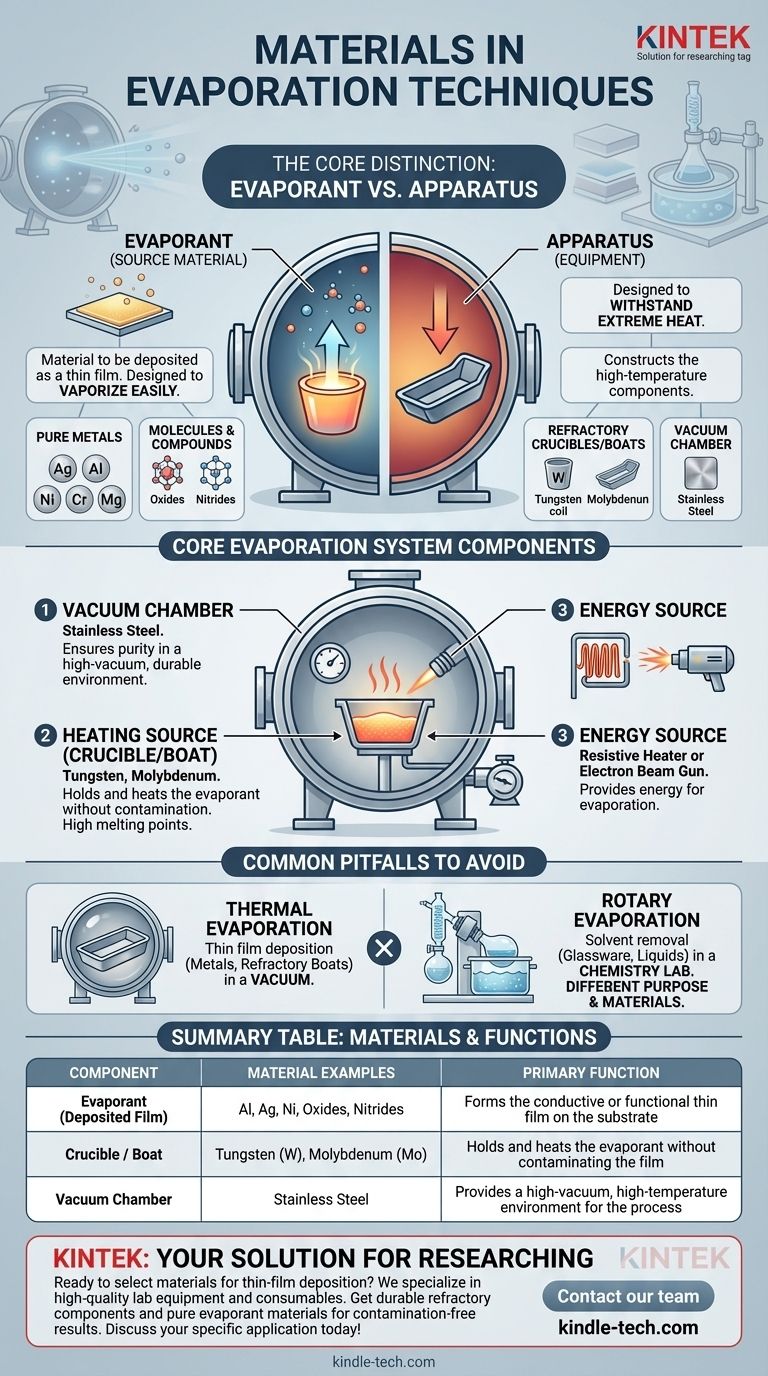
Materials used in evaporation techniques fall into two primary categories: the source materials being deposited as a thin film, such as pure metals like aluminum and silver, and the specialized refractory materials like tungsten or molybdenum used to construct the high-temperature components of the equipment itself. The entire process takes place within a stainless steel vacuum chamber.
The critical distinction in thermal evaporation is between the evaporant (the material you are depositing) and the apparatus (the crucible and chamber holding it). The properties required for each—one designed to vaporize easily and the other designed to withstand extreme heat—are fundamentally different.
The Core Components of an Evaporation System
To understand the materials involved, we must first look at the equipment that makes the process possible. Each component is chosen for its ability to function under high-vacuum and high-temperature conditions.
