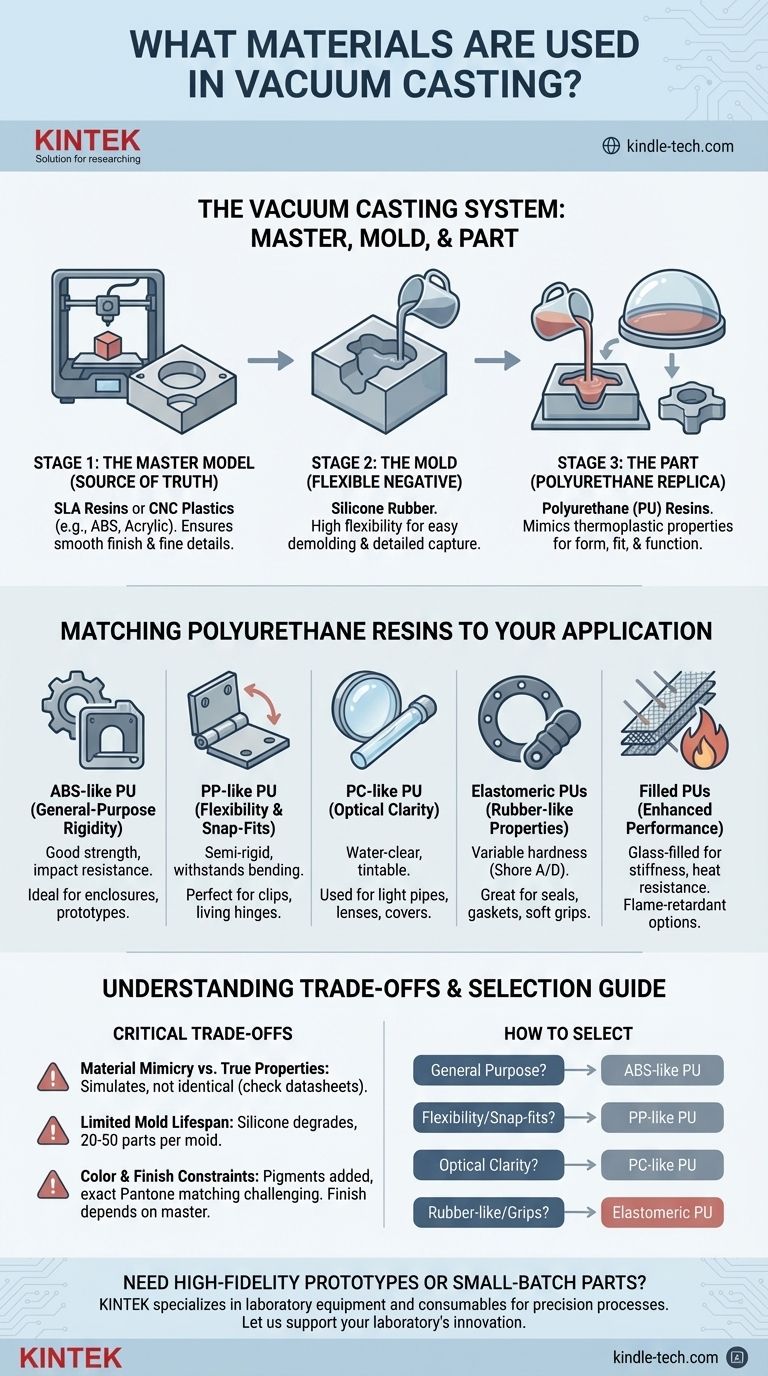
At its core, the vacuum casting process primarily uses two key materials: silicone rubber to create a flexible mold and a wide range of polyurethane (PU) resins to produce the final parts. These polyurethanes are specifically formulated to mimic the mechanical properties, colors, and textures of common production-grade thermoplastics, making them ideal for high-fidelity prototypes and small-batch production runs.
Vacuum casting is not about a single material, but a versatile system. The real power of the process lies in using flexible silicone molds to cast a diverse family of polyurethane resins, each designed to simulate the properties of a specific end-use plastic like ABS, polypropylene, or rubber.

The Role of Each Material in the Process
To understand the material choices, you must first understand their distinct roles in the three stages of vacuum casting: creating the master model, forming the mold, and casting the final part.
The Master Model: The Source of Truth
The master model is the perfect, highly-finished original from which the mold is made. Its quality dictates the quality of every subsequent part.
The most common materials for master models are SLA (Stereolithography) resins. These 3D-printed photopolymers are chosen for their ability to produce exceptionally smooth surface finishes and fine details, which are transferred directly to the silicone mold. Alternatively, CNC-machined plastics like ABS or acrylic can be used for their durability and precision.
The Mold: The Flexible Negative
The mold is the heart of the vacuum casting process, and it is almost universally made from silicone rubber.
Silicone is the ideal choice for several reasons. Its high flexibility allows for the easy removal (demolding) of complex parts, even those with undercuts, without damaging the part or the mold. It also captures microscopic surface details from the master model with extreme fidelity.
The Part: The Polyurethane Replica
The final parts are created by pouring liquid polyurethane (PU) resins into the silicone mold under a vacuum. The vacuum removes air bubbles, ensuring a void-free, perfect copy.
