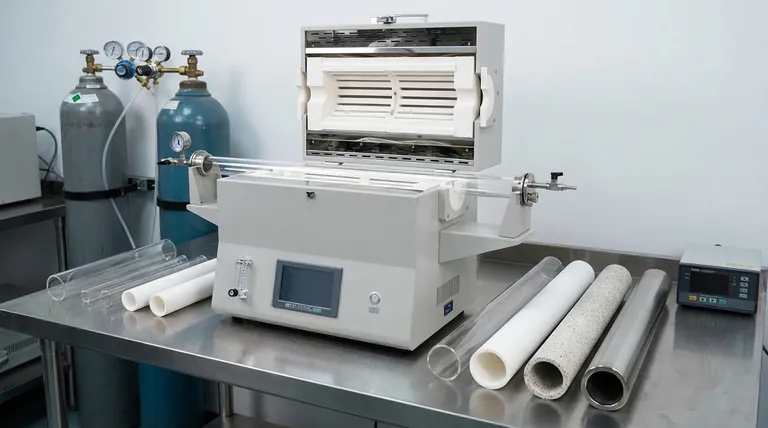
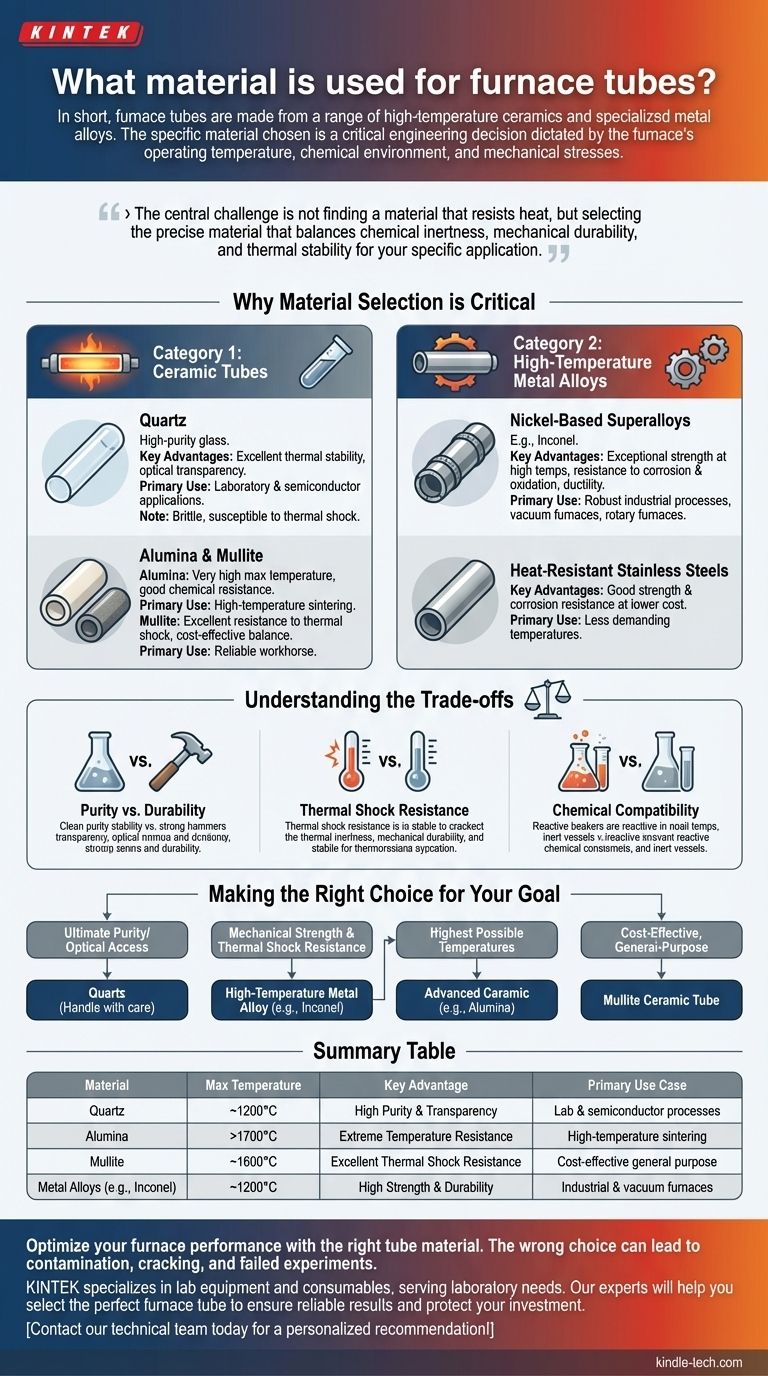
In short, furnace tubes are made from a range of high-temperature ceramics and specialized metal alloys. The specific material chosen is not arbitrary; it is a critical engineering decision dictated by the furnace's operating temperature, the chemical environment of the process, and the mechanical stresses involved.
