD acts as an inert barrier. It protects the base metal from exposure to sweat, salt, air, and other elements that cause tarnish and corrosion.
This makes it an ideal finish for items in constant contact with skin, like jewelry and watches, or items used in harsh environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
"PVD" Is Not a Universal Guarantee of Quality
The most critical point to understand is that the PVD process does not improve the structural integrity of the base metal.
A durable PVD coating on a cheap, soft base metal (like a zinc alloy) will still dent and deform easily. A premium product will feature a PVD coating on a high-quality base metal like 316L stainless steel or titanium.
The Coating is Thin
While incredibly hard, PVD coatings are typically only a few microns thick. They can resist surface scratches from daily wear, but a deep gouge from a sharp impact can penetrate the coating and expose the base metal underneath.
The Cost Factor
The PVD process requires sophisticated machinery and is more complex than other coating methods. This adds to the manufacturing cost, which is why PVD-coated products are generally more expensive than their uncoated or electroplated counterparts.
Making an Informed Decision
When evaluating a product, view PVD as a feature that enhances performance, not as the core material itself.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability: Look for a PVD coating on a high-quality base metal like surgical-grade stainless steel or titanium.
- If your primary focus is aesthetic appeal: PVD offers superior, fade-resistant color compared to plating, but always verify the base metal to ensure the product's overall quality.
- If your primary focus is value for money: PVD is a worthwhile investment for items you will use frequently and want to keep looking new, such as a daily watch or kitchen hardware.
Ultimately, understanding PVD allows you to look past the marketing label and evaluate the true quality of the product in your hands.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | What PVD Is | What PVD Is NOT |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | A high-tech vacuum coating process | A specific type of metal or alloy |
| Result | A thin, hard, bonded ceramic layer (e.g., Titanium Nitride) | A thick, soft finish like electroplating |
| Purpose | Enhances surface durability, corrosion resistance, and appearance | Improves the structural integrity of the base metal |
| Common Colors | Gold (TiN), Black (TiCN), Rose Gold, Silver (CrN) | A dye or paint that can easily fade |
Enhance your products with professional-grade PVD coatings.
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables for surface engineering applications. Our expertise supports industries that require durable, high-performance coatings for tools, medical devices, and consumer goods. Whether you are developing new products or improving existing ones, our solutions can help you achieve superior wear resistance, corrosion protection, and aesthetic appeal.
Let's discuss how our PVD technology can add value to your laboratory or manufacturing process. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings



