These two-part thermosetting polymers are the most critical material choice. They are engineered to simulate the properties of production plastics, allowing you to test form, fit, and function with a high degree of confidence.
Matching Polyurethane Resins to Your Application
The versatility of vacuum casting comes from the wide array of available polyurethane resins. Selecting the right one is about matching the material's properties to the intended function of your part.
For General-Purpose Rigidity: ABS-like PU
This is the most common and versatile choice. ABS-like polyurethanes offer good strength, impact resistance, and dimensional stability. They are the go-to material for enclosures, housings, and general functional prototypes.
For Flexibility and Snap-Fits: PP-like PU
If your part requires flexibility, such as for living hinges, clips, or snap-fit enclosures, a polypropylene (PP)-like PU is the correct choice. These materials are semi-rigid and can withstand repeated bending.
For Optical Clarity: PC-like PU
For parts that need to be transparent, such as light pipes, lenses, or clear covers, you should use a polycarbonate (PC)-like PU. These resins can be cast water-clear and can also be tinted to achieve transparent colors.
For Rubber-like Properties: Elastomeric PUs
When you need to simulate rubber, you use elastomeric polyurethanes. These are available in a wide range of hardness levels, measured on the Shore A scale (for soft rubbers) or Shore D scale (for hard rubbers). They are perfect for gaskets, seals, grips, and overmolds.
For Enhanced Performance: Filled PUs
For applications requiring higher performance, you can use specialty resins. Glass-filled PUs, for example, offer significantly increased stiffness and higher heat deflection temperatures compared to their standard counterparts. Flame-retardant PUs are also available to meet specific regulatory requirements.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the materials used in vacuum casting have inherent limitations that are critical to understand.
Material Mimicry vs. True Properties
A key point to remember is that a polyurethane resin simulates a production plastic; it is not chemically identical. An ABS-like PU will feel and behave very similarly to ABS, but its thermal properties and long-term creep resistance will differ. Always consult a material datasheet for precise engineering specifications.
Limited Mold Lifespan
Silicone molds are not permanent. The chemically aggressive nature of the polyurethane resins causes the mold to degrade over time. A typical silicone mold can produce between 20 and 50 parts before it loses detail and must be replaced. This is why vacuum casting is ideal for prototyping and low-volume production, not mass manufacturing.
Color and Finish Constraints
Color is achieved by adding a pigment to the liquid resin before casting. This provides a consistent, through-body color. However, achieving an exact Pantone match can be challenging. The part's surface finish is entirely dependent on the finish of the master model, as the silicone perfectly replicates it.
How to Select the Right Vacuum Casting Material
Your choice should be driven entirely by the goal of your part.
- If your primary focus is a general-purpose functional prototype: Start with an ABS-like polyurethane for its excellent balance of strength and rigidity.
- If your primary focus is testing snap-fits or living hinges: Choose a flexible PP-like polyurethane to accurately simulate part function.
- If your primary focus is creating aesthetic or marketing models: Use a clear PC-like resin, which can be custom tinted for visual impact.
- If your primary focus is creating seals, gaskets, or soft-touch grips: Select an elastomeric polyurethane with the specific Shore hardness your application demands.
By understanding this material system, you can leverage vacuum casting to create high-fidelity parts that precisely match your project's functional and aesthetic intent.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Primary Use in Vacuum Casting | Key Properties/Simulates |
|---|---|---|
| Silicone Rubber | Creating the flexible mold | High flexibility, captures fine details, allows for easy demolding |
| ABS-like PU Resin | General-purpose rigid parts | Good strength, impact resistance, dimensional stability |
| PP-like PU Resin | Flexible parts, snap-fits | Semi-rigid, withstands repeated bending |
| PC-like PU Resin | Optical clarity, transparent parts | Water-clear, can be tinted |
| Elastomeric PU Resin | Rubber-like parts, gaskets, grips | Range of hardness (Shore A & D scales) |
Need High-Fidelity Prototypes or Small-Batch Production Parts?
KINTEK specializes in providing the laboratory equipment and consumables essential for precision processes like vacuum casting. Whether you are creating prototypes for form, fit, and function testing or producing small batches of end-use parts, the right materials are critical for success.
Let us help you achieve your project goals with high-quality materials and expert support. Contact our team today to discuss your specific material requirements and how we can support your laboratory's innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
- Assemble Lab Cylindrical Press Mold
- Cylindrical Press Mold for Lab Applications
- Square Bidirectional Pressure Mold for Lab Use
- Cylindrical Press Mold with Scale for Lab
People Also Ask
- How do custom graphite molds contribute to Al-20% Si/graphite flake composites? Optimize Microstructure & Conductivity
- What are the advantages of using high-strength graphite molds in the hot press sintering of Ti6Al4V-based composites?
- Why are custom pressure molds used during the hot pressing process for solid polymer electrolytes?
- What are the primary functions of high-density graphite molds in FAST/SPS? Optimizing Thermal and Mechanical Performance
- What role do graphite mold components play in the vacuum hot pressing of Ti-3Al-2.5V? Optimize Alloy Densification



