The central challenge is not finding a material that resists heat, but selecting the precise material that balances chemical inertness, mechanical durability, and thermal stability for your specific application. There is no single "best" material, only the most appropriate one for the job.

Why Material Selection is Critical
A furnace tube's primary role is to create a controlled, isolated environment. It contains the desired atmosphere—be it a vacuum, an inert gas, or reactive air—and separates the material being processed from the furnace's heating elements.
The tube material is the barrier between your high-value process and the outside world. An incorrect choice can lead to process contamination, equipment failure, and compromised results.
Category 1: Ceramic Tubes
Ceramic tubes are valued for their ability to withstand extremely high temperatures and their chemical inertness.
Quartz Quartz is a form of high-purity glass. It is often the default choice for laboratory and semiconductor applications where purity is paramount.
Its key advantages are excellent thermal stability and optical transparency, which allows for visual monitoring of processes like crystal growth. However, quartz is brittle and highly susceptible to thermal shock—rapid temperature changes can cause it to crack.
Alumina and Mullite For temperatures exceeding the limits of quartz, or for applications requiring greater mechanical strength, advanced ceramics like Alumina (Al2O3) or Mullite are used.
Alumina offers a very high maximum operating temperature and good chemical resistance. Mullite provides a cost-effective balance of thermal performance and excellent resistance to thermal shock, making it a reliable workhorse material.
Category 2: High-Temperature Metal Alloys
When durability, ductility, and resistance to mechanical stress are the main concerns, metal alloys are the superior choice.
Nickel-Based Superalloys Alloys like Inconel are frequently used for their exceptional strength at high temperatures and resistance to corrosion and oxidation. They are far less brittle than ceramics and can withstand rapid heating and cooling cycles without failure.
This makes them ideal for robust industrial processes, vacuum furnace applications, and any setup where the tube might experience physical stress, such as a rotary furnace.
Heat-Resistant Stainless Steels For less demanding temperatures, certain grades of stainless steel offer a good combination of strength and corrosion resistance at a lower cost than nickel-based superalloys.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace tube material is a matter of balancing competing priorities. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for making an informed decision.
Purity vs. Durability
This is the classic dilemma. Quartz offers the highest purity but is fragile. Metal alloys offer supreme durability but can introduce trace metallic contaminants into a highly sensitive process. For applications like vacuum sintering, this is managed by using non-metallic inner liners inside a strong metal tube.
Thermal Shock Resistance
If your process involves rapid heating or cooling, a ceramic tube (especially quartz) is a high-risk choice. Metal alloys or thermal shock-resistant ceramics like Mullite are far better suited for these conditions.
Chemical Compatibility
The tube material must not react with your process gases or the material being heated. While most common materials are inert, highly reactive or corrosive environments at high temperatures can degrade the tube, compromising both the equipment and the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be guided by the single most important parameter of your work.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity or optical access: Choose a quartz tube, but be mindful of its fragility and handle it with care.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance: A high-temperature metal alloy like Inconel is the most reliable option.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible temperatures: An advanced ceramic like high-purity Alumina is necessary.
- If your primary focus is a cost-effective, general-purpose solution: A Mullite ceramic tube offers a superb balance of performance for many common applications.
By carefully evaluating your process parameters against these material properties, you can select a furnace tube that ensures both reliable operation and successful results.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature | Key Advantage | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz | ~1200°C | High Purity & Transparency | Lab & semiconductor processes |
| Alumina | >1700°C | Extreme Temperature Resistance | High-temperature sintering |
| Mullite | ~1600°C | Excellent Thermal Shock Resistance | Cost-effective general purpose |
| Metal Alloys (e.g., Inconel) | ~1200°C | High Strength & Durability | Industrial & vacuum furnaces |
Optimize your furnace performance with the right tube material. The wrong choice can lead to contamination, cracking, and failed experiments. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts will help you select the perfect furnace tube—whether you need the ultimate purity of quartz, the extreme temperature resistance of alumina, or the rugged durability of a metal alloy—to ensure reliable results and protect your investment. Contact our technical team today for a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process



