The Vacuum Chamber
The process is conducted in a high-vacuum environment to ensure the purity of the deposited film. These chambers are typically made from stainless steel due to its durability, low reactivity, and ability to maintain a vacuum.
The Heating Source (Crucible or Boat)
The material to be deposited (the evaporant) is held in a container, often called a boat or crucible, which is heated to induce evaporation.
These crucibles must be made from refractory materials, which have extremely high melting points and low vapor pressures. Common choices include tungsten and molybdenum. This ensures the boat itself does not evaporate and contaminate the film.
The Energy Source
Heating is achieved through a powerful energy source. This can be a resistive heater, which passes a large electrical current through the crucible, or an electron beam gun, which fires a focused beam of electrons at the evaporant.
Materials That Can Be Deposited (Evaporants)
The "evaporant" is the source material that is turned into a vapor and then deposits as a thin film onto a substrate. A wide variety of materials can be used, depending on the desired properties of the final film.
Pure Atomic Elements
Metals are the most common class of materials deposited via thermal evaporation due to their excellent conductive and reflective properties.
Common examples include:
- Aluminum (Al)
- Silver (Ag)
- Nickel (Ni)
- Chromium (Cr)
- Magnesium (Mg)
Molecules and Compounds
The technique is not limited to pure elements. Certain molecules can also be evaporated, though the process requires more careful control to prevent them from breaking down.
These can include dielectrics and other functional materials like oxides and nitrides.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
A common point of confusion arises because the term "evaporation" is used in different scientific contexts. Understanding the distinction is crucial for selecting the right materials and process.
Thermal Evaporation vs. Rotary Evaporation
Thermal evaporation, as described here, is a materials science technique for depositing solid thin films in a vacuum. It involves metals and refractory boats.
Rotary evaporation, on the other hand, is a chemistry lab technique used to gently remove solvents from a liquid sample. It uses a different apparatus, including a glass flask, a chiller (often with ethylene glycol), and a vacuum pump, but its purpose and materials are entirely different from thin-film deposition.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your material selection is dictated entirely by your final objective.
- If your primary focus is creating a conductive metallic film: You will use an evaporant like aluminum or silver, which will be heated in a high-temperature crucible made of tungsten.
- If your primary focus is depositing a dielectric layer: You may use a material like a metal oxide, requiring precise control over the heating process to ensure the compound evaporates without decomposing.
- If your primary focus is purifying a chemical sample: You are looking for rotary evaporation, which involves glassware and liquid solvents, not the metal deposition process.
Ultimately, choosing the right materials begins with clearly defining your application and understanding the distinct role each material plays in the process.
Summary Table:
| Component | Material Examples | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Evaporant (Deposited Film) | Aluminum (Al), Silver (Ag), Nickel (Ni) | Forms the conductive or functional thin film on the substrate |
| Crucible / Boat | Tungsten (W), Molybdenum (Mo) | Holds and heats the evaporant without contaminating the film |
| Vacuum Chamber | Stainless Steel | Provides a high-vacuum, high-temperature environment for the process |
Ready to select the perfect materials for your thin-film deposition project?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for evaporation techniques. We provide the durable refractory components and pure evaporant materials you need for reliable, contamination-free results. Our experts can help you choose the right setup for depositing conductive metals or delicate compounds.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and ensure optimal performance for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- E Beam Crucibles Electron Gun Beam Crucible for Evaporation
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is the evaporation method of deposition? A Guide to High-Speed Thin Film Coating
- What are the safety precautions for evaporation? Essential Steps for Managing Flammability, Bumping, and Implosion Risks
- What is the effect of substrate temperature on sputtering? Master Film Density, Crystallinity, and Stress
- Why is sputtering deposition slower than evaporation? Unpacking the Physics of PVD Rates
- What is the principle of physical vapor deposition? A Guide to the PVD Process
- Why is an alumina boat selected for catalyst precursors? Ensure Sample Purity at 1000 °C
- What is the vacuum thermal evaporation deposition technique? A Simple Guide to Thin-Film Coating
- What are two advantages of using sputtering as opposed to evaporation to create a metal interconnect system? Superior Film Quality & Control



















